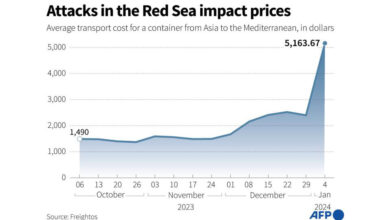
Inflation Markets Stocks Fed Impact & Outlook
Inflation markets stocks fed are intertwined in a complex dance, shaping investment decisions and economic forecasts. This analysis delves into the current inflationary pressures, examining their impact on financial markets, the role of the Federal Reserve, and potential future scenarios. Understanding these dynamics is crucial for navigating the current economic landscape.
We’ll explore historical inflation trends, analyze the factors driving current inflation, and dissect how it affects different asset classes like stocks and bonds. Further, we’ll examine the Federal Reserve’s response to these pressures and how their actions will potentially impact stock market volatility.
Inflationary Pressures
Inflation, the persistent increase in the general price level of goods and services in an economy over a period, is a critical economic indicator. Understanding its historical trends, the forces driving current pressures, and potential consequences is essential for informed financial decision-making. This analysis delves into inflationary pressures, examining historical data, current contributing factors, and the impact on specific sectors and interest rates.The persistent rise in inflation across various economies warrants a thorough investigation into its underlying causes and potential ramifications.
Inflation is wreaking havoc on markets, and stock prices are reflecting the uncertainty. The Federal Reserve’s response to this economic climate is crucial. Meanwhile, the recent developments in the Biden administration’s efforts to broker a cease-fire between Israel and Hamas ( biden israel hamas cease fire ) are adding another layer of complexity to the economic picture. Ultimately, the future of inflation, markets, and stocks depends on a multitude of factors, and the situation remains fluid.
This analysis aims to illuminate the dynamics of inflation, providing context for its evolution and potential future trajectory.
Historical Overview of Inflation Rates
Inflation rates have fluctuated significantly throughout history, impacting economic stability and individual purchasing power. Examining historical data provides a crucial perspective on the current inflationary environment.
| Country | Period | Inflation Rate (%) | Contributing Factors |
|---|---|---|---|
| United States | 1980-1982 | 13.5 | Oil price shocks, supply chain issues, expansionary monetary policy |
| United States | 2022-2023 | 8.2 | Supply chain disruptions, increased energy prices, demand-pull inflation |
| Eurozone | 2022-2023 | 8.4 | Energy price shocks, supply chain bottlenecks, increased demand |
| United Kingdom | 2022-2023 | 10.1 | Energy price shocks, global supply chain disruptions, increased consumer demand |
Factors Contributing to Current Inflationary Trends
Several interconnected factors are contributing to the current inflationary environment. Analyzing these factors provides insight into the complexities of modern inflation.
- Supply chain disruptions: Global supply chain bottlenecks, stemming from factors like the COVID-19 pandemic and geopolitical events, have limited the availability of goods, driving up prices. This has impacted industries ranging from electronics to automobiles.
- Increased energy prices: Fluctuations in energy prices, particularly oil and natural gas, have a ripple effect on various sectors, including transportation, manufacturing, and heating. The recent surge in energy costs has demonstrably contributed to higher inflation rates.
- Demand-pull inflation: Elevated consumer demand, spurred by factors such as government stimulus packages and pent-up savings, has outpaced supply, creating inflationary pressure in certain sectors.
- Geopolitical events: Geopolitical tensions and conflicts can disrupt global trade, impact commodity prices, and exacerbate inflation through various channels. The impact of the war in Ukraine on energy and food prices is a clear example.
Specific Sectors Experiencing High Inflation
Certain sectors are experiencing disproportionately high inflation rates, impacting consumers directly. Understanding these sector-specific pressures is vital for predicting future trends.
- Energy: The cost of gasoline, electricity, and natural gas has risen significantly, impacting transportation costs and household budgets.
- Food: Food prices have increased due to factors including supply chain disruptions, unfavorable weather conditions, and increased demand. Consumers are directly affected by these price hikes.
- Housing: The cost of housing, including rent and homeownership, has been climbing steadily, driven by factors like rising construction costs and demand exceeding supply.
Relationship Between Inflation and Interest Rates
Central banks often use interest rate adjustments to manage inflation. Understanding this relationship is crucial for evaluating the efficacy of monetary policy.
