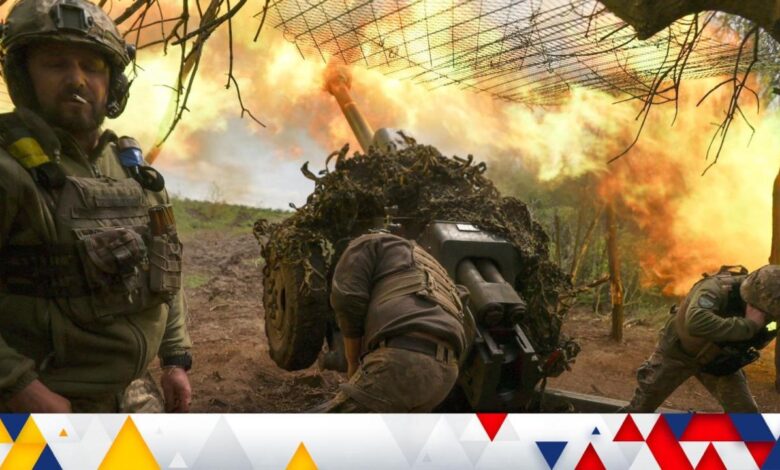
War Middle East Ukraine Russia A Complex Web
War Middle East Ukraine Russia: a complex web of interconnected conflicts, historical tensions, and global consequences. This exploration dives deep into the historical context of these regions, examining the evolving geopolitical landscapes and the impact of the Ukraine war on the Middle East.
From ancient rivalries to modern-day conflicts, the interplay of these nations is fraught with challenges. Understanding the past is key to comprehending the present and anticipating potential future scenarios. This analysis will explore the economic, geopolitical, and human cost of these conflicts, and how they intersect in surprising ways.
Historical Context
The intertwined histories of the Middle East, Russia, and Ukraine are complex and often fraught with conflict. Understanding these past interactions is crucial to comprehending the current geopolitical landscape. From ancient empires to modern-day alliances and rivalries, the region’s past continues to shape its present. This exploration will delve into the historical threads connecting these nations, examining key conflicts, figures, and the evolution of their relationships.
Historical Conflicts in the Middle East
The Middle East has a long and turbulent history marked by numerous conflicts. From ancient empires to modern-day nation-states, the region has been a battleground for various powers and ideologies. Key factors contributing to these conflicts include religious differences, competition for resources (particularly oil), and the legacy of colonialism. The rise and fall of empires, such as the Ottoman Empire, left a complex political landscape with lingering territorial disputes.
Evolution of Geopolitical Dynamics Between Russia and the Middle East
Russia’s relationship with the Middle East has evolved significantly over time. Initially, Russia’s influence was largely focused on its southern borders and securing access to warm-water ports. Later, the Soviet Union’s involvement in the region was characterized by support for various leftist movements and proxy wars. Today, Russia’s interactions with Middle Eastern countries are shaped by economic interests, strategic alliances, and a desire to counter Western influence.
Comparison of Historical Relationships Between the Middle East and Ukraine
Historically, Ukraine and the Middle East have had limited direct interactions. While there have been occasional trade connections, their relationships have not been as prominent as those between the Middle East and Russia. Ukraine’s primary historical engagements have been focused on its European neighbors and its own internal struggles. The current war has significantly altered this dynamic, drawing Ukraine into the broader geopolitical context of the Middle East through its alliances and international relationships.
Table: Historical Conflicts
| Region | Conflict Type | Key Figures | Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|
| Middle East | Ottoman-Persian Wars | Various Ottoman and Persian Sultans and Shahs | Shifting territorial boundaries and power dynamics in the region. |
| Middle East | Arab-Israeli Conflict | Leaders of Arab states and Israel, including Yasser Arafat and Golda Meir | Ongoing conflict with unresolved territorial disputes and humanitarian crises. |
| Middle East | Iranian Revolution | Ayatollah Khomeini, Shah Mohammad Reza Pahlavi | Established an Islamic Republic in Iran, impacting regional politics and alliances. |
| Ukraine | Russian Invasion | Vladimir Putin, Ukrainian President Volodymyr Zelenskyy | Ongoing conflict with significant geopolitical ramifications and humanitarian consequences. |
Current Conflicts in the Middle East: War Middle East Ukraine Russia
The Middle East, a region rich in history and resources, has been plagued by persistent conflicts and tensions. These conflicts are deeply rooted in historical grievances, religious differences, competing political ideologies, and the struggle for power and resources. The region’s geopolitical importance, coupled with its strategic location, has drawn the attention of external actors, further complicating the already complex landscape.The interplay of these internal and external factors has led to protracted and often devastating conflicts, impacting the lives of millions and shaping the regional dynamics.
