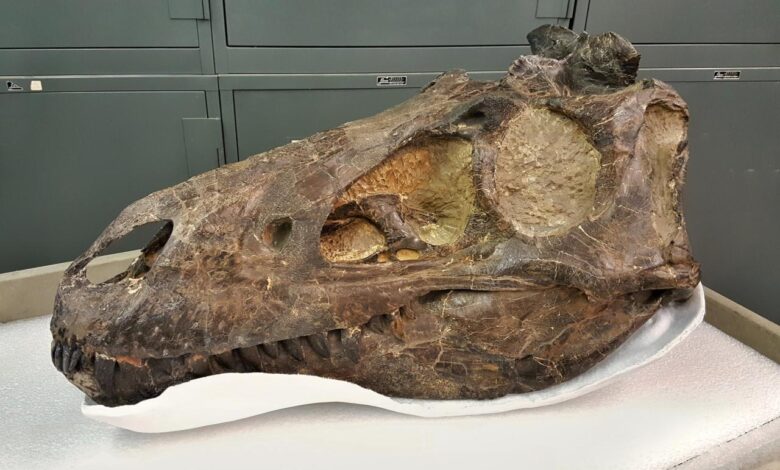

Tyrannosaurus Rex vs. Nanotyrannus Fossils
Tyrannosaurus rex nanotyrannus fossils spark a fascinating debate in paleontology. These ancient giants, once thought distinct species, now challenge our understanding of dinosaur evolution. Were they truly separate creatures, or variations within a single lineage? This exploration dives into the fossil evidence, developmental stages, and evolutionary implications to unravel the mysteries of these prehistoric predators.
This article will delve into the fossil record, examining key discoveries, dating methods, and the morphology of both species. We’ll explore how paleontologists analyze skeletal structures, reconstruct dinosaur lives, and even investigate the process of fossil excavation. It’s a journey through time, piecing together the puzzle of these remarkable creatures.
Introduction to Tyrannosaurus rex and Nanotyrannus
The Tyrannosaurus rex, a name synonymous with prehistoric power, reigned supreme as a formidable apex predator during the Late Cretaceous period. Its massive size, powerful jaws, and sharp teeth were perfectly adapted for hunting and consuming large prey. This apex predator has captured the imaginations of paleontologists and the public alike for decades, fueling a constant quest to understand its biology and behavior.The discovery of Tyrannosaurus rex fossils has unfolded over time, revealing a fascinating picture of this iconic dinosaur.
The debate over Tyrannosaurus rex and Nanotyrannus fossils is fascinating, isn’t it? It’s a bit like the ongoing discussion surrounding the recent news about Chris Young’s charges being dropped. Chris Young’s charges dropped certainly has sparked a lot of discussion. Ultimately, both the fossil debates and the legal cases highlight the complexity of piecing together the past, whether it’s the history of dinosaurs or the intricacies of justice systems.
The debate over the fossils of T-rex and Nanotyrannus continues to fascinate paleontologists and the public alike.
Early finds provided crucial evidence for its existence and characteristics, and subsequent discoveries have refined our understanding of its evolution and ecology. The discovery of Nanotyrannus fossils, closely related to Tyrannosaurus rex, added a layer of complexity to the story, sparking a significant debate regarding their taxonomic classification.
The debate over whether Tyrannosaurus rex and Nanotyrannus are distinct species continues, with fossil evidence often at the heart of the discussion. Sadly, similar struggles with defining species often happen in the human world too. Just as paleontologists puzzle over fossil remains, New York City grapples with the loss of food delivery workers, marked by poignant memorials like those found at food delivery worker memorials nyc.
Ultimately, the mysteries surrounding these ancient predators and the lives lost in our modern world remind us of the interconnectedness of struggles and the importance of recognizing loss, whether of dinosaur species or human lives. This ongoing debate highlights the complex process of scientific discovery and the human need to honor those we’ve lost.
Historical Context of Tyrannosaurus rex
The first Tyrannosaurus rex fossils were unearthed in the early 20th century, marking a pivotal moment in paleontological history. These initial discoveries, piecing together fragmented remains, laid the groundwork for reconstructing this magnificent predator. The gradual accumulation of fossils, revealing more complete skeletons, allowed researchers to build a more accurate picture of its anatomy and lifestyle.
