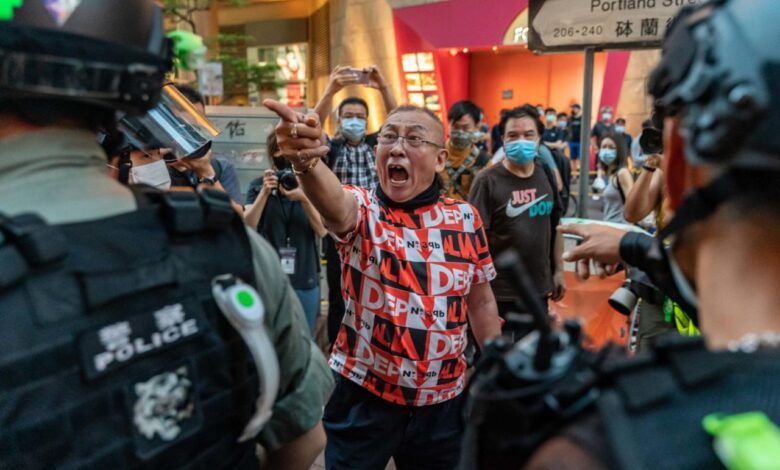
Hong Kong Security Law Unrest A Timeline of Crisis
Hong Kong Security Law Unrest: A tumultuous period in Hong Kong’s history, marked by protests, demonstrations, and a tightening grip of the Chinese government. This unrest, sparked by the controversial national security law, deeply impacted the city’s social fabric, economic stability, and international relations. This blog post will explore the historical context, the law itself, the protests, and the far-reaching consequences of this crisis.
The law’s implementation ignited a firestorm of dissent, with protesters demanding greater autonomy and freedom of expression. The ensuing unrest highlighted the complex interplay of political, social, and economic factors at play in the region.
Historical Context
Hong Kong’s journey towards the enactment of the national security law is deeply rooted in its unique history and the evolving relationship with mainland China. The 1997 handover marked a significant shift, transitioning Hong Kong from British colonial rule to a Special Administrative Region (SAR) of China. This transition, while intended to ensure stability, also brought forth complex political and social tensions.The period preceding the security law saw increasing anxieties and concerns about the future autonomy of Hong Kong.
These anxieties fueled protests and demonstrations, reflecting a complex interplay of historical legacies, economic realities, and evolving political landscapes. This historical context is crucial for understanding the motivations and actions of various stakeholders involved in the unrest and the subsequent implementation of the security law.
Timeline of Events Leading to the Security Law
The path to the Hong Kong National Security Law was paved by a series of events and developments. Key milestones included:
- 1997: The handover of Hong Kong from British to Chinese rule. This marked the beginning of a new chapter, with expectations and concerns regarding Hong Kong’s future autonomy.
- 2014: The Umbrella Movement, a series of pro-democracy protests demanding universal suffrage. This event highlighted the growing political divisions within Hong Kong and the desire for greater democratic reforms.
- 2019: The anti-extradition bill protests. The proposed legislation sparked widespread protests, which escalated into broader demonstrations against perceived erosion of freedoms and autonomy.
- 2020: The enactment of the National Security Law. This law aimed to suppress acts of secession, subversion, terrorism, and collusion with foreign forces. It followed a period of heightened tension and unrest.
Political and Social Climate in Hong Kong Before the Law
Hong Kong, prior to the security law, experienced a complex interplay of political and social forces. A significant part of the population felt that their freedoms and democratic rights were under threat.
- Concerns about autonomy: Hong Kong’s Basic Law, guaranteeing a high degree of autonomy, was at the heart of anxieties about the future of its freedoms.
- Economic shifts: The close economic ties with mainland China also created a tension between maintaining economic benefits and preserving freedoms.
- Pro-democracy movement: The growing pro-democracy movement played a crucial role in shaping the political discourse and activism. This was fueled by the desire for greater democratic representation and the perception of an erosion of freedoms.
Key Figures and Organizations Involved
Numerous figures and organizations played a significant role in the events leading up to and following the security law.
The ongoing unrest surrounding Hong Kong’s security law has been a major talking point. It’s fascinating to see how these global events connect to other significant happenings, like the results of the New Hampshire Democratic primary, results new hampshire democratic primary. Ultimately, the complex interplay of political factors, both local and international, continues to shape the situation in Hong Kong.
- Civic groups: Various civic groups, both pro-democracy and pro-establishment, were actively involved in shaping public opinion and organizing protests.
- Pro-democracy leaders: Figures like Joshua Wong and others emerged as prominent voices of the pro-democracy movement, organizing and leading protests.
- Government officials: Officials from the Hong Kong government, including the chief executive, responded to the protests and concerns in various ways, often facing public criticism.
Historical Background of the Unrest in Hong Kong
The unrest in Hong Kong has deep historical roots.
- Colonial history: Hong Kong’s colonial history under British rule shaped its identity and political landscape. The handover to China, and the anxieties about its future, contributed to the unrest.
- Cultural differences: The interplay between Hong Kong’s unique culture and values and those of mainland China created tensions and contributed to a desire to preserve freedoms and autonomy.
