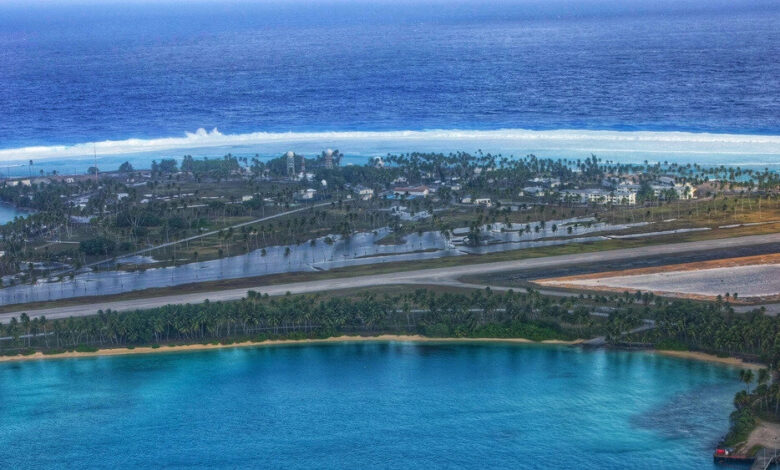
Marshall Islands Flooding Evacuations A Crisis
Marshall Islands flooding evacuations are a stark reminder of the escalating climate crisis. Rising sea levels and increasingly intense storms are forcing communities to confront a harrowing reality: displacement and the loss of their ancestral lands. This article explores the historical context, evacuation procedures, community impacts, infrastructure challenges, international response, and the crucial role of adaptation strategies in the face of this ongoing crisis.
From the devastating impacts of recent floods to the long-term effects of rising sea levels, this detailed analysis sheds light on the complex challenges faced by the Marshallese people. It examines the historical patterns of flooding, the evacuation strategies employed, and the crucial role of international aid in mitigating the effects of these events. Understanding these issues is vital for fostering empathy and supporting efforts to build a more resilient future for the Marshall Islands.
Historical Context of Flooding
The Marshall Islands, a nation of low-lying atolls in the central Pacific, are particularly vulnerable to the impacts of climate change, especially rising sea levels and intensified storms. Flooding events, once infrequent occurrences, are now becoming more frequent and severe, posing significant threats to the islands’ infrastructure and way of life. Understanding the historical context of flooding is crucial to appreciating the urgency of the current situation and the need for adaptation strategies.Rising sea levels, driven by global warming, exacerbate the effects of storms and high tides, increasing the risk of inundation.
This, combined with historical patterns of rainfall and storm surges, creates a complex challenge for the Marshallese people. The long-term effects on the islands are becoming increasingly evident, impacting everything from housing and agriculture to cultural heritage and the overall well-being of the communities.
Timeline of Major Flooding Events
A comprehensive timeline of major flooding events in the Marshall Islands, detailing dates, locations, and estimated impacts, is essential for understanding the increasing frequency and severity of these events. While precise records may be incomplete for earlier periods, the documented events demonstrate a clear trend of growing intensity.
- 2014: Heavy rainfall and storm surges caused widespread flooding across several islands, particularly in Majuro and Kwajalein. Estimated damage to infrastructure and crops was significant, highlighting the vulnerability of the region.
- 2018: A powerful typhoon resulted in extensive flooding across the southern atolls, displacing numerous families and damaging homes and essential services.
- 2022: A series of severe storms and high tides inundated coastal communities, leading to significant water damage, disruption of transport, and economic losses. The extent of the damage was significant, impacting both infrastructure and the livelihood of many people.
Long-Term Effects of Rising Sea Levels, Marshall islands flooding evacuations
Rising sea levels are progressively eroding shorelines, threatening coastal infrastructure and the very landmass upon which Marshallese communities depend. This phenomenon is further compounded by the increased frequency of high tides and storm surges.
- Erosion: The relentless erosion of shorelines is a direct consequence of rising sea levels. This erosion can lead to the loss of homes, businesses, and agricultural land, impacting the economy and the well-being of the community.
- Saltwater Intrusion: Increased saltwater intrusion contaminates freshwater sources, making them unsuitable for drinking and agriculture. This compromises the sustainability of local food systems.