Significance of Nanotyrannus Fossils
The discovery of Nanotyrannus fossils, unearthed in the same geological formations as Tyrannosaurus rex, immediately raised questions about their relationship to the larger predator. The smaller size and certain skeletal features of Nanotyrannus prompted speculation that it represented a distinct species, potentially a juvenile Tyrannosaurus rex or an entirely different lineage. The debate surrounding Nanotyrannus’s validity as a separate species became a significant area of discussion within the paleontological community.
Debate Surrounding Nanotyrannus
The debate surrounding Nanotyrannus’s taxonomic status has been long-standing, with paleontologists on both sides presenting compelling arguments. Some researchers argued that the unique features of Nanotyrannus fossils, such as the slender build and particular tooth morphology, justified its classification as a separate species. However, others contended that these features could be explained as developmental variations or simply as representing a juvenile stage of Tyrannosaurus rex.
Ongoing research and further analysis of fossil evidence are crucial to resolving this controversy.
Comparison of Tyrannosaurus rex and Nanotyrannus, Tyrannosaurus rex nanotyrannus fossils
| Feature | Tyrannosaurus rex | Nanotyrannus |
|---|---|---|
| Size | Massive, reaching lengths of up to 40 feet. | Smaller, estimated lengths ranging from 20 to 25 feet. |
| Skull Shape | Robust, with a large, powerful jaw. | Slender, potentially with a proportionally smaller jaw. |
| Teeth | Large, conical teeth, adapted for crushing bone. | Potentially smaller, sharper teeth, though the precise morphology remains debated. |
| Limb Proportions | Powerful hind limbs, well-suited for rapid movement. | Potential for slightly different limb proportions, though more research is needed. |
| Bone Structure | Thick and robust bones, reflecting immense strength. | Potentially lighter and less robust bones. |
The table above summarizes the key differences in physical characteristics between Tyrannosaurus rex and Nanotyrannus, highlighting the areas of contention and the need for further investigation. These comparisons help to understand the arguments surrounding their taxonomic classification.
Fossil Evidence and Discoveries
Unraveling the mysteries of Tyrannosaurus rex and Nanotyrannus hinges on the meticulous study of their fossilized remains. These ancient relics, preserved over millions of years, offer invaluable insights into their anatomy, behavior, and the environments they inhabited. The process of unearthing and analyzing these fossils reveals a fascinating narrative of prehistoric life.The fossil record, though incomplete, paints a picture of these formidable predators, revealing their strengths and weaknesses.
The meticulous work of paleontologists, painstakingly piecing together fragmented bones, offers glimpses into the lives of these magnificent creatures. Through careful study and comparison, scientists can reconstruct the evolutionary pathways and ecological roles of these giants.
Key Fossil Sites
The discovery of Tyrannosaurus rex and Nanotyrannus fossils is geographically dispersed, highlighting the widespread distribution of these species. Significant fossil sites for both species include the Hell Creek Formation in Montana, USA, and the Lance Formation in Wyoming and Montana. These formations, rich in sedimentary deposits, provide excellent conditions for fossil preservation. Other locations have yielded fragmentary remains, but the Hell Creek and Lance Formations are crucial for comprehensive study.
Fossil Characteristics Table
| Specimen | Age (Approximate) | Estimated Size (Length) | Location | Key Characteristics |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| T. rex “Sue” | 67 million years ago | 40-43 feet | Hell Creek Formation, South Dakota | Nearly complete skeleton, providing detailed insights into T. rex morphology. |
| Nanotyrannus “Jane” | 67 million years ago | 15-20 feet | Hell Creek Formation, Montana | Well-preserved juvenile skeleton, raising questions about its species classification. |
| Various T. rex specimens | 68-66 million years ago | 30-40 feet | Various sites in western North America | Provide a range of sizes and skeletal variations, crucial for understanding population dynamics. |
Dating and Analysis Methods
Precise dating of fossils is crucial for understanding the timeline of dinosaur evolution and interactions. Radiometric dating techniques, particularly using Uranium-Lead or Potassium-Argon methods, are employed to determine the age of the rock layers surrounding the fossils. These methods measure the decay of radioactive isotopes, providing a reliable estimate of the fossil’s age. Comparative analyses of fossil morphology with other known species are essential to establish evolutionary relationships and understand anatomical changes.