The ongoing conflict in the Middle East, coupled with the war in Ukraine and Russia, is a complex and devastating situation. It’s easy to get caught up in the headlines and the sheer scale of suffering, but it’s also important to remember the human stories behind these events. For example, a recent quotation of the day on a news site highlights the devastating impact of a stroke on a man named Manuel, quotation of the day a stroke stole manuels ability to communicate which serves as a stark reminder of the human cost of any conflict, including those in the Middle East, Ukraine, and Russia.
The pain and loss are undeniably interconnected, no matter the origin.
Understanding the complexities and motivations behind these conflicts is crucial for comprehending the current political climate and potential future developments.
Ongoing Conflicts and Tensions
The Middle East is characterized by a multitude of ongoing conflicts, each with its unique set of actors, motivations, and consequences. These conflicts range from protracted civil wars to regional proxy conflicts, often fueled by competition for influence and resources. The involvement of external actors further exacerbates these tensions, adding another layer of complexity to the already intricate web of relationships.
Roles of External Actors
External actors, including Russia, the United States, and other global powers, play significant roles in the Middle Eastern conflicts. Their involvement often stems from strategic interests, economic considerations, or a desire to maintain or expand their influence in the region. These external interventions, while sometimes intended to promote stability, frequently contribute to the escalation of conflicts and the creation of new power vacuums.
The motivations and objectives of these external actors often differ, leading to competing agendas and unintended consequences.
Motivations and Objectives of Parties Involved
The motivations and objectives of the various parties involved in Middle Eastern conflicts are diverse and often intertwined. These include the pursuit of territorial control, the desire for political autonomy, economic gains, and the safeguarding of religious or ethnic identities. These competing interests often clash, creating a volatile environment prone to conflict and violence. The influence of external actors often amplifies these internal tensions, further destabilizing the region.
Impact Assessment
| Country | Conflict Type | Key Actors | Major Impacts |
|---|---|---|---|
| Syria | Civil War | Government forces, various rebel groups, external actors (Russia, US, Iran) | Massive displacement of civilians, widespread destruction of infrastructure, humanitarian crisis, and regional destabilization. |
| Yemen | Civil War and Proxy Conflict | Government forces, Houthi rebels, Saudi Arabia, Iran | Severe humanitarian crisis, widespread famine, and a major threat to regional security. |
| Iraq | Civil War and Terrorism | Government forces, various insurgent groups, external actors (US, Iran) | Political instability, ongoing security concerns, and a lingering impact of the 2003 invasion. |
| Lebanon | Political and Economic Crisis | Political factions, Hezbollah, external actors | Economic collapse, social unrest, and the ongoing struggle for political stability. |
The War in Ukraine and its Global Impact
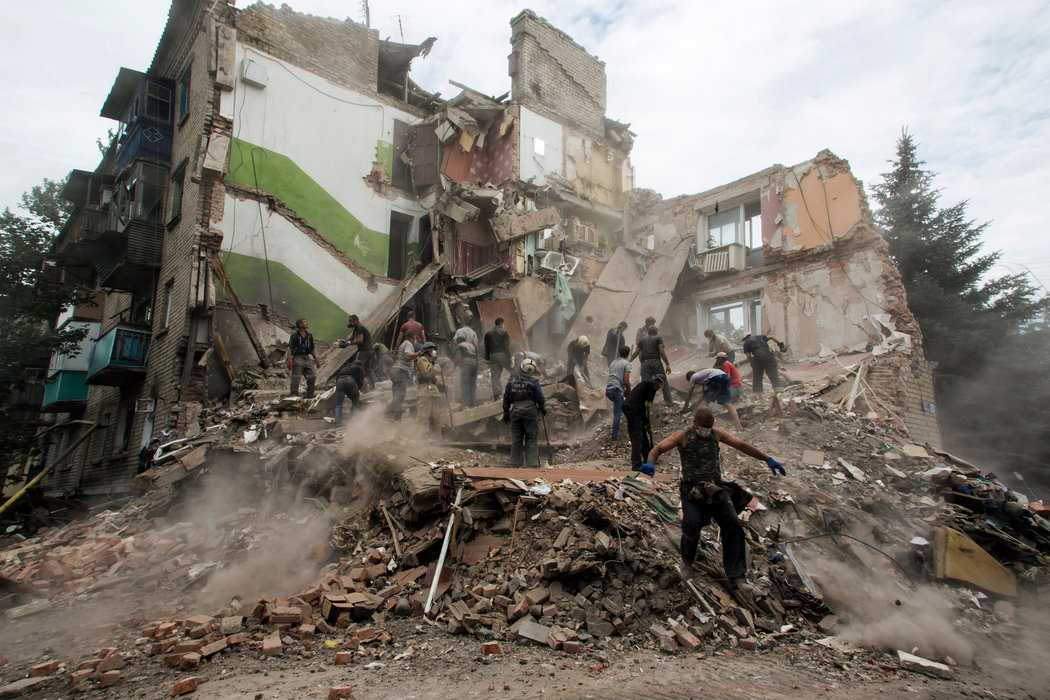

The conflict in Ukraine, sparked by Russia’s unprovoked invasion in 2022, has reverberated across the globe, fundamentally altering international relations and economic landscapes. The invasion, a stark violation of international law and sovereignty, has exposed deep fissures within the global community and ignited a debate about the future of international order. Understanding the origins, escalation, and global ramifications of this war is crucial to comprehending the complex geopolitical climate of our time.The war’s escalation from a simmering territorial dispute to a full-scale invasion was precipitated by a confluence of factors, including Russia’s perceived security concerns, historical grievances, and ambitions of reasserting its global influence.