- Infrastructure Damage: Rising sea levels and storm surges damage roads, bridges, and other vital infrastructure, disrupting transportation, communication, and access to essential services.
Historical Patterns of Rainfall and Storm Surges
Understanding the historical patterns of rainfall and storm surges is vital to predicting and mitigating future flooding events. Data analysis reveals a clear correlation between the intensity of these events and climate change.
The Marshall Islands are facing devastating flooding, forcing evacuations. While these urgent situations highlight the climate crisis, it’s also worth noting that the Pittsburgh Steelers have a new offensive coordinator, Arthur Smith, hired to revamp their offense. arthur smith hired steelers offensive coordinator This hiring news is certainly a distraction from the dire situation in the Marshall Islands, but hopefully, the focus will quickly return to supporting those affected by the flooding.
- Rainfall Trends: Data from weather stations in the Marshall Islands show a rising trend in the frequency and intensity of heavy rainfall events, which can lead to flash floods and runoff problems.
- Storm Surge Analysis: Historical records indicate an increase in the magnitude and frequency of storm surges, particularly during typhoon seasons. This highlights the growing risk of coastal flooding during these periods.
Comparison of Recent Flooding Events
The severity of recent flooding events compared to past occurrences demonstrates a clear upward trend. The intensity and duration of these events are surpassing previous records, demanding immediate attention and action.
- Increased Frequency: The frequency of severe flooding events has significantly increased over the past few decades, posing an escalating threat to the Marshallese people.
- Intensity Increase: Recent events are characterized by higher water levels and longer durations of flooding compared to past occurrences, indicating a more severe impact on infrastructure and communities.
Historical Records and Scientific Data on Climate Change Impacts
Scientific data and historical records confirm the impact of climate change in the region. Rising global temperatures are directly correlated with the observed increases in sea levels, rainfall, and storm intensity.
- Observed Impacts: Evidence from various sources demonstrates a correlation between rising global temperatures and observed increases in sea levels, rainfall, and storm intensity in the Marshall Islands.
- IPCC Reports: The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) reports provide detailed analyses of the impact of climate change on small island nations like the Marshall Islands, highlighting the urgent need for adaptation measures.
Evacuation Procedures and Strategies
The Marshall Islands, facing the escalating threat of rising sea levels and intensified storms, have developed crucial evacuation procedures to safeguard their communities. These strategies, often tested in real-world scenarios, prioritize the safety and well-being of islanders during flooding events. The effectiveness of these plans depends heavily on the preparedness and coordination of various organizations and the active participation of the communities.Evacuation protocols are dynamic, adapting to the specific circumstances of each flood event.
They take into account the severity of the impending threat, the projected impact on vulnerable populations, and the available resources. This proactive approach ensures the timely and safe relocation of residents. The Marshall Islands government and local communities are continually refining these procedures based on lessons learned from past evacuations.
Evacuation Plans and Protocols
The Marshall Islands government, in collaboration with international partners, has established standardized evacuation procedures. These procedures Artikel clear communication channels, designated assembly points, and specific roles for various stakeholders. The plans are regularly reviewed and updated based on the latest scientific assessments and the lessons learned from past events. These protocols are crucial for the timely and safe relocation of populations during flooding.
The Marshall Islands are facing devastating flooding, forcing evacuations. This climate crisis is tragically exacerbated by corporate actions, like those of Koch and Chevron, whose influence on the Supreme Court, as highlighted in this recent article about koch chevron deference supreme court , potentially hinders effective environmental regulations. These issues ultimately leave vulnerable island nations with few options but to flee their homes, highlighting the urgent need for change.
Roles and Responsibilities of Organizations
A multitude of organizations play crucial roles in evacuation efforts. The National Disaster Management Office (NDMO) is responsible for coordinating the overall response, while local government officials manage logistics at the community level. The Red Cross and other humanitarian organizations provide support with essential supplies, medical assistance, and temporary shelter. The participation of community leaders and volunteers is also indispensable, as they play a key role in disseminating information and ensuring smooth evacuation procedures.