Higher inflation typically necessitates higher interest rates to curb demand and cool down the economy. Conversely, lower inflation may signal the need for lower interest rates to stimulate economic activity. Central banks employ these adjustments to manage inflation and stabilize the economy.
Potential Consequences of Persistent High Inflation
Persistent high inflation can have several detrimental consequences for individuals and the economy. Recognizing these consequences is crucial for effective economic management.
Inflation is definitely a hot topic in markets right now, with stocks and the Fed’s response causing ripples. It’s fascinating to see how these interconnected elements play out, and how different factors influence the current state of affairs. For example, the castellucci ring la monnaie is an interesting aspect of this broader picture that adds another layer of complexity to the economic landscape.
Ultimately, the interplay of these forces will determine the future trajectory of inflation markets and stocks.
- Reduced purchasing power: High inflation erodes the purchasing power of consumers, as their money buys less. This can lead to hardship and economic inequality.
- Uncertainty and economic instability: High and unpredictable inflation creates uncertainty, making it difficult for businesses to plan and invest. This uncertainty can lead to economic instability.
- Erosion of savings: Savings lose value when inflation is high, potentially affecting retirement plans and long-term financial goals. Savings are not immune to the negative effects of inflation.
Market Impacts: Inflation Markets Stocks Fed
Inflation’s ripple effect across financial markets is undeniable. From the fluctuating prices of everyday goods to the complex dynamics of investment portfolios, inflation’s presence profoundly impacts the entire financial ecosystem. Understanding these impacts is crucial for investors, policymakers, and anyone navigating the economic landscape.
Inflation’s Effect on Stocks
The relationship between inflation and stock market performance is complex and often contradictory. While high inflation can erode purchasing power, reducing the value of future earnings, a strong economy often accompanies inflationary periods, creating positive conditions for corporate growth and potentially higher stock prices. Companies with pricing power can often pass increased costs onto consumers, maintaining profitability. However, periods of high inflation frequently lead to higher interest rates, which can make borrowing more expensive for businesses and slow economic growth, impacting stock valuations.
Impact on Bonds
Bonds, often seen as a hedge against inflation, typically lose value when inflation rises. Fixed-income securities promise a set amount of interest payments, which, when inflation is high, becomes less valuable. For example, a bond promising a 5% return in a 2% inflation environment yields a real return of 3%. However, if inflation jumps to 7%, the real return is now -2%, eroding the bond’s value.
Investors may seek higher-yielding bonds, or even other investment vehicles, seeking to maintain or improve their real returns.
Commodity Markets and Inflation
Inflationary pressures tend to elevate commodity prices. Raw materials, crucial for manufacturing and production, become more expensive, leading to higher costs for businesses and ultimately impacting consumer prices. For example, during periods of heightened geopolitical uncertainty or supply chain disruptions, commodities like oil, metals, and agricultural products often see significant price increases. This correlation is directly observable in historical data.
Inflation and Investor Sentiment
Inflation expectations play a pivotal role in investor sentiment. Uncertainty about future inflation can lead to apprehension in the market, impacting investment decisions. Investors may become more risk-averse, seeking stable investments, leading to potentially lower returns. Conversely, if inflation expectations are low and stable, investors may be more inclined to take on risk, leading to increased investment activity.
Performance of Stock Indices During High Inflation
| Stock Index | Inflation Period (Example) | Performance |
|---|---|---|
| S&P 500 | 1970s (High Inflation) | Varied, with periods of significant volatility and decline, as well as growth periods |
| NASDAQ Composite | 1970s (High Inflation) | Varied, with periods of significant volatility and decline, as well as growth periods |
| Dow Jones Industrial Average | 1970s (High Inflation) | Varied, with periods of significant volatility and decline, as well as growth periods |
The table above provides a simplified illustration of the performance of major stock indices during periods of high inflation. Historical data reveals that stock market performance is not always consistent during these periods. The complexity of inflation’s impact is demonstrated by the varied performance across different indices. Further research is recommended to gain a more nuanced understanding.
The Role of the Federal Reserve
The Federal Reserve (Fed) plays a crucial role in managing the U.S. economy, including maintaining price stability and full employment. Its actions significantly impact market sentiment and investor decisions. Understanding the Fed’s mandate, tools, and recent actions is essential for navigating the current economic landscape.The Federal Reserve’s primary mandate regarding inflation is to maintain price stability, expressed as a low and stable rate of inflation.