Comparison with Similar Situations in Other Regions
The situation in Hong Kong bears similarities to other instances of political unrest and suppression of dissent.
- Examples of other regions: Comparing the Hong Kong situation to those in other regions, such as the ongoing struggles for democratic rights in other parts of the world, can provide a broader context for understanding the complexities of political transitions.
The Security Law Itself: Hong Kong Security Law Unrest
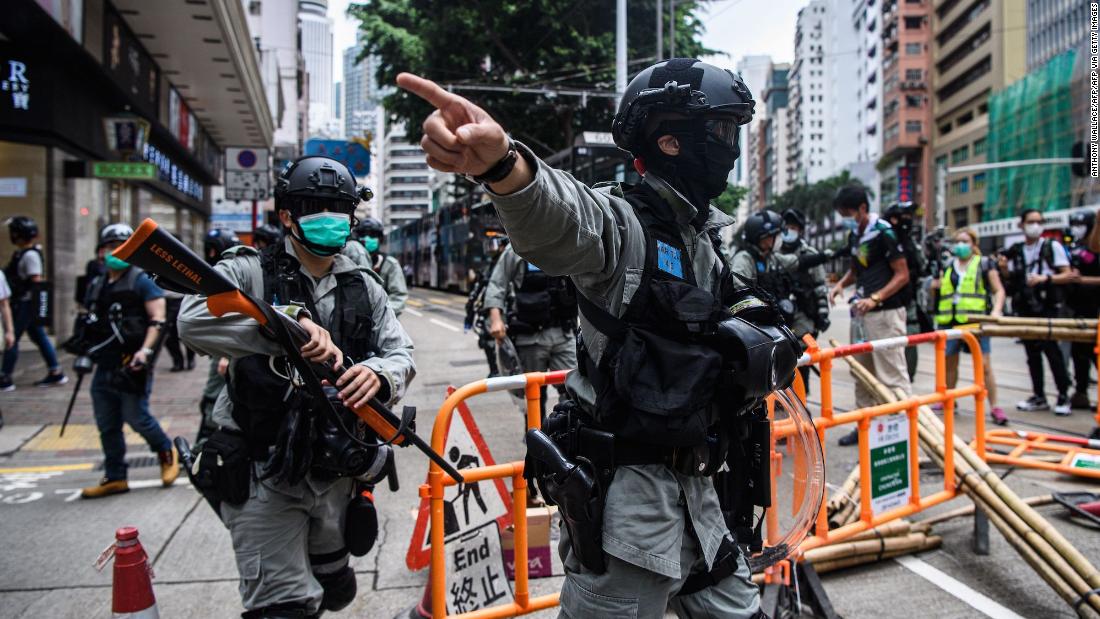

The Hong Kong National Security Law, enacted in 2020, has profoundly reshaped the political landscape of the city. This law, a direct response to escalating protests and perceived threats to national security, has been a source of intense debate and criticism, particularly regarding its impact on fundamental freedoms and democratic processes. Its implementation has significantly altered the social and political climate in Hong Kong.The law, in its broad scope, criminalizes activities deemed detrimental to national security, encompassing secession, subversion, terrorism, and collusion with foreign forces.
Its implementation has resulted in a crackdown on dissent and a tightening of control over the city’s political discourse. This, in turn, has spurred international concern and a reassessment of Hong Kong’s autonomy and future.
Key Provisions of the National Security Law
The law’s provisions are multifaceted and broad-reaching, targeting a range of activities that are viewed as threatening national security. It is important to understand that these provisions, in their broad nature, have caused concern about potential overreach and the chilling effect they could have on freedom of expression and assembly.
The Hong Kong security law unrest has really captured the world’s attention, highlighting the complex political climate. Interestingly, amidst all this, the news of Adrian Beltre’s Hall of Fame induction with the Texas Rangers is a nice reminder of different narratives and inspiring stories, like that of a baseball player who has made his mark in the sport. This, though, doesn’t diminish the serious implications of the ongoing unrest in Hong Kong, showing how events can often intertwine in unexpected ways.
Adrian Beltre hall of fame Texas Rangers and similar news can provide a welcome distraction, yet the struggles in Hong Kong remain a significant global issue.
| Provision | Description | Potential Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Secession | Activities aimed at establishing an independent Hong Kong or advocating for Hong Kong’s separation from China. | Significant curtailment of political discourse and activism related to Hong Kong’s future political status. |
| Subversion | Activities intended to undermine or overthrow the Hong Kong or Chinese governments. | Possible suppression of opposition voices and critical analysis of government policies. |
| Terrorism | Acts intended to cause serious harm or death, or create a significant risk of such harm, to the public. | Potential for overly broad interpretation of acts of protest or dissent as terrorism. |
| Collusion with foreign forces | Actions that involve collaborating with foreign governments or entities to undermine national security. | Increased scrutiny of Hong Kong’s international relations and potential restrictions on interactions with foreign entities. |
Impact on Freedoms of Speech and Assembly
The law’s provisions have directly affected Hong Kong’s long-standing freedoms of speech and assembly. The fear of prosecution under these broadly worded clauses has created a chilling effect, discouraging public discourse and dissent. Self-censorship has become prevalent, impacting the free exchange of ideas and the ability of citizens to participate in public life.