Challenges and Limitations
Evacuating populations in the Marshall Islands presents unique challenges. The dispersed nature of island communities, coupled with limited transportation resources, often complicates the swift and efficient movement of people. The need for temporary shelters, adequate supplies, and proper medical care are also significant concerns. Financial constraints and the potential for infrastructure damage can further hinder the effectiveness of evacuation procedures.
Community Engagement
Community engagement is critical to successful evacuations. Residents are informed about evacuation procedures through regular community meetings, public announcements, and the use of local media. The involvement of community leaders and local organizations is essential to ensuring effective communication and cooperation. Trust and transparency between the government and the community are vital for successful implementation of evacuation plans.
Furthermore, pre-determined evacuation routes and shelters are communicated to residents to reduce confusion and ensure smooth execution.
The Marshall Islands are facing devastating flooding, forcing evacuations of entire communities. It’s a heartbreaking situation, and the displaced families are facing immense challenges. While these issues are certainly significant, it’s also important to consider the naming conventions of the children born during these evacuations, and the associated considerations like the apellido bebe madre padre system.
Ultimately, the focus must return to helping these families rebuild their lives in the face of this catastrophic flooding.
Evacuation Process Flow Chart
| Stage | Key Actors | Actions |
|---|---|---|
| Alert Phase | NDMO, Local Officials, Radio Stations | Issue warnings, activate emergency protocols, inform the public |
| Preparation Phase | Community Leaders, Volunteers, Residents | Gather supplies, confirm evacuation routes, check on vulnerable populations |
| Evacuation Phase | Emergency Personnel, Transportation Teams, Shelters | Transport residents to designated shelters, provide assistance, ensure safety |
| Post-Evacuation Phase | Government, NGOs, Residents | Assess damage, provide relief, rebuild communities, evaluate effectiveness of procedures |
Impacts on Communities
The relentless march of rising sea levels and intensifying storms casts a long shadow over the Marshall Islands, forcing communities into a constant state of preparedness and displacement. Evacuations, while crucial for survival, exact a heavy toll on the fabric of Marshallese society. The socio-economic and psychological ramifications are profound, impacting livelihoods, cultural continuity, and the very spirit of the people.Evacuations, though necessary, often disrupt established patterns of life, impacting various aspects of community well-being.
The psychological impact of repeated displacement on residents is a critical concern. The constant threat of imminent relocation, combined with the disruption of familiar routines, can lead to a range of negative effects, including stress, anxiety, and a sense of profound loss.
Socio-economic Consequences
Evacuations disrupt economic activities, often the primary source of income for many Marshallese families. Fishing, agriculture, and tourism, the backbone of the Marshallese economy, are frequently interrupted or rendered inaccessible due to flooding and relocation. The loss of income can lead to poverty and food insecurity, particularly for vulnerable families and individuals. The disruption of supply chains and access to essential goods can further exacerbate the economic hardships faced by displaced communities.
Temporary housing solutions and financial assistance programs are crucial for mitigating these consequences, yet their effectiveness often depends on the efficiency and promptness of aid delivery.
Psychological Effects of Repeated Displacement
The repeated displacement experienced by Marshallese communities takes a heavy toll on the mental well-being of residents. The constant fear of the next evacuation, the loss of familiar surroundings, and the disruption of social networks can lead to chronic stress, anxiety disorders, and post-traumatic stress. The psychological trauma experienced can be especially pronounced in children, who may not fully understand the implications of repeated displacement or have the coping mechanisms to deal with such intense stress.
Addressing these psychological needs through accessible mental health services is paramount to ensuring the long-term well-being of displaced communities.
Challenges in Maintaining Cultural Continuity
Cultural continuity is a cornerstone of Marshallese identity, deeply intertwined with their traditions, customs, and practices. Evacuations pose significant challenges to preserving this cultural heritage. The disruption of traditional social structures, the separation of families, and the relocation to unfamiliar environments can lead to the erosion of cultural values and practices. Maintaining access to traditional knowledge, language, and cultural ceremonies during and after evacuations is crucial for preserving the identity of the Marshallese people.