This mandate is crucial for a healthy economy, as it fosters confidence and predictability for businesses and consumers. Furthermore, stable prices allow for the efficient allocation of resources and reduce uncertainty in economic planning.
The Federal Reserve’s Mandate Regarding Inflation
The Federal Reserve’s dual mandate, Artikeld in the Federal Reserve Act, encompasses both maximum employment and stable prices. The Fed strives to achieve a balance between these two objectives. Price stability is often measured by a low and stable inflation rate, typically around 2%. This target fosters a stable economic environment where businesses can plan for the future and consumers can make informed decisions.
Maintaining this balance requires careful monitoring of economic indicators and a flexible approach to monetary policy.
Inflation’s impact on markets and stocks, with the Fed’s response, is a hot topic right now. It’s fascinating to see how these factors intertwine, especially considering recent news about the “read like wind recommendations scandal.” This alleged scheme highlights potential conflicts of interest in financial advising, which could ultimately affect investor confidence and, in turn, influence the overall health of the inflation-wracked markets and stock performance.
The Fed’s actions will undoubtedly play a role in how all of this shakes out. read like wind recommendations scandal
Tools Used by the Fed to Manage Inflation
The Federal Reserve employs various monetary policy tools to influence the money supply and credit conditions, ultimately impacting inflation. These tools work by adjusting the cost and availability of money in the economy. Key tools include:
- Federal Funds Rate: This rate, at which banks lend to each other overnight, is a key instrument for influencing short-term interest rates. Adjustments to this rate ripple through the broader economy, affecting borrowing costs for consumers and businesses. A higher federal funds rate tends to curb inflation by making borrowing more expensive.
- Reserve Requirements: These are the percentage of deposits that banks must hold in reserve. Lowering reserve requirements increases the amount of money banks can lend, potentially fueling economic activity and inflation. Conversely, increasing reserve requirements reduces the money supply and can help combat inflation.
- Open Market Operations: The Fed buys or sells U.S. Treasury securities to influence the money supply. Purchases inject money into the market, while sales remove money. This is a highly flexible tool, allowing for precise adjustments to the money supply.
- Discount Rate: The interest rate at which commercial banks can borrow money directly from the Federal Reserve. Changes in the discount rate affect the cost of borrowing for banks, which can impact broader interest rates.
The Fed’s Recent Actions in Response to Inflation
The Fed has aggressively raised interest rates to combat recent inflation, which reached multi-decade highs. This approach aims to cool down the economy by reducing demand and slowing down price increases. Recent interest rate hikes are aimed at bringing inflation back to the desired 2% target.
Timeline of Fed Interventions Related to Inflation
- 2022 – 2023: The Fed embarked on a series of interest rate hikes to address rising inflation. This involved substantial increases in the federal funds rate, impacting borrowing costs across the economy.
- 2022 – Present: Continued monitoring of economic indicators and further adjustments to monetary policy tools as needed. The Fed aims to maintain a balance between controlling inflation and preserving economic growth.
Comparison of Monetary Policy Tools
| Monetary Policy Tool | Mechanism | Impact on Inflation |
|---|---|---|
| Federal Funds Rate | Influences short-term interest rates | Higher rates curb demand, lower inflation |
| Reserve Requirements | Impacts banks’ lending capacity | Lowering increases lending, potentially raising inflation; raising decreases lending, potentially lowering inflation |
| Open Market Operations | Buying/selling government securities | Purchases increase money supply, potentially raising inflation; sales decrease money supply, potentially lowering inflation |
| Discount Rate | Interest rate for banks borrowing from Fed | Higher rates increase borrowing costs for banks, potentially lowering inflation |
Stock Market Volatility

Inflation’s impact on the stock market is multifaceted and often unpredictable. Fluctuations in inflation rates directly affect investor sentiment and the perceived value of companies. The Federal Reserve’s response to inflation, through interest rate adjustments, further complicates the picture, leading to periods of heightened volatility in stock prices. Understanding these dynamics is crucial for investors navigating the complexities of the market.High inflation often leads to increased borrowing costs, which can negatively impact corporate earnings and valuations.
Conversely, in some sectors, inflation can be a boon, as companies may experience higher revenue from increased pricing power. However, the overall impact on the stock market depends on several factors, including the rate of inflation, the Fed’s response, and the specific characteristics of the companies being evaluated.