Morphological Comparison
Comparing the skeletal structures of Tyrannosaurus rex and Nanotyrannus reveals notable differences. T. rex possesses a massive skull with powerful jaws, characteristic of a large predator. Nanotyrannus, while sharing some similarities, displays a more slender build, suggesting potential differences in hunting strategies. Variations in skull proportions, tooth morphology, and limb structure provide evidence for distinct adaptations.
For example, T. rex’s robust hind limbs indicate a powerful gait suitable for chasing large prey, while Nanotyrannus’s comparatively smaller and more slender limbs suggest a potentially faster, more agile predator.
Reconstructing Dinosaur Life
The combination of skeletal analyses, environmental data, and knowledge of modern animals helps to reconstruct the lives of dinosaurs. For example, the size and shape of T. rex’s teeth and jaws suggest a carnivorous diet. The presence of bite marks on other fossils, alongside stomach contents, provides further evidence of feeding habits. The study of bone growth patterns in fossils can reveal aspects of development, such as the age at which these dinosaurs reached maturity.
Fossil Excavation and Preparation
Excavating fossils is a meticulous process requiring specialized tools and expertise. Careful excavation prevents damage to delicate bones and surrounding rock. Preparation involves cleaning and consolidating the fossils, meticulously removing the surrounding rock. This meticulous work reveals the bones’ structure and allows for detailed study. Modern techniques like CT scans and 3D imaging assist in analyzing the fossils without damaging them, providing a detailed view of their inner structures and helping to assemble fragmentary fossils.
Developmental Differences and Ontogeny
Understanding how dinosaurs grew and changed over time, a process called ontogeny, is crucial for accurately classifying fossil remains. This is especially important in cases where juvenile and adult specimens of the same species might exhibit distinct skeletal features, potentially leading to misidentification. The study of ontogeny in paleontology reveals the dynamic nature of dinosaur growth and provides valuable insights into their life history.Ontogeny in paleontology refers to the study of the developmental stages of organisms, including dinosaurs, from birth or hatching to adulthood.
This encompasses changes in size, shape, and skeletal features throughout an individual’s life. By analyzing these changes, paleontologists can gain a better understanding of the evolutionary relationships between different dinosaur species and the ecological roles they played. Careful analysis of fossil evidence is crucial for determining whether apparent differences between specimens represent true species distinctions or simply variations within a single species at different growth stages.
Variations in Tyrannosaurus rex Skeletal Features at Different Growth Stages
Tyrannosaurus rex, like many other dinosaurs, exhibited significant variations in skeletal morphology across its ontogenetic stages. Juveniles often possessed proportionally smaller skulls and limbs compared to adults, and their teeth were more slender and blade-like. As Tyrannosaurus rex matured, its skull grew larger and more robust, and its teeth became wider and more adapted for crushing bone. The proportions of its limbs also changed, reflecting a shift from a potentially more agile lifestyle in juveniles to a more powerful, stationary posture in adults.
Dinosaur debates are fascinating, especially the ongoing discussion surrounding Tyrannosaurus rex and Nanotyrannus fossils. The complexities of these ancient creatures’ relationships often mirror the intricacies of modern political landscapes, like the upcoming Taiwan election, particularly regarding the Democratic Progressive Party’s (DPP) role in shaping the island’s future. Taiwan election democratic progressive party Ultimately, whether Nanotyrannus is a separate species or a juvenile T-Rex remains a fossil puzzle, much like the island’s political future.
Comparison of Skeletal Structures in Nanotyrannus and Tyrannosaurus rex at Various Developmental Stages
A key aspect of the Nanotyrannus debate revolves around whether it represents a distinct species or a juvenile Tyrannosaurus rex. To assess this, a comparative analysis of skeletal structures across different developmental stages is necessary. Unfortunately, the available fossil evidence for Nanotyrannus is limited, hindering a comprehensive comparison.
| Developmental Stage | Nanotyrannus | Tyrannosaurus rex |
|---|---|---|
| Juvenile | Small, slender skull and teeth; proportionally smaller limbs | Small, slender skull and teeth; proportionally smaller limbs |
| Subadult | Potentially intermediate skeletal features, with some debate | Intermediate skeletal features; increasing skull and limb size |
| Adult | Larger, more robust skull and teeth, but possibly differing proportions | Enormous, robust skull and teeth; proportionally larger limbs |
The table above provides a simplified comparison. The precise nature of the intermediate stages remains uncertain due to the limited fossil record.
