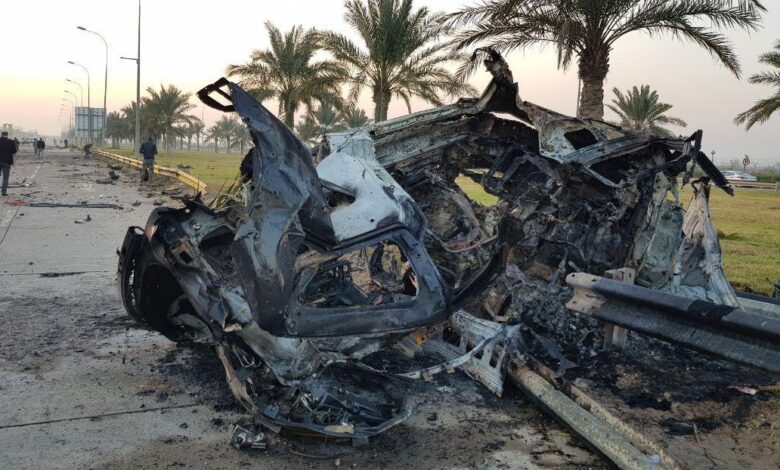
Iraq, US, Europe, Iran, Kurdistan A Complex Web
Iraq us europe iran attack kurdistan – Iraq, US, Europe, Iran, attack Kurdistan: This complex interplay of regional powers has shaped the Middle East for decades. From historical conflicts to current tensions, this article dives deep into the intricate relationships, motivations, and potential future scenarios. Understanding the past is key to grasping the present and the possible paths forward for this volatile region.
The historical context reveals deep-seated conflicts, often fueled by geopolitical ambitions and ethnic tensions. Analyzing the actions of each party – the US, Europe, Iran, and Iraq – alongside the Kurdish question, provides a comprehensive view of the multifaceted challenges facing the region. This exploration will illuminate the forces at play and their impact on global stability.
Historical Context

The volatile geopolitical landscape of the Middle East, particularly concerning Iraq, the US, Europe, Iran, and Kurdistan, has been shaped by a complex interplay of historical grievances, ideological conflicts, and shifting power dynamics. Understanding this intricate web of relationships is crucial to grasping the current tensions and potential future trajectories. This exploration delves into the historical roots of the conflicts, tracing the significant events and evolving relationships between these key players since the 1990s.The legacy of colonialism, the rise of nationalism, and the struggle for self-determination have all played a significant role in shaping the region’s current geopolitical reality.
The collapse of the Soviet Union and the subsequent emergence of new power vacuums further complicated the already delicate balance of power, leading to the rise of new actors and intensified rivalries.
Timeline of Significant Events (1990s-Present)
The 1990s saw the beginning of a period of heightened instability in the region, with the first Gulf War marking a pivotal moment. The subsequent periods of sanctions, the rise of ISIS, and the ongoing conflicts have shaped the current landscape. This timeline Artikels key events that have influenced the relationships between the involved parties.
- 1990-1991: The First Gulf War, triggered by Iraq’s invasion of Kuwait, involved significant international intervention led by the US and other Western powers. This conflict fundamentally altered the regional power dynamics and solidified the US presence in the region. The immediate aftermath included a no-fly zone over Iraqi airspace, setting the stage for future interventions and disputes.
- 1991-2003: Iraq faced international sanctions and isolation, which profoundly impacted the Iraqi population and fostered resentment towards the international community. This period also saw the rise of Kurdish nationalism and the struggle for autonomy within Iraq.
- 2003: The US-led invasion of Iraq marked a significant turning point, removing Saddam Hussein from power. This action resulted in the collapse of the Iraqi state structure and the rise of sectarian violence and instability.
- 2003-2011: The subsequent years saw the rise of various armed groups, including al-Qaeda in Iraq, which later evolved into ISIS. The protracted civil war and conflicts greatly impacted the Kurdish region and neighboring countries.
- 2011-Present: The Syrian Civil War, the rise of ISIS, and the ongoing conflicts have further destabilized the region. The involvement of various regional and international actors has intensified the complexities and challenges.
Evolution of Relationships
The relationships between Iraq, the US, Europe, Iran, and Kurdistan have been characterized by periods of cooperation, rivalry, and outright conflict. These dynamics have been influenced by competing geopolitical strategies, economic interests, and national aspirations. The evolving relationships are reflected in the changing nature of alliances and the shifting balance of power.
- US-Iraq Relations: Initially characterized by intervention and occupation, the relationship has been marked by a fluctuating level of cooperation and mistrust. The US-led intervention, intended to promote democracy, ultimately led to a complex and challenging situation in the region.
- EU-Iraq Relations: European nations have adopted a more cautious approach to Iraq, often focusing on humanitarian aid and economic development efforts, but with less direct military involvement compared to the US.