Impact of Inflation on Stock Market Volatility, Inflation markets stocks fed
Inflation’s influence on stock market volatility is substantial. Higher inflation erodes purchasing power, which can lead to reduced consumer spending and lower corporate profits. This uncertainty in the economic outlook directly translates into increased volatility in the stock market. Investors react to inflation’s unpredictable impact on different sectors, leading to sharp fluctuations in stock prices.
Relationship Between Inflation and Stock Valuations
The relationship between inflation and stock valuations is complex and not always linear. During periods of high inflation, investors often seek assets that can maintain or increase their value in the face of declining purchasing power. This can drive demand for certain stocks, while others may experience decreased valuations. Factors like inflation expectations, the speed of inflation, and the Federal Reserve’s response play crucial roles in shaping stock valuations.
Factors Influencing Stock Prices During Inflationary Periods
Several factors significantly influence stock prices during inflationary periods. Interest rates are a key factor, as higher rates increase borrowing costs for companies and reduce consumer spending. Consumer confidence plays a role, as uncertainty about inflation’s future trajectory can negatively impact consumer confidence and spending. The specific sector of the company also matters, as some sectors are more sensitive to inflation than others.
For example, companies in industries with inelastic demand, like utilities, may see their stock prices less impacted.
Examples of Companies Performing Well or Poorly During High Inflation
Companies’ performance during high inflation periods varies widely. Companies with strong pricing power, often in sectors with inelastic demand, like utilities or essential goods, often perform better. Conversely, companies relying heavily on consumer spending, such as retailers or consumer discretionary companies, may see their stock prices decline due to reduced consumer spending. Specific examples would require a detailed analysis of each company’s financial performance and sector characteristics.
Connection Between Inflation and Corporate Earnings
Inflation directly affects corporate earnings. Rising input costs, like raw materials and labor, can significantly reduce profitability. Companies may respond by increasing prices, but this may also decrease demand. Inflation’s impact on corporate earnings depends on the company’s ability to manage input costs, pass on price increases to consumers, and maintain market share. Strong pricing power in a specific sector is crucial for companies to thrive during inflationary periods.