Misidentification of Juvenile and Adult Specimens as Separate Species
The possibility of misidentifying juvenile and adult specimens as separate species is a significant concern in paleontology. This can occur when the differences between growth stages are misinterpreted as defining characteristics of distinct species. Features like size, proportions, and skeletal detail can vary greatly between juvenile and adult specimens of the same species.
Examples of Other Dinosaur Species Where Ontogeny Played a Significant Role in Classification Debates
The debate over Nanotyrannus’s taxonomic status is not unique. Other dinosaur species, like Ceratosaurus, have also experienced similar debates regarding the recognition of ontogenetic variation. The presence of juvenile and adult specimens with distinct features led to initial classifications that were later revised based on a deeper understanding of growth patterns.
Factors Influencing the Interpretation of Fossil Evidence in Relation to Ontogeny
Several factors can influence the interpretation of fossil evidence in relation to ontogeny. The completeness of the fossil record, the availability of specimens spanning different growth stages, and the accuracy of developmental models are crucial. Additionally, the techniques used to analyze and compare skeletal features can impact the interpretation of results. The interpretation of ontogeny can be particularly challenging in dinosaurs with limited fossil records, as reconstructing complete growth trajectories becomes difficult.
The debate over Tyrannosaurus rex and Nanotyrannus fossils is fascinating, but it’s also a bit like the recent Trump voters in the Iowa caucus – a lot of conflicting evidence and opinions flying around. Some argue that the fossils represent distinct species, while others think they’re just juvenile T-rexes. Ultimately, like the results of trump voters iowa caucus , a clear resolution might remain elusive for quite some time, leaving paleontologists to continue the ongoing study and analysis of these ancient remains.
Paleontologists must also consider the potential impact of taphonomy (the processes that affect fossils after death) on the preservation of skeletal features.
Evolutionary Implications and Relationships
Unraveling the evolutionary history of dinosaurs, particularly theropods, is a fascinating endeavor, relying heavily on fossil evidence and comparative anatomy. The discovery and analysis of Tyrannosaurus rex and Nanotyrannus fossils provide valuable insights into the evolutionary trajectory of these apex predators. Understanding their relationships with other theropods and their adaptations to their environments is crucial to piecing together the intricate tapestry of dinosaur evolution.
Theropod Evolutionary History
Theropods, a diverse group of bipedal dinosaurs, evolved over millions of years. Early forms were often smaller, possessing adaptations for hunting smaller prey. Gradually, some lineages developed larger sizes and powerful jaws, leading to apex predators like Tyrannosaurus rex. This evolutionary progression showcases the dynamic interplay between environmental pressures and biological adaptations.
Tyrannosaurus rex and Other Theropod Relationships
Tyrannosaurus rex, with its massive size and powerful build, occupies a unique position within the theropod family tree. Its close relatives, including other tyrannosaurids, exhibit a range of sizes and features. Analyzing shared derived characteristics, or synapomorphies, allows paleontologists to establish evolutionary relationships. The robust skull, powerful jaws, and short forelimbs of tyrannosaurids are key characteristics that distinguish them from other theropods.
Nanotyrannus’ Role in Tyrannosaurus Rex Evolution
The presence of Nanotyrannus fossils adds another layer of complexity to understanding Tyrannosaurus rex evolution. Determining whether Nanotyrannus represents a distinct species or a juvenile form of Tyrannosaurus rex is a subject of ongoing debate. Analysis of fossil morphology and ontogeny (developmental stages) is crucial in resolving this question. Fossil evidence may reveal crucial information about the evolutionary transitions between these species.
Adaptations to Environments
Both Tyrannosaurus rex and Nanotyrannus, if a distinct species, likely inhabited similar environments. The presence of abundant prey and favorable ecological conditions would have been essential for their survival. Specific adaptations, such as powerful limbs for hunting and robust jaws for consuming large prey, would have been crucial for success in these environments. Comparative studies of the skeletal structure and teeth of both species offer insights into their respective ecological niches.
Evolutionary Relationships Table
| Theropod Group | Key Characteristics | Approximate Time Period |
|---|---|---|
| Early Theropods | Smaller size, varied feeding strategies | Late Triassic to Early Jurassic |
| Tyrannosaurids | Large size, powerful jaws, short forelimbs | Late Jurassic to Late Cretaceous |
| Other Theropods (e.g., Velociraptors) | Diverse forms, varying sizes and adaptations | Late Jurassic to Late Cretaceous |
This table provides a simplified overview of the evolutionary relationships between different theropod groups. The detailed relationships are complex and require consideration of various anatomical features and fossil evidence.