- Iran-Iraq Relations: The history of these two nations is marked by periods of war and tension, which have profoundly impacted the regional security landscape.
- Iran-US Relations: This relationship has been consistently adversarial, characterized by distrust and competing regional influences.
- Kurdistan’s Relationship with Neighboring States: The Kurdish region’s aspiration for autonomy has led to complex relationships with neighboring countries, including Iraq, Turkey, and Iran.
Historical Roots of Conflicts
The conflicts and tensions in the region have deep historical roots, stemming from factors such as territorial disputes, religious differences, and the struggle for self-determination. The legacy of colonialism, the arbitrary drawing of borders, and the rise of nationalism all contributed to the complex web of grievances and conflicts.
Major Political Shifts
The region has experienced significant political shifts in the past decades. These shifts have impacted the power dynamics between the various actors, leading to new alliances and conflicts. These include the fall of the Soviet Union, the rise of radical Islamist groups, and the emergence of new power centers.
Geopolitical Strategies
| Nation | Geopolitical Strategy |
|---|---|
| United States | Historically focused on maintaining regional stability and preventing the rise of hostile powers, often involving military intervention and alliances. |
| Europe | Prioritizing economic cooperation and humanitarian aid, often taking a more cautious approach to military intervention. |
| Iran | Seeking to expand its influence and regional dominance, often through proxies and support for regional allies. |
| Iraq | Historically focused on regional dominance, although its strategies have been significantly altered by external pressures and internal conflicts. |
| Kurdistan | Seeking autonomy and self-determination, navigating complex relations with neighboring states. |
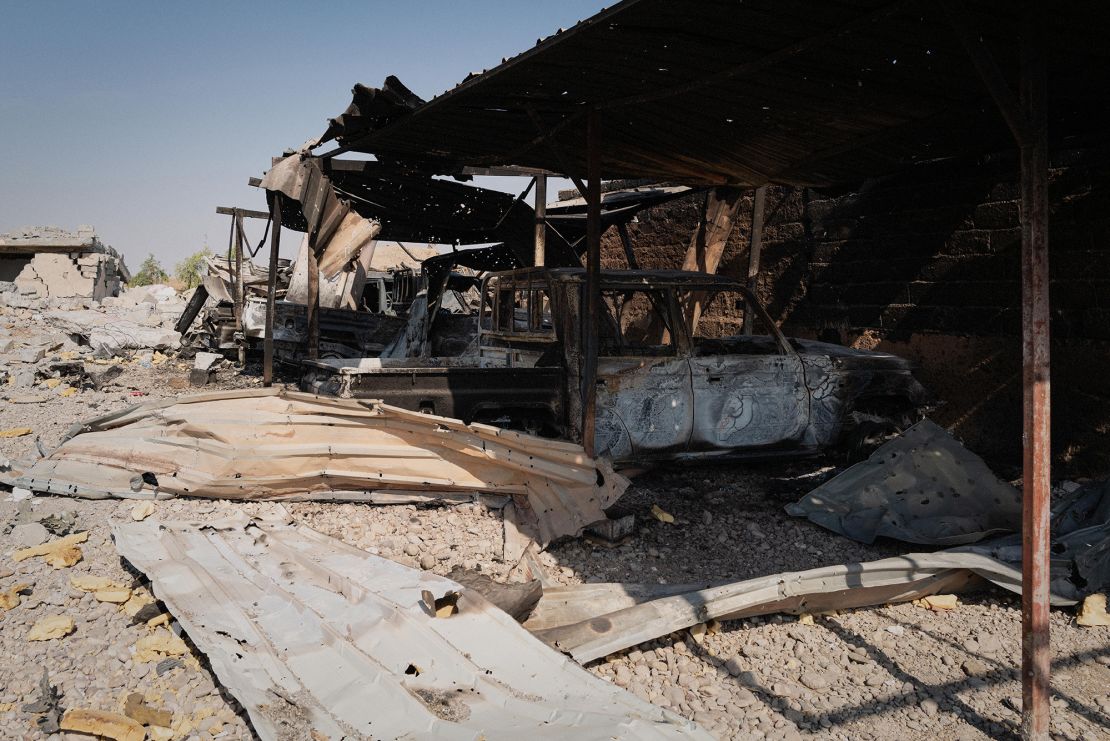
Regional Conflicts and Tensions
The intricate web of regional conflicts in the Middle East is a complex tapestry woven from historical grievances, resource competition, and ideological clashes. The interplay of internal political dynamics and external pressures creates a volatile environment, often with unpredictable consequences. Understanding these underlying tensions is crucial to comprehending the current state of affairs and the potential for further escalation.The region’s history is marked by periods of intense conflict and instability.