Long-term Impact on Livelihoods and Traditional Ways of Life
Evacuations profoundly impact the long-term sustainability of traditional livelihoods. The destruction of ancestral lands, the loss of access to traditional fishing grounds, and the disruption of agricultural practices can significantly impact the ability of Marshallese communities to sustain their traditional ways of life. Finding ways to adapt traditional practices to new environments and ensuring access to resources and land are crucial for maintaining the viability of these livelihoods.
Comparison of Impacts on Different Demographics
The impacts of evacuations differ across different demographics within Marshallese communities. Elderly individuals, for instance, may face greater challenges in adapting to new environments and accessing essential services. Children and young adults may experience greater psychological distress due to the disruption of education and social networks. Women, who often play a critical role in maintaining cultural continuity and family structures, may face unique challenges in balancing these responsibilities with the demands of relocation.
Understanding these disparities is crucial for tailoring support systems and ensuring equitable access to resources for all members of the community.
Infrastructure and Resilience
The Marshall Islands, a low-lying nation in the Pacific, faces escalating threats from rising sea levels and intensified storms. Vulnerable infrastructure, especially in coastal areas, is critical to the safety and well-being of its communities. Protecting and improving this infrastructure is crucial for long-term resilience, allowing the nation to adapt and thrive in the face of climate change.
Rebuilding and strengthening these structures requires a concerted effort from local and international stakeholders.
Vulnerable Infrastructure Overview
The Marshall Islands’ infrastructure is highly susceptible to flooding due to its low elevation and proximity to the ocean. Coastal roads, homes, and public buildings are directly exposed to storm surges and saltwater intrusion. Poor drainage systems exacerbate the issue, leading to widespread inundation during heavy rainfall or high tides. Many structures lack proper flood-resistant design and construction materials.
These vulnerabilities make the islands especially susceptible to damage during extreme weather events.
Critical Infrastructure for Protection
Several critical infrastructure elements require immediate attention and enhanced protection. These include: coastal roads, bridges, essential services like hospitals and schools, and residential homes. Protecting these infrastructure components is essential for maintaining the continuity of basic services, emergency response, and community stability during and after natural disasters. Prioritizing these structures ensures the safety and well-being of the community.
Strategies for Improving Infrastructure Resilience
Improving the resilience of Marshallese infrastructure requires a multi-pronged approach, incorporating advanced flood mitigation measures. This includes constructing seawalls, elevating buildings, and implementing effective drainage systems. Employing flood-resistant building materials and techniques is essential to minimize damage. Utilizing climate-resilient design principles and incorporating sustainable construction practices will help ensure the long-term viability of the structures. Implementing these strategies requires a detailed understanding of the specific flood risks and vulnerabilities in each location.
Roles of Aid Organizations
International aid organizations and governments play crucial roles in rebuilding and strengthening the Marshall Islands’ infrastructure. Their contributions encompass financial support, technical expertise, and logistical assistance. International cooperation is vital in providing the resources and knowledge needed to implement sustainable solutions. Local communities are also vital partners in the process, contributing their expertise and understanding of the local environment and needs.
Their participation ensures that the solutions meet the specific needs of the community.
Resilience Comparison Table
| Infrastructure Type | Vulnerability to Flooding | Resilience Strategies | Resilience Rating (1-5, 5 being most resilient) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Roads | Frequent inundation, damage from storm surges, erosion | Elevated roadbeds, reinforced drainage systems, use of flood-resistant materials | 3 |
| Homes | Saltwater intrusion, structural damage, loss of property | Elevated foundations, flood-resistant building materials, flood-proofing techniques | 2 |
| Schools | Loss of educational facilities, disruption of learning, damage to equipment | Elevated buildings, reinforced structures, backup power systems, disaster preparedness plans | 4 |
Improved resilience is not just about protecting structures but about creating a more sustainable and resilient community.