These factors were compounded by a failure of diplomacy and a breakdown in trust between Russia and the West. The invasion’s swiftness and brutality caught many off guard, leading to widespread condemnation and a coordinated international response.
Origins and Escalation of the Conflict
The origins of the conflict trace back to a complex interplay of historical factors, including Russia’s historical ties to Ukraine, its concerns about NATO expansion, and its perceived need to secure its sphere of influence. The 2014 annexation of Crimea by Russia, following a pro-Russian uprising, marked a significant escalation of tensions. This act was followed by a protracted conflict in eastern Ukraine, further fueling the underlying instability.
Russia’s escalating military buildup along Ukraine’s border in the lead-up to the 2022 invasion served as a clear signal of its intent to exert control over the region.
Global Consequences of the War
The war in Ukraine has had far-reaching consequences for international relations, fundamentally altering the geopolitical landscape. The international community’s unified response, including sanctions and aid packages, has exposed both the strength and limitations of international cooperation. This coordinated response also exposed divisions within the international community, highlighting the complexities of navigating global disagreements in the face of aggression.
Different Perspectives on the War
Understanding the various geopolitical viewpoints is crucial for comprehending the complexities of the conflict. Russia’s perspective frames the conflict as a defensive measure to protect its security interests and prevent NATO expansion. Western perspectives, conversely, see the invasion as a blatant violation of international law and a threat to global security. These opposing perspectives underscore the profound ideological differences at play and the challenges of achieving a peaceful resolution.
Impact of the War on Various Countries
The war’s impact extends beyond the immediate conflict zone, affecting economies, international relations, and global security. The table below provides a glimpse into the diverse consequences across various countries.
| Country | Impact Category | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ukraine | Humanitarian Crisis | Massive displacement, loss of life, destruction of infrastructure | Millions of Ukrainians have fled their homes, seeking refuge in neighboring countries. |
| Russia | Economic Sanctions | Imposition of significant economic sanctions by international community | Restrictions on trade and access to financial markets have impacted Russia’s economy. |
| United States | Increased Military Spending | Increased defense spending to counter potential threats | Increased budget allocation for military operations and equipment procurement. |
| European Union | Energy Security Concerns | Increased reliance on alternative energy sources and diversification of supply chains | Diversification of energy imports away from Russia. |
Interconnectedness of Conflicts
The global landscape is increasingly interconnected, with events in one region reverberating through others. The wars in Ukraine and the Middle East, while geographically distinct, share complex threads of geopolitical rivalry, economic interdependence, and regional instability. Understanding these connections is crucial to comprehending the multifaceted challenges facing the international community.