Paleontological Data and Evolutionary Process
Paleontological data, including fossil remains and comparative anatomy, provides critical insights into the evolutionary process. The study of fossils allows researchers to reconstruct evolutionary lineages, understand adaptations, and trace the changes in species over time. The use of radiometric dating and other techniques further refines the temporal context of these evolutionary events. By analyzing these data, paleontologists can piece together the complex evolutionary history of dinosaurs, including the relationships between Tyrannosaurus rex and Nanotyrannus.
Current Scientific Consensus and Ongoing Research
The debate surrounding Nanotyrannus and its relationship to Tyrannosaurus rex continues to be a fascinating area of paleontological inquiry. While the consensus leans towards Nanotyrannus being a juvenile Tyrannosaurus rex, ongoing research is crucial for refining our understanding of these apex predators and their evolutionary trajectories. New fossil discoveries and advanced analytical techniques are constantly pushing the boundaries of our knowledge, offering new perspectives on the evolution and paleoecology of these dinosaurs.The scientific community is actively engaged in analyzing existing fossil material and developing new research methodologies to further refine our understanding of these dinosaurs.
Key areas of focus include ontogenetic changes, biomechanical analyses, and comparisons of fossil morphology. These studies seek to clarify the evolutionary relationships between Tyrannosaurus rex and Nanotyrannus, and to shed light on the intricacies of their paleoecological roles.
Current Scientific Consensus on Nanotyrannus
The prevailing scientific consensus leans towards Nanotyrannus being a juvenile Tyrannosaurus rex. Comparative studies of skeletal features, particularly skull and tooth morphology, show strong similarities between the two. The size differences often cited as distinguishing characteristics are now understood to be consistent with developmental stages of a single species, rather than representing separate species. This interpretation aligns with the observed variability in the size and morphology of T.
rex fossils.
Key Ongoing Research Questions
Key research questions revolve around definitively proving or disproving the separate species status of Nanotyrannus. This includes the study of growth patterns in Tyrannosaurus rex, using advanced methods such as isotopic analysis of bones. Understanding the ontogenetic changes in bone structure and the rate of growth in different populations of Tyrannosaurus rex is critical. Additional research into the fossil record, particularly from the Late Cretaceous period, may offer further evidence to support or refute the Nanotyrannus hypothesis.
Recent Publications and Findings
Several recent publications have presented analyses of existing fossils, employing various paleontological methodologies to support the juvenile T. rex hypothesis. These studies frequently compare the features of Nanotyrannus specimens to those of known T. rex specimens at different developmental stages. One example is the use of CT scans to analyze the internal structures of skulls, revealing subtle differences in cranial features between purported Nanotyrannus and adult T.
rex. The study of bone microstructure and histology can also reveal the age and growth rate of the dinosaurs, adding crucial data to the debate.
Research Methodologies in Paleontological Studies
Paleontologists employ a diverse range of methodologies to investigate the past. One significant method is comparative anatomy, which involves comparing the skeletal features of different specimens. This method helps in identifying similarities and differences that might reflect evolutionary relationships. Histology and isotopic analysis of bone provide insights into the growth patterns and dietary habits of the dinosaurs.
Furthermore, biomechanical modeling is used to understand the forces exerted on the bones during movement and feeding. For instance, finite element analysis can estimate the stresses on the skull and jaws, providing insights into the feeding mechanisms of T. rex.
Potential Implications of Future Research
Future research on the paleoecology of these dinosaurs has the potential to reveal new insights into the ecosystems of the Late Cretaceous period. Understanding the precise evolutionary relationships between T. rex and Nanotyrannus can improve our understanding of the ecological niches occupied by these predators. A comprehensive understanding of their feeding habits and behaviour, combined with an analysis of their environments, can help us to reconstruct more accurately the environments they inhabited.
For instance, studies of coprolite (fossilized feces) could reveal information about their diets and prey preferences.