Consequences for Violations
The law carries severe penalties for those found guilty of violating its provisions. These penalties can include lengthy prison sentences, hefty fines, and other restrictions. The implementation of these consequences has been widely criticized as disproportionate to the alleged offenses, particularly in cases involving peaceful protest or expression of dissent. Examples of such cases have been documented, illustrating the potentially harsh outcomes under the law.
Potential Effects on Hong Kong’s Autonomy
The implementation of the National Security Law has raised concerns about Hong Kong’s autonomy and its ability to maintain its unique identity and legal system. Critics argue that the law’s broad scope and the subsequent crackdown on dissent erode Hong Kong’s autonomy, transforming it into a more tightly controlled region of China. This has prompted discussions about the long-term implications for Hong Kong’s future governance and its relationship with China.
The Unrest
The Hong Kong protests of 2019-2020, often referred to as the anti-extradition movement, were a series of large-scale demonstrations and civil disobedience actions. These events were deeply rooted in anxieties about the erosion of Hong Kong’s autonomy and freedoms, culminating in the imposition of the National Security Law. The unrest was characterized by a diverse array of tactics and motivations, and involved significant international attention and involvement.
Forms of Protest and Demonstration
The protests displayed a broad spectrum of methods, reflecting the diverse motivations and demands of the protesters. These ranged from peaceful marches and sit-ins to more confrontational tactics like road blockades and clashes with police. The demonstrations were not monolithic; different groups and individuals employed different strategies depending on their specific goals and the local context. This diversity of tactics was a defining characteristic of the unrest.
Motivations Behind the Protests
The motivations behind the protests were multifaceted and intertwined. A central concern was the perceived erosion of Hong Kong’s autonomy and freedoms, which many felt were being threatened by increasing influence from mainland China. The proposed extradition law, which would have allowed the transfer of criminal suspects to mainland China, was a catalyst for the protests, sparking fears of unfair trials and a lack of due process.
Economic anxieties, concerns about political freedoms, and a broader desire for self-determination played crucial roles as well.
Key Demands of the Protesters
The protesters articulated a series of demands, reflecting their concerns about the future of Hong Kong. These included the withdrawal of the extradition bill, an investigation into police brutality, greater democratic reforms, and an end to perceived encroachment on Hong Kong’s freedoms and autonomy. The protests highlighted a fundamental divergence in perspectives between the Hong Kong government and its citizens.
Role of International Actors
International actors, including governments, human rights organizations, and media outlets, played a role in the protests. Some countries expressed concerns about the human rights situation in Hong Kong, while others offered support to protesters. The global attention focused on the protests had a significant impact on the events unfolding in Hong Kong. The diverse international responses highlighted the global implications of the unrest.
Timeline of Key Events
The following timeline highlights some key events in the unrest.
| Date | Event |
|---|---|
| June 9, 2019 | Protests begin against the extradition bill. |
| June 16, 2019 | Large-scale protests erupt. |
| July 1, 2019 | Anniversary of Hong Kong’s handover. Protests occur. |
| August 31, 2019 | Protests intensify, with significant clashes with police. |
| September 1, 2019 | Large-scale protest, including civil disobedience. |
| September 2019 – November 2019 | Protests continue with varied tactics. |
| November 2019 | Escalation of violence, including confrontations and clashes. |
Impacts on Hong Kong
The Hong Kong security law and subsequent unrest have profoundly reshaped the city’s economic, social, and political landscape. The once-vibrant hub of commerce and freedom now faces challenges in maintaining its global standing and attracting investment. The turmoil has cast a long shadow, impacting everyday life and creating uncertainty for the future.
Economic Consequences
The unrest significantly disrupted Hong Kong’s economy. Protests and demonstrations caused widespread business closures, impacting retail, tourism, and hospitality sectors. Foreign investment decreased as investors worried about the political instability and the erosion of the city’s perceived rule of law. The decrease in consumer spending and business confidence further contributed to the economic downturn. Reduced tourism, a vital component of Hong Kong’s economy, led to job losses and a decline in revenue for related industries.
Effects on Hong Kong’s International Reputation
Hong Kong’s international reputation suffered a considerable blow. The perception of a decline in democratic freedoms and the erosion of the rule of law tarnished the city’s image as a bastion of international trade and investment. This shift in perception prompted a re-evaluation of Hong Kong’s attractiveness as a financial center and a destination for business. Businesses and individuals sought more stable and predictable environments for their operations.
Foreign governments and international organizations voiced concerns, affecting the city’s standing in the global community.
Changes in the City’s Political Landscape
The unrest triggered a fundamental shift in Hong Kong’s political landscape. The security law and the ensuing protests significantly altered the city’s political discourse and the relationship between the government and its citizens. The space for open political expression shrank, and the perception of democratic values was questioned. The protests underscored the growing divide between the government and segments of the population, highlighting the need for reconciliation and a return to dialogue.