Potential Spillover Effects from the Ukraine War to Middle Eastern Conflicts
The war in Ukraine has introduced new complexities into the already volatile Middle East. Economic repercussions, including rising energy prices and supply chain disruptions, are impacting the region’s stability. These challenges could exacerbate existing tensions, potentially leading to increased competition for resources and further conflict. Furthermore, the conflict’s impact on global security has created a vacuum that could be exploited by extremist groups, potentially leading to increased radicalization and violence.
Impact on Regional Alliances and Power Dynamics in the Middle East
The war in Ukraine has prompted shifts in regional alliances and power dynamics in the Middle East. Some nations, traditionally aligned with Russia, may now re-evaluate their positions, while others, previously hesitant to confront Russia, might find their stance toward the conflict affecting their foreign policy in the region. The geopolitical maneuvering will impact the balance of power, potentially altering existing alliances and creating new ones.
The competition for influence will be fierce.
Interconnectedness Table
| Conflict | Connection | Impact Type | Evidence |
|---|---|---|---|
| War in Ukraine | Increased energy prices and supply chain disruptions | Economic | Global energy markets are highly sensitive to geopolitical events, and the war has caused a surge in energy prices. This is impacting countries that import energy, including those in the Middle East. |
| War in Ukraine | Geopolitical maneuvering and realignment of alliances | Political | Some Middle Eastern countries are reassessing their relationships with Russia, potentially affecting their involvement in regional conflicts. |
| War in Ukraine | Potential for extremist groups to exploit the situation | Security | The global security vacuum created by the conflict could encourage extremist groups to recruit and operate in the Middle East, as seen in other historical examples of geopolitical instability. |
| War in Ukraine | Increased competition for resources and further conflict | Resource competition | Scarcity of resources and the potential for conflicts over access and control are intensified when global markets are disrupted. |
Economic Implications
The interconnected nature of global economies means that conflicts in the Middle East and the war in Ukraine have far-reaching consequences. These conflicts disrupt supply chains, inflate prices, and create economic instability, impacting countries beyond the immediate battle zones. The ripple effects are felt in various sectors, from energy and agriculture to finance and trade.The economic repercussions are complex and multifaceted, with different countries experiencing varying degrees of impact.
The ongoing war in the Middle East, with the Ukraine-Russia conflict adding another layer of complexity, is undeniably a global concern. Meanwhile, NFL news continues to emerge, like the recent hiring of Arthur Smith as the Steelers’ offensive coordinator. This hire highlights the continued activity in professional sports, even amidst the global geopolitical tensions. These seemingly disparate events, however, are all interconnected pieces of a much larger, and often unsettling, global puzzle.
Sanctions imposed by international bodies further complicate the situation, leading to economic hardship for targeted nations and potentially impacting global financial stability.
Economic Consequences of Middle Eastern Conflicts
The ongoing conflicts in the Middle East, marked by political instability and regional tensions, have substantial economic repercussions for participating countries. Reduced trade, disrupted energy supplies, and the displacement of populations directly impact the economies of affected states. For example, prolonged instability in a key oil-producing region can lead to price volatility in the global market, impacting economies reliant on oil imports.
The ongoing war in the Middle East, with Ukraine and Russia embroiled in conflict, highlights the complexities of global tension. These conflicts often overshadow stories of resilience and human spirit, like the inspiring journey of Olympic intersex athlete Maximila Imali, who navigates societal challenges with grace and determination. Maximila Imali’s story reminds us that even amidst the turmoil of war, individuals can find strength and purpose, which is a stark contrast to the struggles faced in the Middle East, Ukraine, and Russia.
Furthermore, the cost of conflict, including military spending and humanitarian aid, diverts resources away from essential economic development initiatives.
Economic Implications of the War in Ukraine
The war in Ukraine has significantly impacted the global economy, with cascading effects across various sectors. The disruption of agricultural exports, particularly wheat and other grains, has caused food price increases worldwide, particularly in vulnerable regions. Furthermore, the war has exacerbated energy price volatility, impacting countries heavily reliant on Russian energy supplies. The conflict also highlights the vulnerability of global supply chains, as disruptions in manufacturing and transportation further exacerbate the economic fallout.