From the legacy of colonialism to the rise of nationalism and religious extremism, various factors have contributed to the current climate of tension. This complex history, coupled with contemporary issues like resource scarcity and political rivalries, fuels the ongoing conflicts.
Primary Sources of Conflict and Tension
The primary sources of conflict are multifaceted and interconnected. Competition for resources, particularly oil and water, is a significant driver of tension. Differing interpretations of religious and cultural identities, often exacerbated by political opportunism, also contribute to the conflict. Furthermore, historical grievances and unresolved territorial disputes continue to fuel animosity. These factors, intertwined with the legacy of colonialism and the pursuit of political power, create a potent cocktail of instability.
Key Events Exacerbating the Situation
Several key events have significantly escalated the tensions between the involved parties. The 2003 US-led invasion of Iraq, for example, destabilized the region, leading to the rise of extremist groups and further fracturing existing power structures. The Syrian civil war, beginning in 2011, has drawn in regional actors and further complicated the situation. The rise of ISIS and other extremist groups, capitalizing on the chaos, has exacerbated the conflicts and humanitarian crisis.
Role of External Actors
External actors play a critical role in escalating or mitigating the conflict. The involvement of major global powers, through military interventions, economic sanctions, or diplomatic efforts, has significantly influenced the course of events. The actions of these external actors, sometimes intended to stabilize the region, can inadvertently create further instability. The support given to various factions by external powers further complicates the situation, with each side potentially receiving assistance from a different external actor.
Perspectives of Involved Nations
The perspectives of each nation regarding the conflicts are vastly different. For example, Iran views the presence of US troops in the region as a threat to its security interests. Iraq, grappling with its own internal divisions and security challenges, often sees external actors as complicating its efforts to achieve stability. Different nations have different interests in the region, often leading to contrasting interpretations of the events and conflicting perspectives on the way forward.
Summary of Key Players and Roles
| Player | Role |
|---|---|
| United States | External actor, involved in military interventions and diplomatic efforts |
| Iran | Regional power, supporting various factions in the region |
| Iraq | Nation grappling with internal conflicts and external pressures |
| Syria | Nation embroiled in a civil war, impacting regional stability |
| Various Kurdish groups | Factions involved in regional conflicts, often seeking autonomy |
US Involvement and Policies: Iraq Us Europe Iran Attack Kurdistan
The United States has a long and complex history of involvement in the Middle East, particularly in the region surrounding Iraq, Iran, and the broader Persian Gulf. This involvement has been driven by a mix of geopolitical strategic concerns, economic interests, and ideological factors. Understanding the motivations and consequences of US actions is crucial to comprehending the current tensions and conflicts in the region.US foreign policy objectives in the region often revolve around maintaining stability, countering perceived threats, and safeguarding access to vital resources.
These objectives, however, are frequently interpreted and executed in ways that exacerbate existing conflicts and create new ones. The US approach to these regions is not monolithic and has shifted significantly over time.
US Military Interventions and Impact
Military interventions have been a defining feature of US involvement in the region. These interventions, ranging from direct military actions to covert operations, have had profound and often unintended consequences. The impact has been multifaceted, affecting the political landscape, the economic infrastructure, and the social fabric of affected countries. The long-term consequences of these interventions are still being assessed, but evidence suggests they have contributed to instability and resentment in the region.
Economic and Political Consequences of US Actions
US actions in the region have had substantial economic and political repercussions. These repercussions extend beyond the immediate battlefield, impacting trade relations, political alliances, and regional power dynamics. The consequences of sanctions, military interventions, and support for specific political factions often ripple throughout the region, affecting neighbouring countries and international relations. Economic sanctions, for example, can lead to humanitarian crises and create fertile ground for extremist ideologies to gain traction.
Comparison of US Policies Toward Iraq, Iran, and Other Regions
US policies toward Iraq, Iran, and other regions have exhibited varying degrees of engagement and intervention. These differences are influenced by perceived threats, economic interests, and the specific political landscape of each country. A comparison reveals a complex pattern, where motivations and outcomes differ significantly. For instance, the approach to Iraq following the 2003 invasion differed significantly from the US approach to Iran, highlighting the complexity of US foreign policy decision-making.
US Military Actions in Iraq
| Date | Event | Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| March 2003 | Invasion of Iraq | Overthrow of Saddam Hussein’s regime; establishment of a new government; significant loss of life and long-term instability. |
| 2004-2011 | Sustained military presence and operations | Ongoing conflict, insurgent activity, and a shifting political landscape. |
| 2014 | Rise of ISIS and increased military involvement | Further escalation of conflict; intervention by US-led coalition to combat ISIS. |
| 2017 | Withdrawal of US troops (partial) | Political instability and uncertainty in Iraq’s future; ongoing challenges. |
This table illustrates the timeline of US military actions in Iraq, showcasing the various phases of involvement and their associated outcomes.