Methods for Studying Feeding Habits and Behavior of Tyrannosaurus Rex
Studying the feeding habits and behavior of Tyrannosaurus rex is complex. Researchers analyze the morphology of the teeth and jaws, considering the shape and size of the teeth, the strength of the jaw muscles, and the size and shape of the skull. Analysis of bite marks on fossilized prey remains can also provide crucial information about the feeding behaviors of T.
rex. Furthermore, the study of trackways and fossilized nests can offer insights into the social interactions and nesting habits of these animals. For example, finding evidence of coordinated hunting behavior or communal nesting would significantly impact our understanding of their social dynamics.
The debate over whether Tyrannosaurus rex and Nanotyrannus are distinct species continues, with fossil evidence still hotly contested. While paleontologists pore over the details, the world of high fashion is celebrating a milestone. The 50th anniversary of Didier Ludot’s couture shows in Paris is a stunning example of artistic expression, showcasing incredible detail and innovation, like the meticulous work of assembling fossil evidence.
Ultimately, the complexity of Tyrannosaurus rex and Nanotyrannus fossils remains a fascinating area of study, demanding further research to resolve the taxonomic mysteries. couture didier ludot 50th anniversary paris
Visual Representation and Communication
Bringing the prehistoric world to life requires effective visual tools. Understanding the sheer scale and features of dinosaurs like Tyrannosaurus rex and Nanotyrannus is crucial for appreciating their place in Earth’s history. Visualizations, from detailed skeletal reconstructions to environmental depictions, help us connect with these extinct giants and comprehend their evolutionary story.
Tyrannosaurus Rex and Nanotyrannus Size Comparison
Visualizing the differences in size between these two theropods is essential for understanding their potential ecological roles. The table below highlights the estimated size ranges for both species. Note that these are estimates, and further research may refine these measurements.
| Dinosaur | Length (meters) | Height (meters) | Weight (kilograms) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tyrannosaurus rex | 11-13 | 3.5-4.5 | 6,000-9,000 |
| Nanotyrannus | 6-8 | 2-3 | 1,000-2,000 |
Evolutionary Relationships of Theropods
Visualizing the evolutionary relationships among various theropod dinosaurs, including Tyrannosaurus rex and Nanotyrannus, provides insights into their shared ancestry and evolutionary pathways. This infographic illustrates a simplified phylogenetic tree showing the branching patterns of theropod evolution.
Note: The infographic would visually represent a branching diagram showcasing the common ancestors and evolutionary divergence of different theropod groups, including Tyrannosaurus rex and Nanotyrannus. It would clearly show the relationships and help understand the evolutionary timeline.
Tyrannosaurus Rex Skeleton
A Tyrannosaurus rex skeleton showcases its powerful build. The massive skull, with prominent teeth, reflects its predatory lifestyle. The robust hind limbs and powerful tail demonstrate its ability to move and hunt efficiently. The overall structure emphasizes its strength and ferocity. The long, flexible neck provides balance.
Nanotyrannus Skeleton
The Nanotyrannus skeleton displays a more slender build compared to Tyrannosaurus rex. The skull, while possessing teeth, is proportionally smaller. The limbs suggest a slightly less powerful build. The overall proportions suggest a potentially different ecological role compared to Tyrannosaurus.
Dinosaur Habitat
The environment where Tyrannosaurus rex and Nanotyrannus lived would have been characterized by a mix of forests and open grasslands. The presence of various plant species, like conifers and ferns, would have supported a diverse ecosystem. The climate would have been relatively warm, with seasonal variations.
Fossil Excavation Method
The method of fossil excavation is a painstaking process that involves meticulous work to unearth and preserve the fossils. The process typically involves careful brushing away of surrounding sediments to reveal the fossil. The steps would be illustrated with a diagram showing the layers of sediment being removed and the fossil being carefully exposed.
Growth Stages of Dinosaurs
The following series of images would illustrate the growth stages of both Tyrannosaurus rex and Nanotyrannus. The images would progressively show the increasing size and changes in skeletal features as the dinosaurs matured. The images would help to visualize the developmental differences and potential implications for their evolution.