Impact of International Sanctions, War middle east ukraine russia
International sanctions, imposed in response to the war in Ukraine and other conflicts, have substantial economic consequences for targeted countries. Sanctions restrict access to international financial markets, impacting trade and investment. The imposition of sanctions often leads to a decline in economic activity and a reduction in foreign direct investment, creating hardships for targeted populations. Examples include restrictions on the import and export of goods, freezing of assets, and limitations on financial transactions.
The ongoing war in the Middle East, with the Ukraine-Russia conflict dominating headlines, is undeniably complex. Meanwhile, the results of the New Hampshire Democratic primary, available here , are highlighting shifting political landscapes and strategies. Ultimately, these internal and external pressures continue to shape the global geopolitical climate and the trajectory of the war in the Middle East.
These measures can have unintended consequences, such as humanitarian crises, as well as creating economic hardship for both the targeted and sanctioning countries.
Table: Economic Impacts and Mitigation Strategies
| Country | Economic Sector | Impact | Mitigation Strategy |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ukraine | Agriculture | Significant disruption of agricultural exports, leading to food shortages and price increases. Destruction of infrastructure further exacerbates the problem. | International aid to support agricultural production and distribution, and reconstruction efforts. |
| Russia | Energy | Sanctions have severely limited Russia’s ability to export energy, leading to a decline in revenue and economic downturn. | Diversification of energy markets and development of alternative energy sources. |
| Turkey | Tourism | The war in Ukraine and regional tensions have decreased tourism in the country. | Promoting alternative tourist destinations and diversifying the economy. |
| United States | Inflation | Increased prices for energy and food products due to global disruptions, leading to higher inflation. | Implementing policies to manage inflation, such as increasing domestic production and improving supply chains. |
Geopolitical Implications
The intertwined conflicts in the Middle East and Ukraine are fundamentally reshaping global power dynamics. These crises are not isolated events but rather interconnected threads woven into the fabric of international relations. The implications extend far beyond the immediate battlefields, impacting regional security, global institutions, and economic stability in profound ways. The shifting alliances and power vacuums create a complex landscape that requires careful consideration and understanding.The escalating conflicts are forcing nations to re-evaluate their strategic partnerships and security interests.
The ongoing war in the Middle East, particularly the conflict between Ukraine and Russia, highlights the devastating impact of global unrest. Meanwhile, the recent events surrounding Al Shabab and the UN helicopter in Somalia, as detailed in al shabab un helicopter somalia , underscore the complex web of conflicts and power struggles in various regions. These separate conflicts, though geographically distant, demonstrate the interconnectedness of global issues and the ripple effect of violence across the world.
Ultimately, the situation in the Middle East and the Ukraine-Russia war demonstrate how these events can have lasting and wide-reaching consequences.
The traditional geopolitical landscape is undergoing a significant transformation, with new actors emerging and established powers adjusting to the changing circumstances. This recalibration of power is creating a complex and unpredictable environment.
Alterations in Global Power Dynamics
The conflicts are altering global power dynamics by shifting alliances and creating new power vacuums. Established powers are reevaluating their strategic partnerships and security interests, while new actors are emerging. This process is not linear and is characterized by complex interactions and unpredictable outcomes. For example, the war in Ukraine has prompted a re-evaluation of NATO’s role and has led to increased military spending in several European nations.
Regional Security and Stability Implications
The conflicts have significant implications for regional security and stability. The Middle East is facing multiple overlapping conflicts, while the war in Ukraine is destabilizing Eastern Europe and the broader Eurasian region. These interconnected crises create a cascading effect, amplifying instability and potentially leading to further conflicts. For example, the Syrian civil war has created a humanitarian crisis and a breeding ground for terrorism, while the conflict in Ukraine has triggered a humanitarian crisis and a potential for regional escalation.
Impact on Global Institutions and International Cooperation
The conflicts are placing significant strain on global institutions and international cooperation. The UN’s ability to mediate and resolve conflicts is being tested, while international agreements and norms are being challenged. The lack of consensus and cooperation among major powers is further hindering efforts to address shared challenges. For instance, the failure to achieve a unified response to the Syrian crisis has highlighted the limitations of international cooperation in addressing complex humanitarian and security issues.