European Perspectives and Responses
Europe’s involvement in the Middle East, particularly Iraq, Iran, and the broader region, is multifaceted and deeply rooted in historical, economic, and political interests. From colonial legacies to contemporary energy security concerns, Europe’s relationship with the region is complex and often fraught with tension. This influence is exerted not just through military might, but also through economic leverage and diplomatic engagement.
The recent tensions in Iraq, with the US, Europe, Iran, and attacks in Kurdistan, are quite complex. It’s fascinating to consider how these geopolitical events play out, especially when juxtaposed with the remarkable career of a figure like Chita Rivera, whose key moments are well documented in this article. chita rivera key moments career. These global conflicts continue to shape the world stage in ways we’re still trying to understand.
Understanding Europe’s perspective is crucial to comprehending the dynamics of the conflicts and the potential for resolution.
European Union’s Foreign Policy Strategies
The European Union (EU) employs a multifaceted foreign policy approach, often prioritizing diplomatic solutions and economic incentives. This approach, while generally avoiding direct military intervention, is not without its limitations. The EU’s foreign policy strategies are largely focused on promoting stability, democracy, and human rights. They often involve targeted sanctions and financial aid packages, designed to influence the behavior of governments and promote positive change.
Economic and Political Interests of European Nations
Europe’s economic interests in the region are substantial, particularly concerning energy resources. Significant investments in infrastructure projects and energy partnerships reflect a desire for secure energy supplies. These economic interests are intertwined with political considerations, including the need for stability in the region to ensure a predictable supply chain. Political influence is also sought through engagement with regional actors, aiming to foster dialogue and cooperation.
These interests are not without conflict, however, as different European nations might have competing or even conflicting geopolitical agendas.
Factors Influencing European Responses to Conflicts
European responses to conflicts in the region are shaped by a multitude of factors. These include domestic political pressures, public opinion, and the perceived threat to European security. The level of perceived threat often influences the degree of intervention or engagement. Public opinion, often shaped by media narratives and humanitarian concerns, can significantly affect policy decisions. Furthermore, historical context and past experiences play a critical role in shaping current perspectives and responses.
Sanctions Imposed by Europe
| Country | Type of Sanctions | Specific Examples | Year of Imposition |
|---|---|---|---|
| Iraq (various periods) | Arms Embargoes, Economic Sanctions, Travel Restrictions | Restrictions on trade, financial transactions, and investment. Restrictions on military sales and technology transfer | Multiple |
| Iran (various periods) | Economic Sanctions, Financial Restrictions, Nuclear-Related Restrictions | Restrictions on the import and export of goods, particularly those related to oil and gas. Restrictions on financial transactions. Restrictions on the development of nuclear technology | Multiple |
| Syria (various periods) | Economic Sanctions, Travel Bans, Asset Freezes | Restrictions on trade and investment, including sanctions against individuals and entities. Restrictions on financial transactions | Multiple |
Note: This table provides a concise overview of some sanctions. The specifics and duration of sanctions can vary significantly and have evolved over time. Furthermore, this table does not encompass all sanctions imposed by Europe on countries in the region.
Iranian Influence and Actions
Iran’s regional policies and ambitions have been a persistent source of tension and conflict in the Middle East. Its multifaceted approach, combining religious ideology, strategic interests, and historical grievances, has shaped its relationships with neighboring countries and influenced regional dynamics. Understanding Iran’s actions requires considering its historical and cultural context alongside its current geopolitical objectives.Iran’s actions in the region are not solely driven by a desire for dominance, but also by a complex interplay of historical grievances, ideological aspirations, and a need to secure its national interests.
This often manifests in support for proxies and militias, creating a ripple effect that exacerbates existing conflicts and fuels instability.
Iran’s Regional Policies and Ambitions
Iran’s regional policies are rooted in a complex mix of historical and ideological motivations. A cornerstone of its strategy is the promotion of its interpretation of Shia Islam, which is often interwoven with political and strategic objectives. This approach can involve backing proxy groups and militias, contributing to instability in neighboring countries. Iran’s ambitions extend beyond simply promoting its religious ideology, encompassing the pursuit of greater regional influence and the challenge of perceived adversaries.
Iran’s Relationships with Other Countries in the Region
Iran’s relationships with other countries in the region are often characterized by a mix of cooperation and conflict. Historical rivalries and differing interpretations of regional power dynamics contribute to the tensions. While Iran maintains diplomatic relations with some countries, its support for proxies and militias in other nations often creates friction and hostility. These relationships are highly dynamic, shifting based on perceived threats and opportunities.
Iran’s Influence on Regional Conflicts
Iran’s influence on regional conflicts is substantial and multifaceted. Its support for various groups, including militias and armed factions, has been a key factor in prolonging and intensifying conflicts. This support, often intertwined with ideological and strategic considerations, has contributed to the escalation of violence and the destabilization of regional security.