International Response and Aid
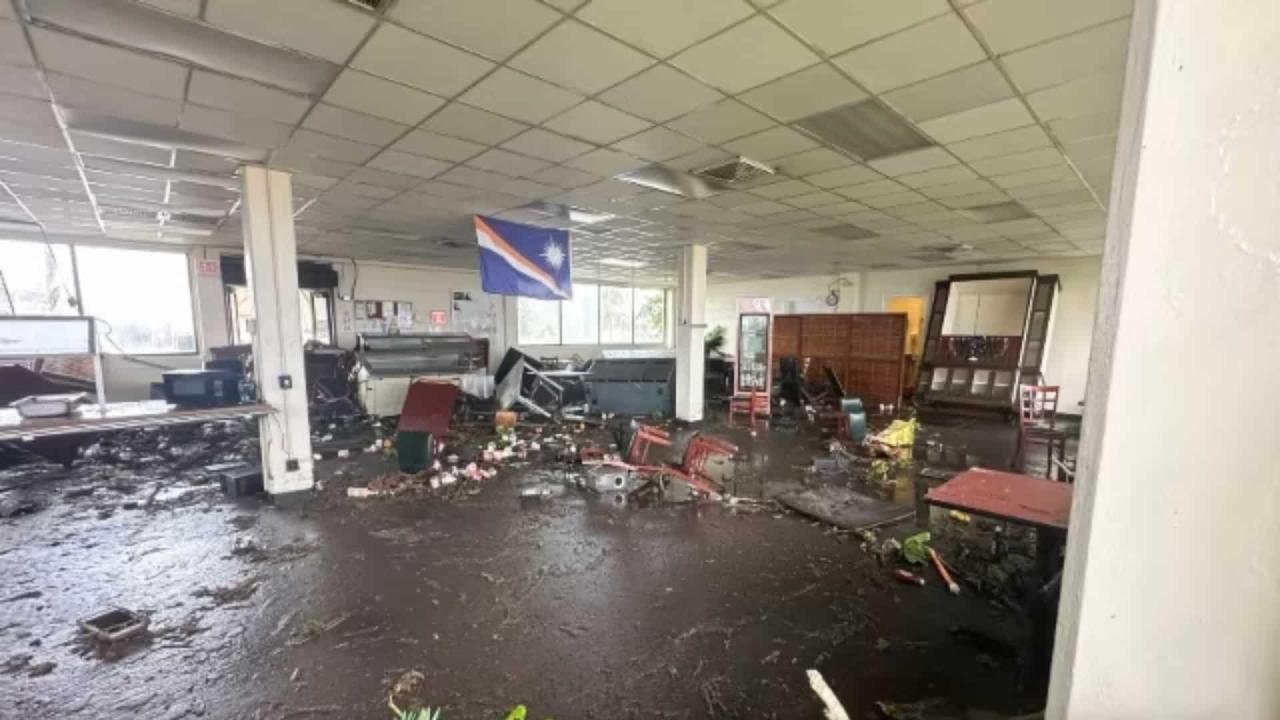

The Marshall Islands, facing frequent and devastating flooding, relies heavily on international support during evacuations and recovery efforts. This assistance is crucial for providing essential resources, expertise, and coordination to navigate the complex challenges of disaster response in a remote island nation. International organizations play a vital role in the overall effort, from initial relief to long-term rebuilding.International aid organizations, driven by humanitarian principles, play a crucial role in providing immediate and long-term assistance to affected communities.
Their expertise in logistical planning, resource mobilization, and community support is invaluable in the aftermath of a disaster. However, challenges such as geographical isolation, limited infrastructure, and the specific needs of vulnerable populations often complicate the delivery of aid. Effective international cooperation is paramount in coordinating efforts and maximizing the impact of aid, which often includes funding, supplies, and personnel.
Roles of International Organizations
International organizations, such as the United Nations Office for the Coordination of Humanitarian Affairs (OCHA), the International Red Cross and Red Crescent Movement, and various non-governmental organizations (NGOs), play a multi-faceted role in disaster response. They often act as a central coordinating body, mobilizing resources, coordinating relief efforts, and ensuring aid reaches those most in need. Their expertise in disaster preparedness, emergency response, and long-term recovery planning is vital.
They can provide essential supplies like food, water, shelter materials, and medical assistance, as well as support for psychological well-being.