Impact on Everyday Life for Residents
The unrest undeniably affected the daily lives of Hong Kong residents. Anxiety and fear were widespread, particularly among those directly affected by the protests or concerned about the future. The uncertainty surrounding the political situation impacted personal safety and economic stability. The restrictions on public gatherings and the general climate of fear had a chilling effect on social interactions and everyday activities.
Comparison of Pre- and Post-Unrest Hong Kong
| Aspect | Pre-Unrest Hong Kong | Post-Unrest Hong Kong |
|---|---|---|
| Economic Stability | A thriving financial hub with significant foreign investment and a strong economy. | Economic downturn, reduced foreign investment, and uncertainty about the future. |
| International Reputation | Renowned for its rule of law, freedom, and international standing. | Diminished reputation, concerns about political stability, and perceived erosion of democratic values. |
| Political Landscape | A relatively free and open political environment with a degree of public discourse. | Reduced space for open political expression, growing divide between the government and citizens, and limited public dialogue. |
| Everyday Life | A vibrant and dynamic city with a high quality of life. | Increased anxiety and fear, restrictions on public gatherings, and a more subdued social environment. |
International Responses
The Hong Kong national security law sparked a wave of international concern and condemnation. Countries and international organizations responded in diverse ways, ranging from diplomatic protests to economic sanctions. These responses reflected a spectrum of opinions on the implications of the law for human rights, democracy, and the future of Hong Kong.
The Hong Kong security law unrest has been a major event, deeply impacting the city’s future. While the political climate remains tense, it’s fascinating to see how other significant figures, like Chita Rivera, have navigated challenging times in their own fields. Exploring her key career moments in chita rivera key moments career offers a different perspective on resilience and navigating difficult periods, which perhaps has some relevance to the ongoing struggles in Hong Kong.
The ripples of this unrest are still felt throughout the region.
Reactions of Countries and International Organizations
Various nations and international bodies expressed their views on the security law. Some voiced strong criticism, while others opted for a more cautious approach. The reactions varied based on pre-existing geopolitical relationships and national interests. These responses, ranging from public statements to formal diplomatic notes, highlighted the complexities of international relations in the face of such a significant political development.
- Many Western nations, including the United States, the United Kingdom, and Canada, issued statements condemning the security law and expressing concerns about its impact on human rights and freedoms in Hong Kong. These statements often emphasized the importance of upholding democratic values and the rule of law. They highlighted the potential for the law to undermine Hong Kong’s autonomy and erode its unique identity.
- Some European countries, while expressing concerns, adopted a more measured tone in their responses, possibly due to a desire to maintain economic ties with China. This more cautious approach reflected a nuanced understanding of the geopolitical situation and the potential consequences of stronger actions.
- Other nations, primarily those with strong economic ties to China, maintained a more neutral stance or offered limited criticism. This approach often reflected the importance of economic considerations in their foreign policy decisions. These nations carefully navigated the complex interplay of economic interests and geopolitical tensions.
- International organizations like the United Nations Human Rights Council also addressed the security law, highlighting the potential infringement on human rights and freedoms. These statements often served as platforms for the international community to voice collective concerns and advocate for the protection of human rights in Hong Kong.
Reasons Behind the Responses
The varied reactions to the security law stemmed from a complex interplay of factors, including geopolitical considerations, human rights concerns, and economic interests. Countries often weighed these factors in their responses, leading to diverse approaches.
- Human rights concerns were central to many countries’ condemnations. The perceived erosion of democratic freedoms and the potential for repression prompted a strong international reaction, with a focus on upholding fundamental rights.
- Geopolitical considerations, particularly the growing rivalry between major powers, also played a role. Some countries viewed the security law as a challenge to the international order and a potential threat to regional stability. This influenced the tone and strength of their responses.
- Economic interests often tempered the responses of some nations. The significant economic ties with China prompted a cautious approach to avoid potential repercussions.
Diplomatic Efforts
International efforts to resolve the situation were multifaceted, ranging from diplomatic dialogues to targeted sanctions. The complex nature of the issue, coupled with the political sensitivities involved, hindered swift and effective resolutions.
- Several countries initiated diplomatic dialogues with China, aiming to address concerns and explore potential solutions. These dialogues aimed to foster communication and find common ground in resolving the situation.
- These dialogues, however, often yielded limited progress due to the differing perspectives and entrenched positions of the parties involved. The fundamental disagreements between the involved parties made effective dialogue difficult.
Sanctions Imposed and Their Impact
Some countries imposed sanctions on individuals and entities perceived as responsible for undermining Hong Kong’s autonomy. The impact of these sanctions was often debated, with some arguing they were effective deterrents, while others questioned their overall impact.
- The United States, Canada, and the UK imposed sanctions on Chinese officials and entities, targeting those deemed responsible for undermining Hong Kong’s autonomy. These sanctions aimed to pressure China to change its policies.
- The impact of these sanctions has been a subject of debate. While some believe they have put pressure on China, others argue they have had limited impact due to China’s economic strength and resilience.