Table: Iranian Support for Regional Groups
| Region | Groups Supported | Nature of Support |
|---|---|---|
| Syria | Various Shia militias, including Hezbollah | Military training, financial aid, provision of weapons and equipment |
| Iraq | Shia-led political groups and militias | Political influence, financial support, training, and military equipment |
| Lebanon | Hezbollah | Financial support, military training, provision of weapons |
| Yemen | Houthi rebels | Military support, financial aid, and political backing |
This table provides a snapshot of Iran’s support for various groups in the region. The specific nature and extent of this support vary depending on the context and the perceived threat.
Historical and Cultural Context of Iran’s Presence
Iran’s presence in the region has a deep historical and cultural context. Its history is intertwined with the region’s religious and political landscape. Historical events and cultural influences have shaped Iran’s identity and its relationship with neighboring countries. These factors contribute to the complexities of Iran’s current actions and regional policies.
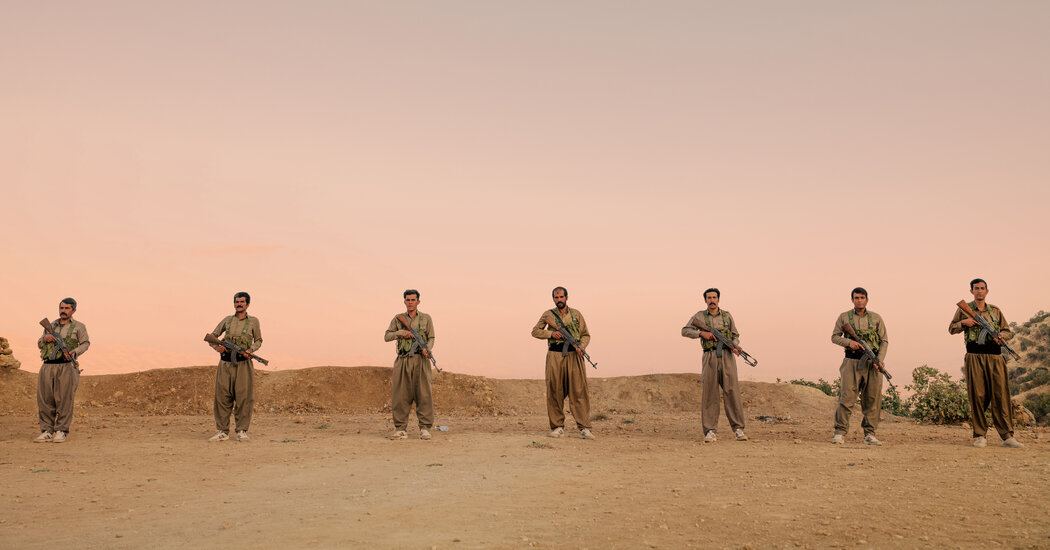
Kurdish Question and Aspirations

The Kurdish people, spread across a vast region encompassing parts of Turkey, Iraq, Syria, and Iran, have a long and complex history marked by struggles for self-determination and cultural preservation. Their quest for autonomy and recognition has often been intertwined with regional conflicts and geopolitical maneuvering, creating a multifaceted and challenging situation. This struggle is deeply rooted in a unique cultural heritage, shaped by historical events, and influenced by the ambitions of neighboring states.The Kurdish people possess a distinct language, culture, and identity that has evolved over centuries.
This distinct identity has been a source of both pride and conflict, as neighboring states have sought to integrate or marginalize the Kurdish population. Their aspirations for self-determination are multifaceted, ranging from cultural autonomy to full statehood. Understanding the Kurdish question requires examining the historical context, the various Kurdish groups, and their specific goals, as well as the ongoing political dynamics in the region.
Historical and Cultural Context of Kurdish Identity
The Kurdish people have a rich history spanning millennia, with their roots tracing back to ancient civilizations. They are not a monolithic entity, but rather a collection of diverse groups, unified by a shared language, culture, and historical experiences. Their identity is often expressed through language, customs, and traditions, which are integral to their cultural heritage. The Kurdish language, a branch of the Iranian language family, is spoken across the region, reflecting the historical migration and settlement patterns of the Kurdish people.
This shared cultural heritage has fostered a sense of collective identity and a desire for self-determination.
The recent attacks in Iraq, involving the US, Europe, Iran, and targeting Kurdistan, are certainly concerning. Understanding the political landscape is key, and a good place to start is by looking at the upcoming Nevada caucus primary, which is crucial to see how different candidates are positioning themselves. A deeper understanding of this process can offer valuable insights into how these regional conflicts are viewed and potentially influenced by domestic US politics, helping us better contextualize the ongoing tensions in Iraq, US-Europe relations, and Iran’s role in the region.
Check out this nevada caucus primary explainer for a more detailed view.