Epilogue
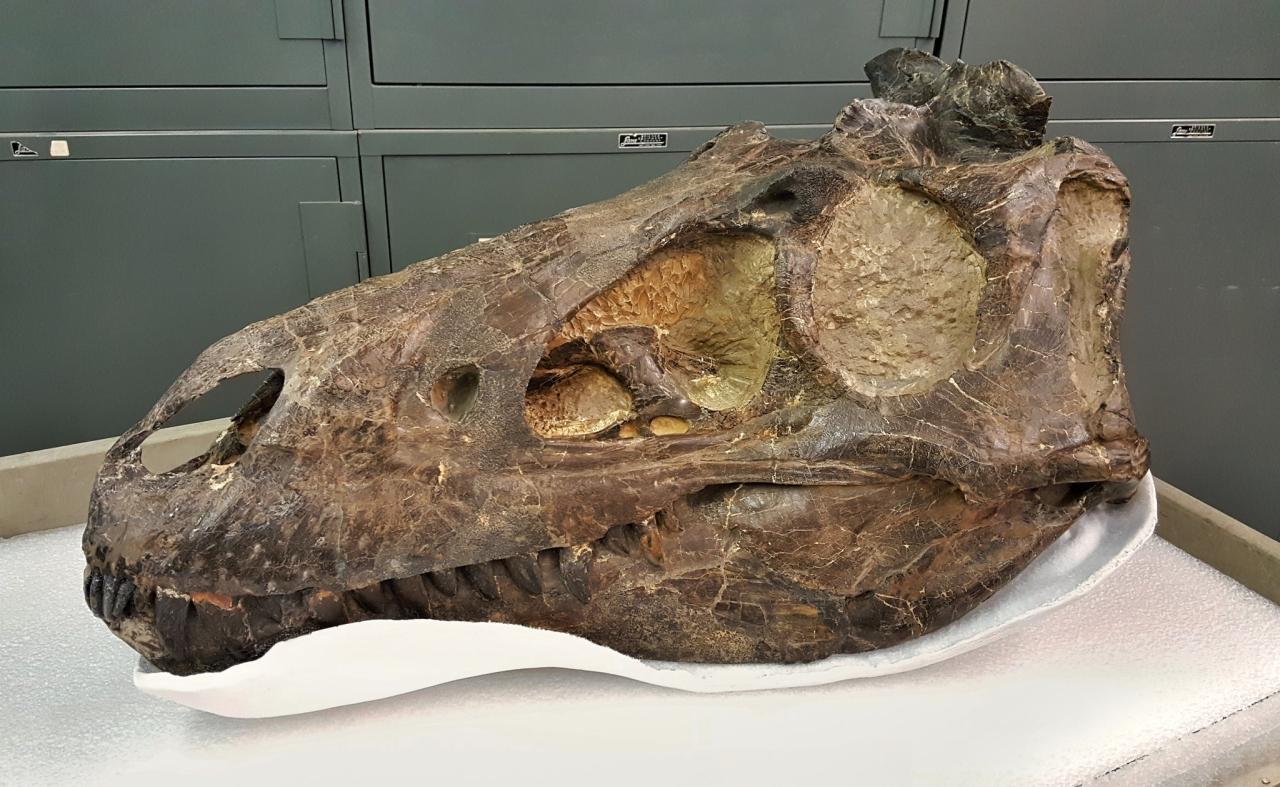

In conclusion, the debate surrounding Tyrannosaurus rex and Nanotyrannus fossils highlights the ongoing quest to understand dinosaur evolution. While a definitive answer remains elusive, the fossil evidence, developmental analysis, and evolutionary context provide compelling insights into these apex predators. Further research will undoubtedly refine our understanding of their relationship and place within the broader theropod family tree. Exciting discoveries await as paleontologists continue to unearth and analyze these remarkable fossils.
Helpful Answers: Tyrannosaurus Rex Nanotyrannus Fossils
Q: How are fossils dated?
A: Various methods, including radiometric dating, stratigraphic analysis, and comparing fossil layers with known geological timelines, are used to estimate the age of fossils.
Q: What is ontogeny?
A: Ontogeny refers to the development of an organism throughout its lifespan. In paleontology, it’s crucial for distinguishing between different species, especially juvenile and adult specimens that might appear vastly different.
Q: What are some common misconceptions about fossil analysis?
A: Misinterpretations can arise from incomplete fossil records, varying preservation quality, and the difficulty of reconstructing past environments. Paleontologists constantly refine their methods to address these challenges and increase the accuracy of their analyses.
Q: Are there any ongoing research projects concerning these dinosaurs?
A: Yes, researchers are actively investigating the paleoecology of the environments these dinosaurs inhabited, focusing on their diets, behaviors, and social structures. Advanced technologies are being used to study fossil material more comprehensively.