International Reactions and Actions Summary
| Country/Organization | Reaction | Reason | Actions |
|---|---|---|---|
| United States | Strong condemnation | Human rights concerns, geopolitical considerations | Sanctions on individuals and entities |
| United Kingdom | Condemnation, sanctions | Human rights concerns, historical ties with Hong Kong | Sanctions on individuals, relocation of consular staff |
| Canada | Strong condemnation | Human rights concerns, international norms | Sanctions on individuals, suspension of extradition treaty |
| EU | Concerns expressed, cautious approach | Economic ties with China, diverse national interests | Limited sanctions, diplomatic dialogues |
| China | Defense of national security law | Sovereignty, national interests | Criticism of international pressure, counter-sanctions (in some cases) |
Protests and Demonstrations
The Hong Kong security law protests were not a singular event but a complex and evolving series of demonstrations, reflecting the diverse range of grievances and the changing political landscape. From peaceful marches to more confrontational actions, the protests showcased the depth of public dissatisfaction with the perceived erosion of freedoms and autonomy. The methods employed, from traditional organizing to innovative social media strategies, highlight the dynamic nature of dissent in the digital age.
Different Types of Protests
The protests encompassed a wide spectrum of activities, each with unique aims and impacts. Peaceful marches, often involving large numbers of participants, served as visible expressions of dissent and solidarity. Sit-ins, where protesters occupied public spaces for extended periods, aimed to disrupt normal activities and draw attention to their demands. Strikes, involving work stoppages by various sectors, demonstrated the economic impact of the protests and their ability to cripple essential services.
Protest Organizing Methods
Organizing protests in Hong Kong required intricate planning and coordination. Local community groups, political organizations, and activist networks played a crucial role in mobilizing support and disseminating information. Digital platforms, including social media, became indispensable tools for disseminating information, coordinating actions, and building solidarity among protesters.
Social Media’s Role in the Protests
Social media platforms, such as Facebook and Twitter, played a critical role in organizing and amplifying the protests. They facilitated rapid information sharing, allowing protesters to coordinate demonstrations, disseminate updates, and recruit participants. The ability to quickly mobilize and disseminate information through social media was instrumental in the protests’ success.
Creative and Innovative Protest Strategies
The protests witnessed innovative and creative strategies to challenge the authorities and express dissent. Protesters used creative visual displays, including elaborate banners and posters, to express their grievances and demands. The use of creative, non-violent forms of protest became a vital component of the protests, reflecting the desire to challenge the status quo in a manner that did not rely on violence.
Evolution of Protest Tactics, Hong kong security law unrest
| Timeline | Protest Tactics | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Early 2019 | Peaceful marches, rallies | Large-scale marches through major streets, symbolic demonstrations |
| Mid-2019 | Sit-ins, blockades | Protesters occupying public spaces, disrupting transportation routes |
| Late 2019 | Strikes, civil disobedience | Strikes by various sectors, acts of civil disobedience |
| 2020 onwards | Increased use of digital tools, focus on online mobilization | Online petitions, virtual rallies, use of social media for communication and organization |
This table demonstrates the evolving nature of protest tactics during the Hong Kong security law unrest. The methods used shifted from traditional demonstrations to more innovative approaches, highlighting the dynamic nature of protest movements.
Social and Cultural Impacts
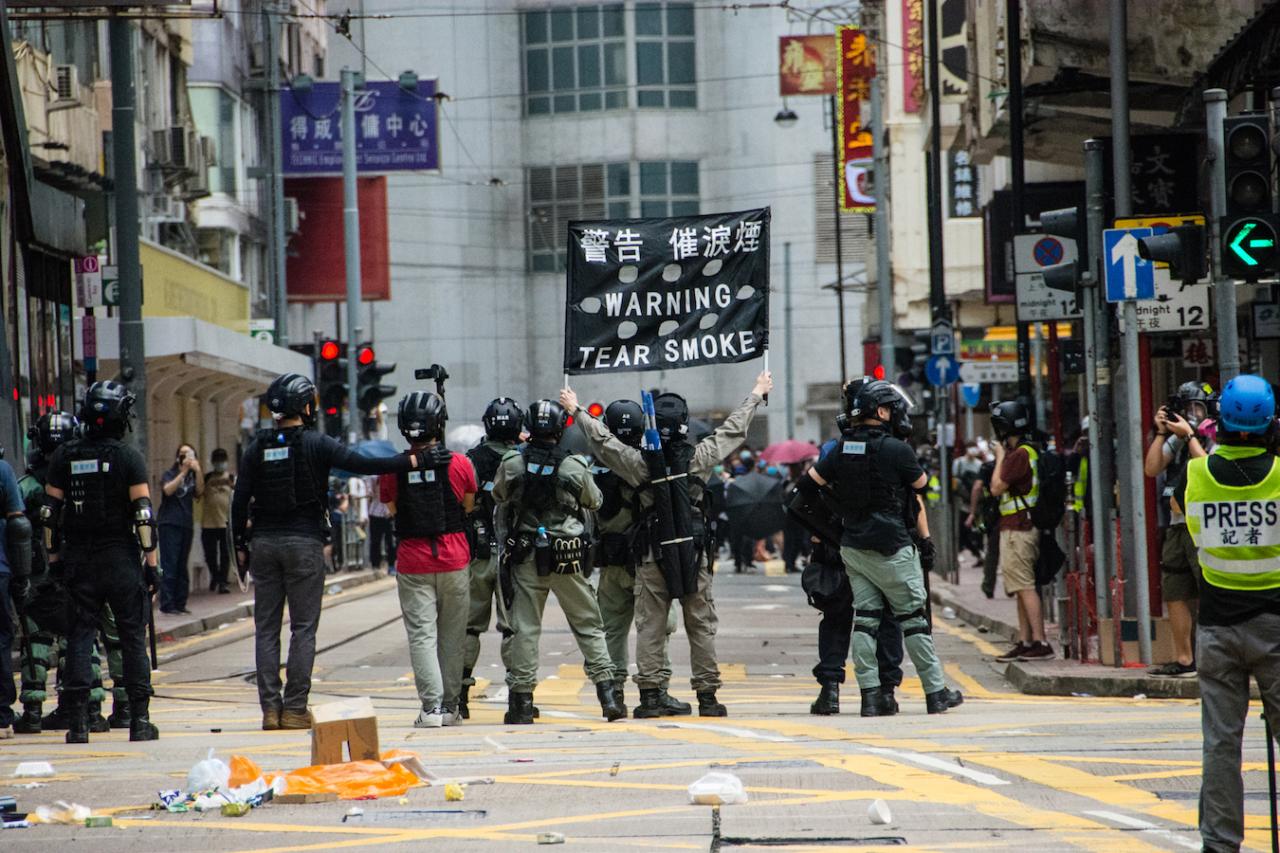

The Hong Kong security law, and the ensuing unrest, have profoundly impacted the social fabric and cultural expressions of the city. The atmosphere of fear, uncertainty, and division has altered daily interactions, eroded trust, and reshaped the very essence of Hong Kong’s identity. The long-term effects on the city’s psychological well-being and cultural landscape remain to be fully understood.