Various Kurdish Groups and Their Goals
Kurdish groups across the region exhibit variations in their political and social outlook. These variations often stem from differing historical experiences, regional factors, and exposure to various political ideologies. Some groups may prioritize cultural autonomy within existing nation-states, while others may advocate for an independent Kurdish state. Their goals often reflect the specific political and social contexts within which they live, and the historical and contemporary political climate of the region.
Timeline of Kurdish Uprisings and Movements
The Kurdish struggle for self-determination has been marked by numerous uprisings and movements throughout history. These events demonstrate a persistent desire for greater autonomy and self-governance, often met with resistance from neighboring states. From the early 20th century uprisings to contemporary movements, the timeline reflects a continuous struggle for recognition and political rights. Understanding this timeline provides a deeper context for the current challenges and aspirations of the Kurdish people.
- 1918-1922: Initial struggles for self-determination in the aftermath of World War I, amidst the division of the Ottoman Empire. These early efforts laid the groundwork for subsequent Kurdish movements.
- 1920s-1940s: Continued resistance and sporadic uprisings, often met with repression by neighboring states. These uprisings were characterized by varying levels of organization and leadership.
- 1940s-Present: Continued efforts for autonomy and self-governance, with varying degrees of success and resistance. Modern political movements and organizations have emerged in response to evolving regional dynamics.
Kurdish Political Parties and Their Platforms
Different Kurdish political parties and organizations have emerged, each with their own specific platforms and goals. These platforms reflect the diversity of opinions and approaches within the Kurdish community, ranging from those advocating for autonomy within existing states to those seeking complete independence. Understanding these diverse platforms is essential to grasping the complexity of the Kurdish struggle.
| Party Name | Platform |
|---|---|
| KDP (Kurdistan Democratic Party) | Advocates for Kurdish autonomy within Iraq, with a focus on regional cooperation and political stability. |
| PUK (Patriotic Union of Kurdistan) | Similar to KDP, focusing on Kurdish autonomy within Iraq, emphasizing the need for a strong Kurdish identity and political representation. |
| Other Parties | Diverse array of parties with various approaches to Kurdish self-determination, ranging from advocating for cultural autonomy to complete independence. |
International Implications
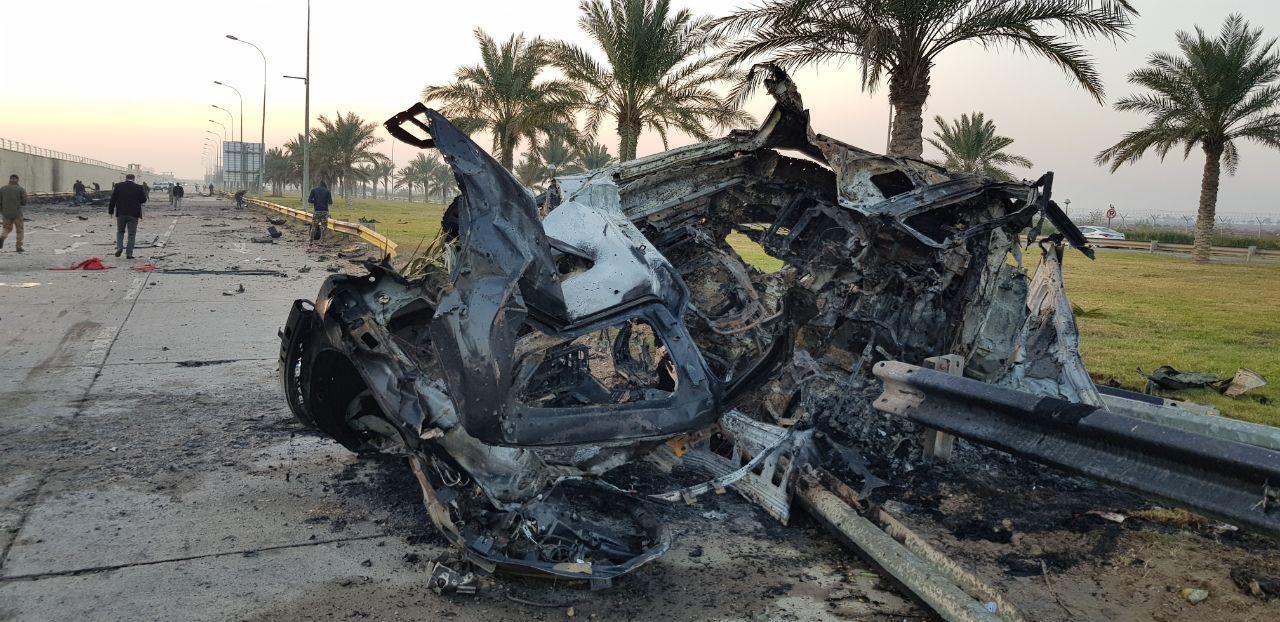

The escalating conflicts in the Middle East, encompassing Iraq, the US, Europe, Iran, and Kurdistan, have profound and multifaceted implications for global security, regional stability, international trade, and humanitarian efforts. The intricate web of regional and international actors involved creates a complex scenario with far-reaching consequences. Understanding these ramifications is crucial for comprehending the broader impact of these events.