Analysis Table: Power Shifts and Potential Outcomes
| Region | Power Shift | Impact | Possible Outcomes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Middle East | Rise of regional powers, weakening of traditional allies, and emergence of new actors. | Increased instability, potential for further conflicts, humanitarian crises, and a resurgence of extremist groups. | Possible escalation of regional conflicts, further fragmentation, and potentially new alliances based on shared interests. |
| Eastern Europe | Shifting security alliances, increased military spending, and growing anxieties about regional security. | Increased risk of regional conflicts, potential for a broader conflict involving major powers, and potential for nuclear escalation. | Strengthened defense alliances, increased military expenditures, and further instability in the region. |
| Global | Realignment of global power, erosion of international cooperation, and challenges to the existing global order. | Weakening of international institutions, reduced ability to address global challenges, and potential for a multipolar world. | Further fragmentation of the international community, rise of protectionist policies, and potential for new global conflicts. |
| Eurasia | Increased tensions, shifting alliances, and heightened competition among major powers. | Potential for a wider conflict, impact on global trade and supply chains, and increased humanitarian crises. | Possible realignment of alliances, increased military spending, and new strategic partnerships. |
Potential Future Scenarios
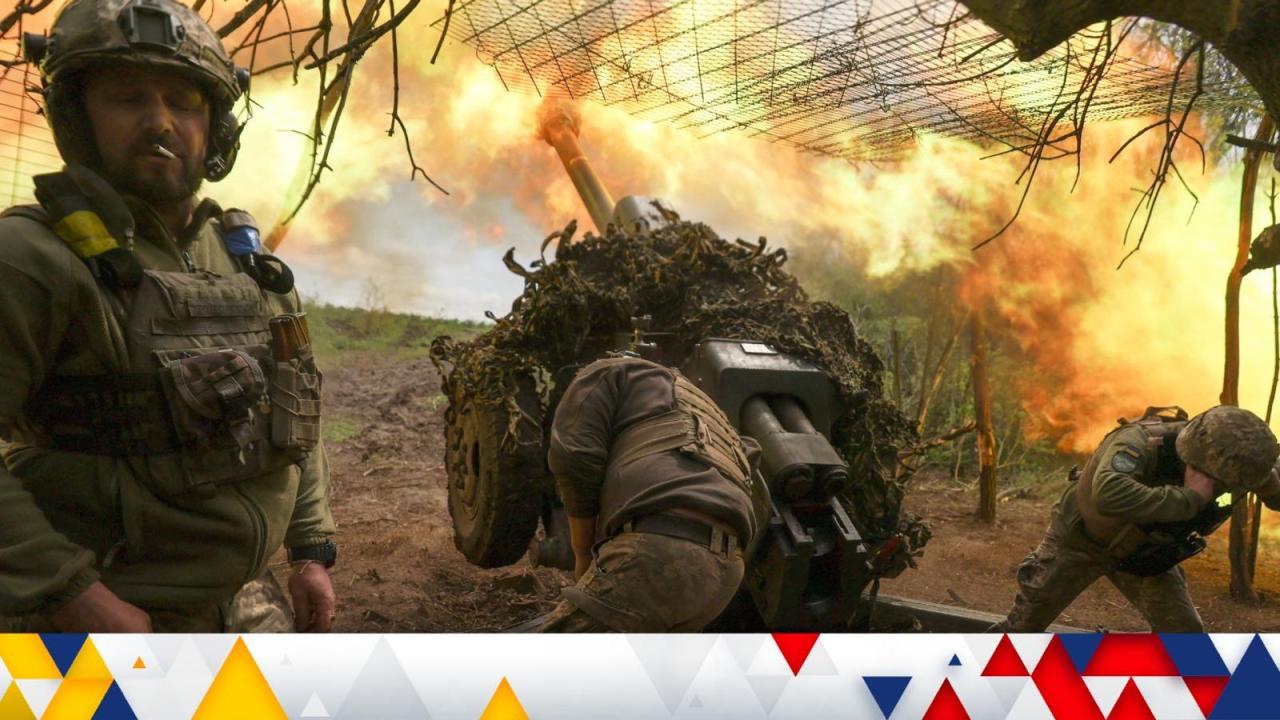

The complex interplay of conflicts in the Middle East and Ukraine, intertwined with global economic and geopolitical forces, suggests a future marked by uncertainty and potential for both escalation and de-escalation. Understanding potential future scenarios requires analyzing the underlying drivers of these conflicts, including historical grievances, resource competition, and ideological differences. Predicting the precise trajectory of these events is impossible, but by examining plausible scenarios, we can better anticipate potential challenges and opportunities.Examining past conflicts provides valuable context.