Changes in Social Interactions and Relationships
The security law and protests have significantly altered social interactions. A palpable sense of unease and suspicion permeates public spaces. Informal conversations and social gatherings have become more guarded, with individuals hesitant to express dissenting opinions openly. The once-vibrant exchange of ideas and viewpoints has been replaced by a cautious and reserved atmosphere. Trust between individuals and groups has diminished, particularly among those holding differing political views.
Community solidarity has fractured in some areas, with long-standing friendships and relationships strained or broken.
Impact on Cultural Expressions and Artistic Freedom
Artistic expression, a cornerstone of Hong Kong’s cultural identity, has faced limitations. Concerns over censorship and self-censorship have emerged, as artists grapple with the delicate balance between creative freedom and potential repercussions. The fear of reprisal has led some to refrain from expressing politically charged views in their work. This self-imposed restraint has stifled the dynamism and diversity of cultural expression, creating a chilling effect on artistic endeavors.
Furthermore, the media landscape has also witnessed a significant shift in the types of artistic works being produced and shared.
Changes in the Media Landscape
The media landscape in Hong Kong has undergone a transformation. Stricter regulations and self-censorship have become more common, leading to a reduction in the range of viewpoints presented to the public. Independent news outlets have faced pressure and difficulties, while pro-government media have gained greater prominence. This shift in the media landscape has created a skewed and potentially incomplete picture of events, limiting access to diverse perspectives and affecting public understanding.
Furthermore, the credibility of some news outlets has been questioned, leading to a decline in public trust.
Long-Term Psychological Effects on Citizens
The prolonged unrest has had a significant impact on the psychological well-being of Hong Kong citizens. Prolonged exposure to conflict, uncertainty, and fear can lead to anxiety, stress, and depression. Post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) may also develop in some individuals. Furthermore, the loss of personal freedom and the perceived erosion of democratic values have contributed to a sense of powerlessness and hopelessness.
These psychological consequences are likely to have long-lasting effects on the mental health of the city’s population.
Emotional and Psychological Consequences of the Unrest
The unrest has triggered a range of emotional and psychological consequences, including anxiety, fear, and trauma. Citizens have experienced intense emotions, from grief and anger to sadness and despair. The collective trauma experienced by the community has fostered a climate of heightened sensitivity and vulnerability. The disruption of daily routines and the fear of violence have also taken a toll on the mental well-being of residents.
The psychological impact of the unrest will likely continue to be felt for years to come.
Media Coverage
The Hong Kong security law unrest was a global event, generating extensive media coverage. Different outlets presented varying perspectives, often shaped by their own biases and editorial stances. This varied reporting significantly impacted public understanding and perception of the events.Understanding the diverse narratives presented by various media outlets is crucial for a comprehensive understanding of the situation. Different outlets often presented the protests and government responses from contrasting viewpoints, leading to a complex and often conflicting picture for the public.
Different Perspectives in Media Reports
Media reports on the Hong Kong security law unrest often presented different perspectives. Some outlets focused on the protesters’ grievances and the government’s perceived heavy-handedness, while others emphasized the need for maintaining law and order. This divergence in viewpoints reflects the political and social divides surrounding the issue. International news organizations, with their diverse global reach, often tried to provide a more balanced approach, but their coverage still reflected different editorial priorities.