The escalating tensions in Iraq, involving the US, Europe, Iran, and attacks on Kurdistan, are certainly a global concern. Meanwhile, the results of the New Hampshire Democratic primary, results new hampshire democratic primary , are highlighting key issues and potential shifts in political strategy. These domestic political shifts, though seemingly disparate, could inadvertently impact the geopolitical landscape, potentially influencing how the international community addresses the conflicts in the Middle East, including the ongoing issues in Iraq, Iran, and the Kurdish region.
Impact on Global Security and Stability
The conflicts have heightened tensions in the region and beyond, potentially leading to a wider escalation. The use of advanced weaponry and the involvement of multiple powerful nations increase the risk of miscalculation and unintended consequences. The actions of various actors have the potential to destabilize existing alliances and partnerships, disrupting international order and cooperation. This complex interplay of geopolitical interests can potentially exacerbate existing conflicts or trigger new ones in other parts of the world.
Regional Consequences of the Conflicts, Iraq us europe iran attack kurdistan
The conflicts have severely impacted the stability and development of the region. Economic disruptions, infrastructure damage, and displacement of populations have led to humanitarian crises. The political instability has created a vacuum for extremist groups to flourish and expand their influence. The resulting instability and conflict can create a breeding ground for terrorism and further destabilize the region, potentially spilling over into neighboring countries.
Impact on International Trade and Relations
The conflicts have already disrupted international trade routes, particularly in the Middle East. Supply chains have been disrupted, impacting the availability of essential goods and commodities. The escalating tensions and uncertainty have led to a rise in insurance premiums and reduced investment in the region. These factors have led to economic losses for numerous countries and have significantly hampered the economic development of the affected nations.
The uncertainty also discourages international investment, potentially hindering long-term economic growth.
Humanitarian Consequences
The conflicts have created a significant humanitarian crisis, causing widespread displacement and suffering. Millions of people have been forced to flee their homes, seeking refuge in neighboring countries or within their own regions. The lack of access to essential services, including food, water, and medical care, has exacerbated the suffering. The humanitarian consequences are profound and necessitate a coordinated international response to alleviate the suffering of the affected populations.
The escalating tensions in Iraq, with the US, Europe, and Iran all involved in the conflict impacting Kurdistan, are deeply concerning. Simultaneously, the geopolitical dynamics surrounding Guatemala, particularly the relationship between President Giammattei and the United States, as detailed in this article giammattei estados unidos guatemala , highlight the complex web of international relations at play. These issues, though seemingly disparate, underscore the interconnected nature of global conflicts and the need for careful diplomacy to prevent further escalation in regions like the Middle East.
Migration Patterns Caused by Conflicts
| Region | Originating Countries | Destination Countries | Estimated Numbers (Approximate) | Reasons for Migration |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Middle East | Iraq, Syria, Afghanistan | Turkey, Lebanon, Jordan | Millions | Conflict, violence, persecution |
| Europe | Ukraine, Syria | Germany, France, Italy | Hundreds of Thousands | War, conflict, seeking refuge |
| Africa | Sudan, South Sudan | Neighboring countries, Europe | Hundreds of Thousands | Civil war, violence, famine |
The table above provides a glimpse into the migration patterns caused by conflicts. It illustrates the widespread displacement and the complex challenges faced by migrants and refugees. The sheer scale of these migrations highlights the need for coordinated international efforts to address the humanitarian crisis and provide support to those affected. These migrations often strain resources and infrastructure in host countries, highlighting the global impact of regional conflicts.
Potential Future Scenarios
The volatile interplay of regional powers, historical grievances, and external interventions paints a complex picture for the future of the Middle East. Predicting specific outcomes is inherently challenging, but analyzing current trends and potential responses can offer a glimpse into possible futures. The region’s future trajectory hinges on the choices made by its actors, and the unpredictable nature of international relations adds another layer of complexity.Understanding the dynamics of power struggles, resource competition, and the aspirations of various groups is crucial to comprehending the potential future scenarios.
The interplay between internal conflicts, external interventions, and evolving geopolitical alignments will shape the region’s destiny.
Potential Outcomes Based on Current Trends
Current trends suggest a continuation of instability and conflict in the region, with the potential for escalation. Increased competition for resources, ideological differences, and unresolved territorial disputes will likely continue to fuel tensions. The likelihood of further fragmentation and regional proxy conflicts cannot be discounted.