Potential Future Scenarios
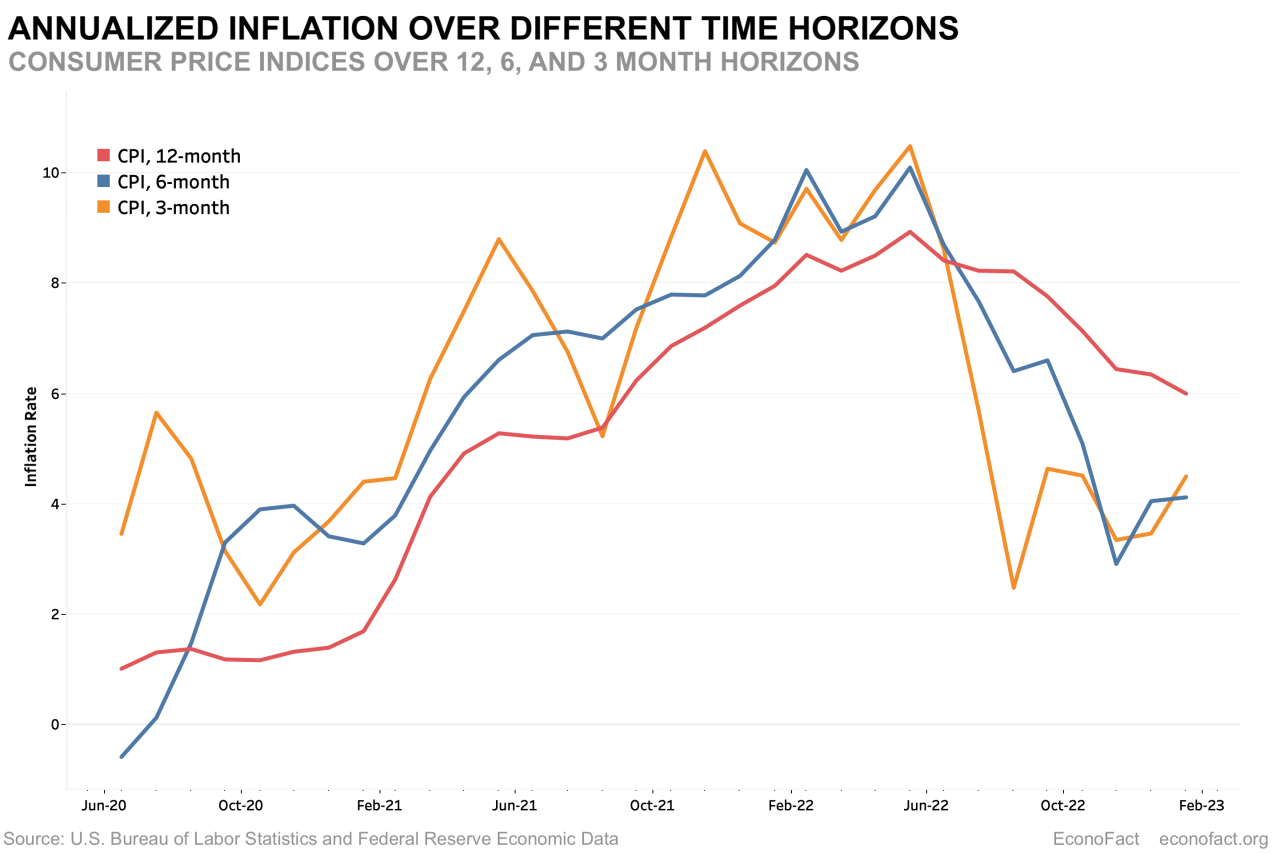
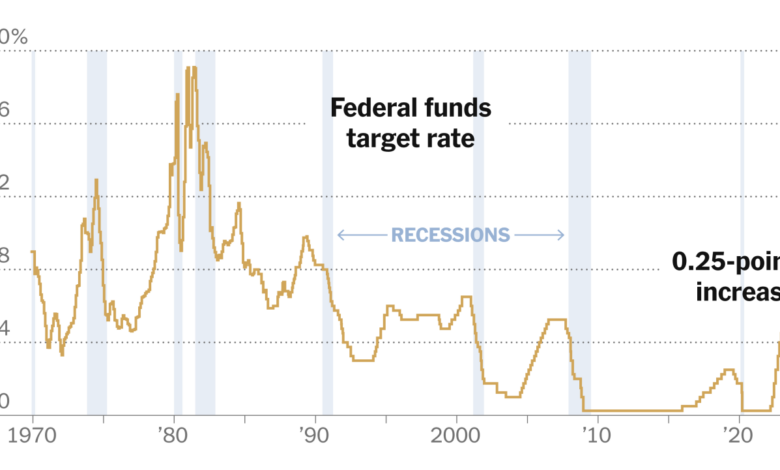
The ongoing interplay between inflation, the Federal Reserve’s monetary policy, and the stock market presents a complex landscape of potential future scenarios. Understanding these possibilities allows investors to anticipate potential market reactions and adjust their strategies accordingly. Navigating these uncertainties requires a careful assessment of the factors at play, including the Fed’s response to inflation pressures and the resulting impact on various market segments.These potential scenarios encompass a range of outcomes, from continued inflation to a rapid cooling-off period.
Inflation is definitely impacting markets and stocks, and the Fed’s response is keeping everyone on edge. It’s interesting to consider how these economic anxieties might compare to the anxieties of Sweeney Todd’s victims, though. Exploring the emotional landscape of that period through Broadway cast albums like broadway cast albums sweeney todd could offer a fascinating contrast.
Ultimately, the current state of the inflation markets and stocks, and the Fed’s strategy, still feels very much tied to human emotions and the choices we make. So maybe it’s all just a more complex version of a dark and thrilling story, in the end.
The Federal Reserve’s actions will play a crucial role in shaping the ultimate trajectory. Market reactions will depend on investor sentiment and the perceived likelihood of each scenario. The stock market’s performance will be particularly sensitive to these developments, as changes in inflation and interest rates directly affect corporate earnings and investor confidence.
Inflation is definitely a hot topic right now, affecting everything from markets to stocks and the Fed’s decisions. Recent speculation about interest rate hikes and their impact on the overall market is certainly interesting. Meanwhile, the St. Louis Blues are reportedly showing some interest in trading for Pavel Buchnevich, which could have a ripple effect on the team’s future.
blues pavel buchnevich trade interest This kind of news often gets woven into the bigger picture of economic concerns, which in turn affects how investors are thinking about the market and stocks. The current state of the market is still very much a complex interplay of various factors, including inflation and interest rates.