Role of Biased Reporting
Bias in media reporting can significantly influence public opinion. Certain outlets might favor one side of the conflict over another, shaping the narrative to support their pre-existing beliefs or political agendas. This bias can stem from various factors, including political affiliations, financial interests, or cultural backgrounds. Readers must be aware of this potential bias when evaluating news reports, cross-referencing information from multiple sources, and seeking out diverse viewpoints to form a well-rounded understanding.
Impact of Censorship on Media Outlets
Censorship, whether direct or indirect, can significantly impact media outlets’ ability to report on events. In cases of direct censorship, the government or other controlling parties may directly restrict reporting or impose penalties on outlets that publish certain information. Indirect censorship, through pressure or self-censorship, can also restrict reporting by media organizations. In Hong Kong, for instance, concerns regarding self-censorship were raised by some news organizations in the face of possible government reprisals.
The Hong Kong security law unrest has definitely been a significant event, and it’s fascinating to see how seemingly unrelated things can sometimes feel connected. For example, while the protests raged on, the news of the Steelers hiring Arthur Smith as their new offensive coordinator, as reported on arthur smith hired steelers offensive coordinator , makes you wonder about the broader societal shifts and how they might be impacting various aspects of life.
Ultimately, the impact of these events on Hong Kong remains a complex and ongoing story.
Different Media Outlets and Their Coverage
Various media outlets covered the Hong Kong security law unrest. Their approaches and perspectives differed significantly, reflecting their editorial policies, affiliations, and target audiences. News outlets from different countries, with differing geopolitical interests, also shaped their coverage, resulting in different angles and emphasis.
Hong Kong’s security law unrest has been a major global concern. Understanding the complexities of political maneuvering, like those surrounding the upcoming Nevada caucus primary, can offer valuable insights into how these kinds of situations develop. A good starting point for understanding the current political landscape is this nevada caucus primary explainer , which helps contextualize the current political climate.
Ultimately, the unrest in Hong Kong continues to be a critical issue demanding attention and resolution.
Table Contrasting Media Outlets and Perspectives
| Media Outlet | General Perspective | Focus/Emphasis | Potential Bias |
|---|---|---|---|
| CNN | Generally balanced, seeking to provide multiple viewpoints. | Broad international context, global impact. | Potential bias towards Western perspectives. |
| BBC | Neutral and impartial, seeking to provide objective reporting. | Historical context, international reactions. | Potential bias towards a nuanced and objective portrayal. |
| South China Morning Post (SCMP) | Often more aligned with pro-government narratives. | Emphasis on maintaining order, addressing concerns about unrest. | Potential pro-government bias, though not exclusively. |
| HKFP | Generally pro-democracy and pro-protest. | Highlighting protesters’ grievances, government repression. | Potential pro-democracy bias. |
Potential Future Scenarios
The future of Hong Kong, following the implementation of the national security law and the subsequent unrest, remains uncertain. Multiple factors, including the ongoing international disputes and the evolving political landscape, will shape the region’s trajectory. This section explores potential scenarios, considering the implementation of the security law, long-term consequences for the region, and the impact of international disputes.
Potential Scenarios for the Security Law’s Implementation
The national security law’s implementation has profound implications for Hong Kong’s autonomy and freedoms. Different interpretations and applications of the law can lead to varying outcomes. The law’s impact on the legal system, freedom of speech, and the political environment will shape the future of Hong Kong.
- Increased Surveillance and Restrictions: A scenario where the security law is aggressively implemented could see a significant expansion of surveillance technologies and restrictions on freedom of expression. This could lead to a chilling effect on dissent and limit public participation in political processes. Examples of similar scenarios exist in other regions where authoritarian governments have used broad security laws to suppress dissent and limit freedoms.
The potential impact on Hong Kong’s international reputation would be considerable.
- Gradual Erosion of Autonomy: A more gradual approach might see the law used to subtly erode Hong Kong’s autonomy, with increasing interference from the central government in areas like the judiciary and the legislature. This could involve a slow but steady erosion of freedoms, potentially mirroring patterns observed in other regions where gradual control was exerted over time.
- Limited Impact and Adaptation: A less restrictive implementation could involve the law being used primarily to target specific individuals or groups perceived as threats to national security. This could involve more targeted actions, rather than a broad suppression of dissent. The actual implementation could vary, depending on the political climate and leadership in Beijing.
Potential Long-Term Consequences for the Region
The consequences of the security law extend beyond Hong Kong’s borders. The impact on the region’s economic stability, political relations, and social fabric will be felt throughout the area.
- Economic Deterioration: A decline in investor confidence and decreased foreign investment could severely impact Hong Kong’s economy. The loss of international prestige and reduced freedom of movement could deter businesses and skilled workers, leading to a potentially significant downturn. This has been observed in similar instances where political unrest has impacted economic stability.
- Increased Tensions in the Region: The security law and its implementation could heighten tensions between Hong Kong and certain international partners, possibly leading to trade sanctions or diplomatic isolation. The escalation of international disputes, if they involve the security law, could lead to significant regional instability.
- Shifting Political Landscape: The security law could contribute to a more polarized political landscape in the region, impacting cross-border relations and potentially leading to regional conflicts. Examples of political polarization in other regions can highlight the potential for long-term societal division.