The recent attacks in Iraq, involving the US, Europe, Iran, and Kurdistan, are a complex issue. While the geopolitical situation remains tense, it’s worth remembering that baseball heroes like Adrian Beltre, a Texas Rangers legend, have also left an enduring impact on fans. Adrian Beltre’s Hall of Fame career with the Texas Rangers reminds us of the powerful stories that transcend global events, highlighting the importance of both athletic achievement and peace.
This global unrest continues to demand attention and resolution.
- Escalation of Existing Conflicts: Existing conflicts, particularly those related to territorial disputes and ethnic tensions, may escalate into wider regional conflicts. Examples of this include the Syrian Civil War and the ongoing tensions in the Caucasus, illustrating how localized conflicts can quickly spread and become major regional conflicts.
- Regional Proxy Wars: The potential for proxy wars, where external actors support opposing sides in a conflict, remains high. The involvement of regional powers like Iran and Saudi Arabia, and external actors like the US and Russia, will continue to be a significant factor in the escalation of these proxy wars. The ongoing conflicts in Yemen and Syria exemplify this pattern, demonstrating how external involvement can significantly worsen a conflict.
- Shifting Alliances: Existing alliances and rivalries may shift and realign. New alliances may emerge, potentially leading to new configurations of power. Historical examples include the shifting alliances during the Cold War, demonstrating the fluidity of international relations.
Potential Risks and Opportunities
The region faces significant risks, including further violence, humanitarian crises, and economic instability. However, there are also potential opportunities for regional cooperation and development, particularly in areas like infrastructure and energy.
- Humanitarian Crises: Continued conflicts and instability may lead to significant humanitarian crises, impacting populations across the region. Examples include the Syrian refugee crisis and the ongoing displacement of populations in Yemen, showcasing the devastating impact of prolonged conflict on civilians.
- Economic Instability: Instability and conflict can severely impact the region’s economic development, potentially leading to further poverty and social unrest. The impact of the economic crises on the region, particularly on the Iraqi and Syrian economies, can be seen as a direct consequence of instability.
- Opportunities for Regional Cooperation: Despite the challenges, there is potential for regional cooperation in areas like infrastructure development, energy projects, and cross-border trade. Successful examples include regional agreements on trade and transportation, showcasing the potential for cooperation in addressing common challenges.
Different Perspectives on Potential Outcomes
Different actors in the region and beyond hold varying perspectives on the potential outcomes. These perspectives are shaped by their interests, priorities, and geopolitical considerations. The US, Russia, Iran, and various regional actors have different agendas and concerns that will affect the region’s future.
- US Perspective: The US seeks to maintain regional stability, counter Iranian influence, and protect its strategic interests. Their approach may involve a combination of military presence, diplomatic engagement, and support for regional allies.
- Iranian Perspective: Iran aims to expand its influence in the region, challenge US dominance, and support its allies. Their approach may involve regional interventions, support for proxies, and potentially confrontational policies.
- Regional Perspectives: Individual regional actors, such as Iraq, Turkey, and Saudi Arabia, may prioritize their national interests and security concerns, which may lead to different approaches and alliances.
Potential Future Alliances and Rivalries
The evolving geopolitical landscape suggests shifting alliances and rivalries. The formation of new alliances and the strengthening of existing ones will significantly impact the regional balance of power.
| Potential Alliance | Potential Rivalry |
|---|---|
| US-Israel-Saudi Arabia | Iran-Syria-Hezbollah |
| Turkey-Israel-Gulf States | Iran-Iraq-Lebanon |
| Russia-Syria-Iran | US-NATO-Gulf States |
Epilogue
In conclusion, the multifaceted conflict involving Iraq, the US, Europe, Iran, and Kurdistan is a complex web of historical grievances, geopolitical ambitions, and ethnic tensions. The interplay of these factors has shaped the region for decades, and the future remains uncertain. Understanding the historical context, regional conflicts, and the role of external actors is crucial to comprehending the present and navigating the potential future scenarios.
The Kurdish question adds another layer of complexity to the equation, emphasizing the urgency of finding lasting solutions for peace and stability.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the primary sources of conflict between these nations?
Historical grievances, differing geopolitical ambitions, and competing economic interests are key drivers of the conflict. Ethnic tensions, particularly the Kurdish question, also play a significant role.
What is the current status of the Kurdish struggle?
The Kurdish struggle for self-determination continues, marked by periods of both relative peace and heightened conflict. The various Kurdish groups and their goals are complex, and the region’s current political landscape greatly influences the outcome.
What are the potential future scenarios for the region?
Future scenarios range from continued instability to the emergence of new alliances and rivalries. The outcome will depend on numerous factors, including the actions of key players and the willingness to find peaceful solutions.
What is the role of sanctions in the region?
Sanctions have had varying effects, sometimes exacerbating tensions and other times contributing to regime change. Their impact is complex and often unpredictable.