Potential Inflationary Trends
Inflationary pressures could persist at elevated levels, driven by supply chain disruptions, geopolitical events, or continued strong consumer demand. Alternatively, inflation could moderate as supply chains normalize and the impact of previous shocks dissipates. A more drastic scenario involves a sudden and sharp decline in inflation, potentially triggered by a significant economic downturn. These varying trajectories highlight the inherent uncertainty in predicting future inflation trends.
Federal Reserve Responses
The Federal Reserve’s response to inflation will significantly influence the trajectory of various markets. If inflation persists, the Fed might maintain or even increase interest rates to curb price increases. This strategy could lead to slower economic growth and potential recessionary pressures. Conversely, if inflation cools down significantly, the Fed might signal a potential reduction in interest rates, stimulating economic activity.
The Fed’s communication and actions will be key in shaping market sentiment and investor expectations.
Market Reactions to Different Inflation Outcomes
The stock market’s response to various inflation scenarios will be diverse. A sustained period of high inflation could negatively affect corporate earnings, potentially leading to stock price declines. A controlled decline in inflation, on the other hand, might signal a more favorable economic environment, prompting positive market reactions and increased investor confidence. A rapid disinflationary period could cause a significant sell-off in stocks if investors fear a recession.
Different Opinions on the Likelihood of Scenarios
Economists and analysts hold varying opinions on the likelihood of each inflation scenario. Some predict a prolonged period of elevated inflation, while others anticipate a more rapid return to price stability. The ongoing debate highlights the complexity of the economic environment and the difficulty in accurately forecasting future trends. Factors like global supply chain disruptions, geopolitical tensions, and consumer behavior all play significant roles in influencing the outlook.
Impact on Stocks
The stock market’s performance is directly correlated with inflation and the Federal Reserve’s response. Stocks in sectors sensitive to interest rate changes, such as financials and real estate, may experience significant volatility. Companies with strong earnings and pricing power may perform relatively better during inflationary periods, while those facing cost pressures might experience negative impacts. A rapid and unexpected change in inflation could lead to significant market fluctuations and uncertainty for investors.
Illustrative Data Visualization
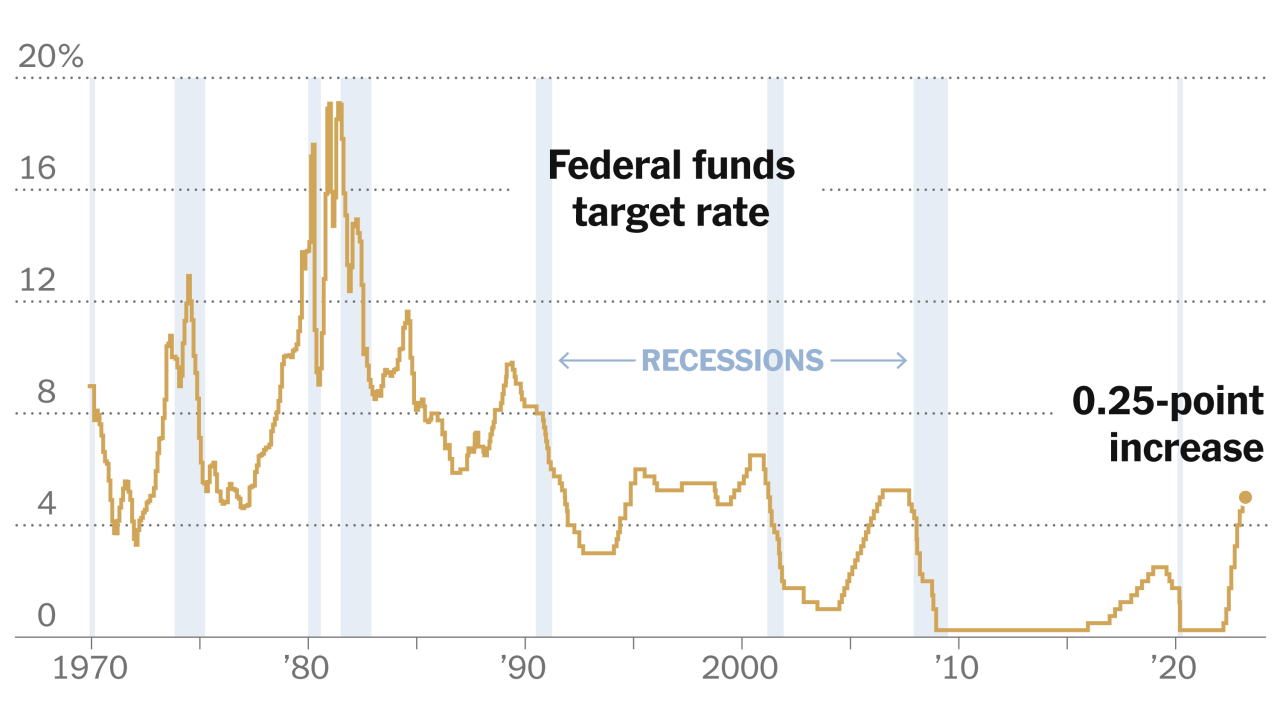
Understanding the complex interplay between inflation, stock markets, and Federal Reserve policy requires a visual representation of the key relationships. Data visualization allows us to quickly grasp trends and patterns, enabling more informed interpretations and predictions. This section presents illustrative charts and tables to better understand the dynamics at play.