Challenges in Delivering Aid
Several significant challenges hinder the efficient delivery of aid to affected communities in the Marshall Islands. The remote and dispersed nature of the islands presents logistical hurdles, requiring careful planning and coordination to ensure aid reaches those most vulnerable. Limited infrastructure, such as inadequate transportation networks and communication systems, further complicates the process. Cultural sensitivity and awareness of local customs and traditions are crucial for effective aid delivery.
Ensuring that aid is aligned with the specific needs of the affected population, including marginalized communities, is also a critical challenge.
The Marshall Islands are facing devastating flooding, forcing evacuations due to rising sea levels. This isn’t just a local issue; it’s a global crisis, mirroring concerns about the impact of climate change on sports like snow polo in St. Moritz. For example, snow polo st moritz climate change highlights how changing weather patterns threaten traditional winter sports, just as the Marshall Islands’ communities face the immediate threat of losing their homes to the rising tide.
The interconnectedness of these issues is alarming, and the need for global action is clear.
Importance of International Cooperation
International cooperation is essential in coordinating aid efforts and maximizing their impact. Joint efforts between governments, international organizations, and NGOs allow for a more comprehensive and well-rounded response to the disaster. This collaboration ensures that all aspects of relief, from immediate needs to long-term recovery, are addressed effectively. Sharing expertise, resources, and best practices between nations can lead to more efficient and effective aid efforts.
Effective communication and coordination are vital to prevent duplication of efforts and ensure that aid reaches those who need it most.
Different Models of International Assistance
Various models of international assistance exist, each with its own strengths and weaknesses. Bilateral aid, provided directly from one government to another, can offer tailored assistance aligned with specific needs and priorities. Multilateral aid, channeled through international organizations, offers a broader reach and a more coordinated approach. NGO-led initiatives often provide direct services and community engagement, fostering local ownership and sustainability.
The effectiveness of each model depends on factors like the specific context of the disaster, the resources available, and the capacity of the recipient nation.
The Marshall Islands are facing devastating flooding, forcing evacuations. It’s a stark reminder of the climate crisis’s impact. Meanwhile, the ethical considerations around purchasing “stranger letters,” those letters from people who have passed away, are quite fascinating, and raise some complex questions. This raises the question of how much is too much to pay for something like this?
You can learn more about the ethical quandaries surrounding the purchase of these letters at stranger letters purchase ethics. Regardless, the Marshall Islands situation highlights the urgent need for global action on climate change to prevent future disasters.
Aid Provided by Various Organizations
| Organization | Type of Aid | Beneficiaries |
|---|---|---|
| United Nations | Emergency supplies (food, water, shelter), medical assistance, coordination of aid efforts. | Affected communities, particularly vulnerable populations like children and the elderly. |
| International Red Cross | Emergency relief (water purification, first aid), psychosocial support, long-term recovery planning. | Individuals and families affected by the disaster. |
| NGOs (e.g., Doctors Without Borders) | Medical care, health services, emergency medical support. | Victims of the disaster requiring medical attention. |
| Governmental agencies (e.g., USA, Japan) | Financial assistance, rebuilding infrastructure, humanitarian support. | Marshall Islands government and affected communities. |
Climate Change and Future Projections
The Marshall Islands, a low-lying nation in the central Pacific, are facing an escalating threat from rising sea levels and increasingly intense weather patterns. These are direct consequences of global climate change, a phenomenon driven by human activities and their impact on the Earth’s atmosphere. The nation’s vulnerability to flooding is exacerbated by its geographic location and the limited elevation of its islands.
Understanding the projected future impacts is critical for developing effective adaptation strategies.The link between climate change and flooding in the Marshall Islands is undeniable. The increasing concentration of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere leads to a warming planet, causing thermal expansion of ocean water and melting of glaciers and ice sheets. This, in turn, results in a gradual rise in sea levels, making coastal areas more susceptible to flooding, even during relatively moderate weather events.
Furthermore, changes in atmospheric circulation patterns due to climate change are intensifying storms, increasing the frequency and severity of extreme weather events, which can also lead to devastating flooding.
Projected Future Impacts of Rising Sea Levels
Rising sea levels will lead to more frequent and severe coastal inundation. This will impact crucial infrastructure, such as roads, bridges, and housing, leading to significant economic losses and disruptions. Communities will face the prospect of displacement and the loss of their ancestral lands. The long-term sustainability of the nation’s economy and culture is at risk. Seawater intrusion into freshwater sources will further complicate the issue of water security.