The Cold War, for example, demonstrated how regional conflicts can become entangled in global power struggles, with unforeseen consequences. Similarly, the ongoing conflicts in the Middle East and Ukraine show the interconnected nature of these crises, highlighting the difficulty of isolating solutions.
Potential for Further Escalation and Conflict Expansion
The current conflicts, despite their distinct origins, exhibit alarming potential for expansion. Regional rivalries and proxy wars can easily escalate into larger conflicts, as seen in the Middle East. The involvement of major global powers adds another layer of complexity, as their actions can inadvertently spark further escalation. For instance, the supply of weapons and military support to opposing factions can quickly escalate tensions.
Furthermore, the potential for miscalculation or unintended consequences remains high.
Possible Scenarios of Conflict Resolution and Peaceful Coexistence
While escalation remains a possibility, alternative scenarios focusing on conflict resolution and peaceful coexistence are also conceivable. Diplomatic initiatives, international mediation, and the establishment of regional security mechanisms can help mitigate tensions and promote stability. The success of such initiatives depends on the willingness of all parties to engage in good faith negotiations and compromise. For example, the Oslo Accords, while imperfect, represent a precedent for achieving a degree of peace through negotiation.
Potential Scenarios Table
| Scenario | Key Events | Potential Outcomes | Implications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Frozen Conflict | Continued stalemate in Ukraine, limited escalation in the Middle East, continued regional tensions. Limited diplomatic progress. | High level of regional instability, potential for sporadic violence, continued economic hardship, and international pressure. | Sustained humanitarian crises, potential for further refugee flows, and global economic instability. |
| Escalated Proxy War | Further involvement of external actors, expansion of the conflict geographically, increased use of advanced weaponry, rise of asymmetrical warfare. | Significant loss of life, mass displacement, potential for regional collapse, and global economic downturn. | Global instability, rise of extremist groups, and humanitarian catastrophe. |
| Negotiated Settlement | Successful diplomatic initiatives in both regions, implementation of peace agreements, establishment of regional security mechanisms, and international support. | Reduced tensions, improved relations between countries, restoration of economic stability, and international cooperation. | Improved international relations, reduced threat of global conflict, and potential for sustainable development. |
| Regional Cooperation | Formation of regional alliances and security partnerships, focused on addressing shared challenges like terrorism, resource management, and economic development. | Reduced regional tensions, enhanced economic opportunities, and improved international image for the participating nations. | Improved economic conditions, increased cooperation between nations, and a more stable global environment. |
Closure
In conclusion, the conflicts in the Middle East and the war in Ukraine are deeply intertwined, impacting global power dynamics, regional stability, and economic systems. The interconnectedness of these events highlights the urgent need for diplomacy and peaceful resolutions. This complex web requires careful consideration and understanding to navigate towards a future with reduced conflict and greater cooperation.
User Queries
What is the historical relationship between Russia and the Middle East?
Russia’s relationship with the Middle East has been complex and multifaceted, involving both cooperation and competition. Historically, it has been involved in regional politics, trade, and military engagements. This has evolved significantly over time, with shifts in power dynamics shaping the current landscape.
How does the war in Ukraine affect regional alliances in the Middle East?
The war in Ukraine has the potential to alter regional alliances and power dynamics in the Middle East. Shifting global power balances, economic pressures, and the involvement of external actors can lead to new alliances and reconfigurations of existing ones.
What are the potential economic consequences of sanctions on countries involved in these conflicts?
Sanctions imposed on countries involved in these conflicts can have severe economic repercussions, potentially leading to disruptions in trade, investment, and economic growth. The specific impacts vary greatly depending on the country and the nature of the sanctions.
What are some possible future scenarios for conflict resolution in these regions?
Potential future scenarios for conflict resolution range from diplomatic negotiations and peace agreements to the continuation of existing conflicts, with varying degrees of escalation. The outcome depends on various factors including political will, international cooperation, and regional dynamics.