Relationship Between Inflation and Stock Market Returns
Visualizing the relationship between inflation and stock market returns helps to identify potential correlations. A line graph showing monthly inflation rates against the S&P 500 index returns over a five-year period would be illustrative. This graph could show periods where inflation and returns move in tandem, diverge, or exhibit a negative correlation. For instance, periods of high inflation often correlate with higher volatility in stock markets.
This visual representation aids in identifying potential patterns and trends that may guide investment strategies.
Correlation Between Inflation Rates and Bond Yields
A scatter plot demonstrating the correlation between inflation rates and bond yields over a ten-year period provides valuable insight. Each data point on the graph represents a specific month or quarter, plotting the inflation rate against the corresponding yield of a benchmark bond. A strong positive correlation would indicate that as inflation rises, bond yields tend to increase, and vice versa.
This visualization aids in understanding the market’s response to changing inflation expectations.
Effect of Federal Reserve Interest Rate Changes on Inflation Expectations
A time series graph showing the Federal Reserve’s interest rate changes against inflation expectations (measured by surveys or market-based indicators) provides insights into the impact of monetary policy on inflation. The x-axis represents time, while the y-axis displays both the interest rate and the inflation expectation. This graph would clearly show if changes in interest rates lead to a corresponding adjustment in inflation expectations.
Historical examples of the Fed raising rates in response to rising inflation and observing the subsequent impact on inflation expectations can be effectively highlighted.
Inflation and Stock Performance in Different Sectors
This table illustrates the correlation between inflation and stock performance in different sectors over a three-year period.
| Sector | Average Inflation Rate (%) | Stock Performance (Annualized Return %) |
|---|---|---|
| Technology | 2.5 | 15 |
| Consumer Staples | 2.8 | 8 |
| Financials | 3.0 | 12 |
| Energy | 4.0 | 20 |
| Healthcare | 2.2 | 10 |
The table demonstrates how inflation rates can affect stock performance in various sectors differently. This analysis can be helpful in sector-specific investment strategies. For instance, energy stocks might show a stronger correlation with inflation due to the direct link between energy prices and inflation.
Closure
In conclusion, inflation markets stocks fed present a multifaceted challenge requiring careful consideration. The interplay between inflation, market sentiment, and Federal Reserve policy decisions is significant. This analysis has provided a comprehensive overview, but the future remains uncertain. Investors need to adapt their strategies to navigate these evolving conditions. The information presented here is for educational purposes only and does not constitute financial advice.
FAQ Guide
What is the relationship between inflation and interest rates?
Central banks often raise interest rates to combat inflation. Higher rates make borrowing more expensive, reducing spending and potentially slowing economic growth. This action can curb demand-pull inflation.
How does inflation affect stock market valuations?
Inflation can affect stock valuations in several ways. High inflation often reduces the purchasing power of future earnings, which can decrease the present value of a company’s future cash flows, thus potentially affecting stock prices.
What are some common factors influencing stock prices during inflationary periods?
Several factors, such as the company’s ability to raise prices to offset higher input costs, the overall economic climate, and investor sentiment, all play a role in determining stock performance during inflationary periods.
What are the potential future scenarios for inflation?
Potential future scenarios for inflation could include sustained high inflation, a period of disinflation, or even deflation. These scenarios can differ based on global economic conditions, supply chain disruptions, and other factors.