Projected Frequency and Intensity of Flooding
Scientific reports project an increase in the frequency and intensity of flooding events in the coming decades. The rate of sea-level rise is accelerating, and this is expected to exacerbate existing vulnerabilities. The frequency of extreme rainfall events is also projected to increase, further increasing the risk of flooding. Historical data shows a clear correlation between rising temperatures and increased rainfall in the region.
Data from Scientific Reports on Future Climate Scenarios
Numerous scientific reports, including those from the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC), Artikel future climate scenarios for the region. These reports project a continuation of warming trends and rising sea levels, with increasingly severe impacts on the Marshall Islands. Key data points include projected increases in global mean temperatures, projected sea-level rise by the end of the century, and the projected intensification of tropical cyclones.
The IPCC’s Sixth Assessment Report, for example, Artikels a range of possible future scenarios, each with varying levels of greenhouse gas emissions and resulting impacts.
Visual Representation of Projected Sea Level Rise
A graph illustrating projected sea level rise by the end of the century, based on various emission scenarios, would be a helpful visualization. The graph would show a clear upward trend, with different scenarios displaying varying rates of rise. A comparison of the projected sea level rise with historical data would demonstrate the accelerating nature of this phenomenon.
For instance, if the average sea level rise in the past 100 years is depicted, a future projection graph should illustrate an exponential increase, demonstrating a significant difference.
Community Adaptation and Mitigation
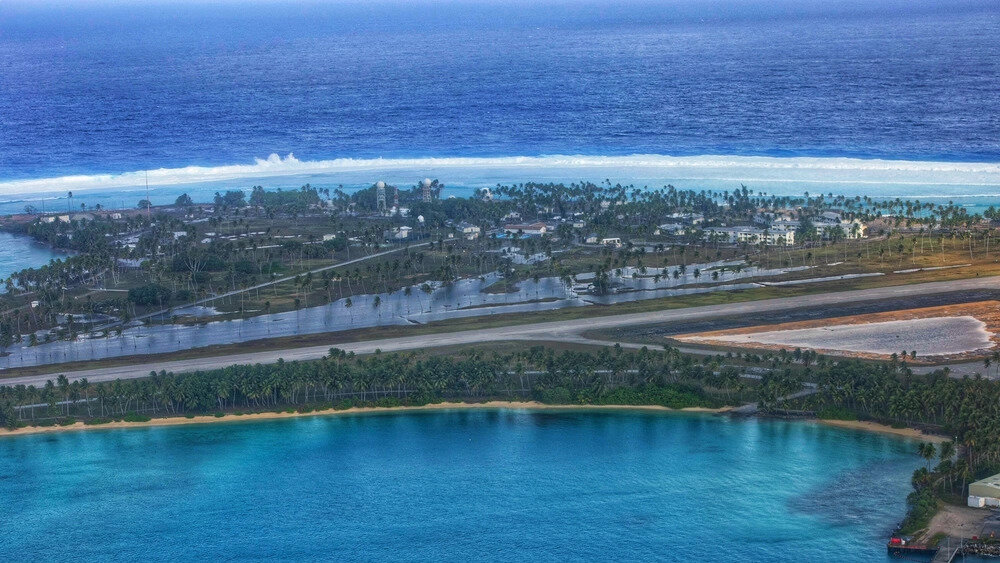

The Marshall Islands, facing the escalating threat of rising sea levels and more frequent extreme weather events, are actively developing strategies to adapt and mitigate the impacts of climate change. These strategies are not merely theoretical; they represent a vital, community-driven response to a profound environmental crisis. Communities are central to these efforts, drawing upon their traditional knowledge and innovative spirit to build resilience.Community-based approaches to adaptation and mitigation are crucial, as they empower local people to develop solutions tailored to their specific needs and circumstances.
This localized understanding is vital for sustainable adaptation, recognizing the unique vulnerabilities and resources within each island. Recognizing that climate change is not a distant threat, but a tangible reality, the Marshallese people are implementing a variety of strategies to enhance their community’s ability to endure.
Strategies for Adapting to the Changing Environment
The Marshallese are employing diverse strategies to adapt to the changing environment. These include coastal protection measures, such as building seawalls and elevating infrastructure, alongside water conservation techniques and diversifying food sources. These practical steps are designed to enhance the community’s capacity to withstand and recover from the impacts of rising sea levels and increased storm surges. This comprehensive approach recognizes the interconnectedness of environmental and societal well-being.
Importance of Community-Based Adaptation and Mitigation Strategies
Community-based adaptation and mitigation strategies empower local communities to develop and implement solutions tailored to their unique contexts. This approach recognizes the vital role of traditional knowledge and local expertise in crafting sustainable solutions. Local communities have a deep understanding of their environments and possess invaluable insights into effective adaptation measures. These strategies prioritize community participation, fostering ownership and ensuring the long-term sustainability of adaptation efforts.
Potential of Climate-Resilient Infrastructure Solutions
Climate-resilient infrastructure solutions are critical for bolstering the Marshall Islands’ ability to withstand the escalating impacts of climate change. These solutions incorporate the principles of sustainability and resilience, creating structures that can withstand extreme weather events. This includes building infrastructure on higher ground, utilizing flood-resistant materials, and incorporating early warning systems for potential disasters. For example, the design of new buildings and infrastructure should consider projected sea level rise and storm surge heights, to ensure their long-term viability.
Innovative Solutions Developed by the Marshallese Community
The Marshallese people are demonstrating remarkable ingenuity in developing innovative solutions to combat flooding. This includes the development of raised agricultural platforms, which allow for continued food production even during high-tide events. Furthermore, they are exploring the use of alternative water sources and developing water conservation strategies to reduce vulnerability to drought. The Marshallese community’s resourcefulness and adaptability are key to their resilience in the face of climate change.
Summary Table of Adaptation Strategies
| Adaptation Strategy | Description | Potential Effectiveness |
|---|---|---|
| Coastal Protection Measures (e.g., seawalls, breakwaters) | Structures designed to prevent or reduce coastal erosion and flooding. | High, but may require significant resources and careful design to minimize ecological impacts. |
| Elevation of Infrastructure | Raising buildings and other infrastructure to higher elevations. | High, but can be costly and may not be feasible for all structures. |
| Water Conservation Techniques | Implementing measures to reduce water consumption and improve water management. | Medium to High, depending on the specific techniques implemented. |
| Diversification of Food Sources | Developing alternative food sources to reduce dependence on vulnerable agricultural lands. | Medium to High, depending on the success in establishing alternative food sources. |
| Early Warning Systems | Developing systems to provide timely warnings of impending storms and flooding. | High, as timely warnings can help communities prepare and evacuate. |
Final Conclusion: Marshall Islands Flooding Evacuations
In conclusion, the Marshall Islands flooding evacuations highlight the urgent need for global action on climate change. The escalating crisis demands immediate and comprehensive support for the Marshallese people, who are on the front lines of this environmental catastrophe. While evacuations and aid efforts are critical, long-term solutions focusing on adaptation, resilience, and sustainable infrastructure are equally essential.
The future of the Marshall Islands depends on a global commitment to mitigating climate change and supporting the communities most vulnerable to its effects.
Clarifying Questions
What are the most common causes of flooding in the Marshall Islands?
Increased rainfall, storm surges, and rising sea levels due to climate change are the primary drivers of flooding in the Marshall Islands. Historical patterns of rainfall and storm surge intensity are also contributing factors.
What types of aid are provided by international organizations during evacuations?
International organizations typically provide emergency supplies like food, water, shelter, and medical assistance. Financial aid and support for infrastructure rebuilding are also common.
How is the Marshallese community adapting to the changing environment?
Marshallese communities are developing various adaptation strategies, including building elevated homes, relocating villages, and implementing sustainable farming practices. Community-led initiatives are crucial to these efforts.
What are the psychological effects of repeated displacement on residents?
Repeated displacement can lead to significant psychological distress, including trauma, anxiety, and depression. Maintaining cultural continuity and community support is vital for mental well-being during and after evacuations.