Potential Outcomes of Ongoing International Disputes
International disputes over Hong Kong’s future have the potential to significantly affect the region. These disputes can lead to different scenarios, ranging from diplomatic isolation to international intervention.
| Potential Outcome | Influencing Factors |
|---|---|
| International Condemnation and Sanctions | Strong international condemnation of the security law, potentially including trade sanctions or diplomatic pressure. This depends on the level of international support for Hong Kong’s freedoms. |
| Limited International Response | A lack of significant international response, potentially due to concerns about escalating regional conflicts or economic interests. The response would be influenced by the international community’s perceived risks. |
| Increased Regional Tensions | International disputes escalating into direct confrontations or military actions. This depends on the severity of international disagreements and the willingness of stakeholders to escalate the situation. |
Closure
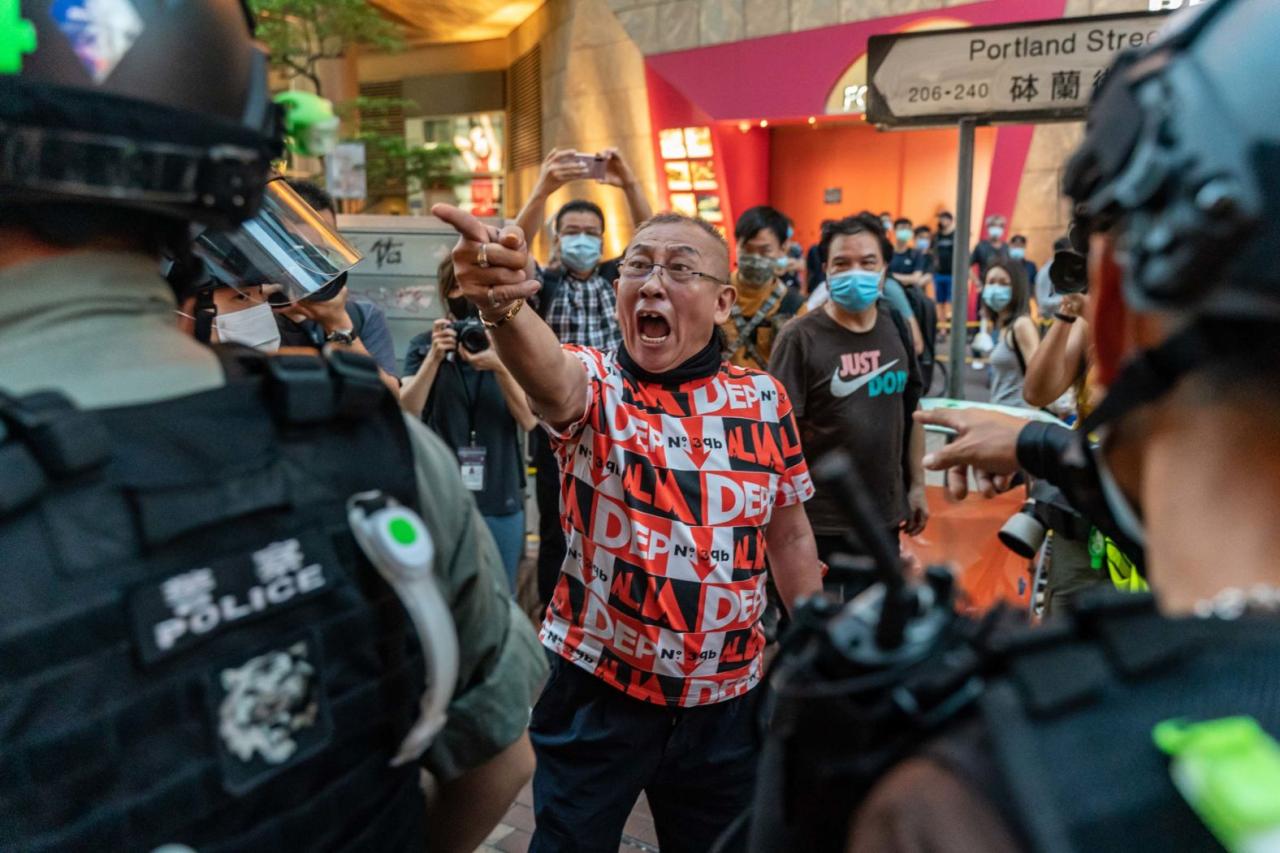
In conclusion, the Hong Kong Security Law Unrest stands as a stark reminder of the complexities of political and social change. The event exposed the fault lines between different ideologies and the struggles for autonomy and self-determination. This crisis continues to resonate in Hong Kong and beyond, shaping the future of the region and raising critical questions about the future of freedoms.
FAQ Overview
What were the key demands of the protesters?
Protesters demanded greater autonomy, freedom of expression, and an end to perceived government overreach. Specific demands varied, but the core theme was the protection of fundamental rights.
How did the international community respond?
International reactions varied, with some countries imposing sanctions and expressing concern over human rights violations, while others maintained a more neutral stance.
What were the long-term economic consequences of the unrest?
The unrest significantly impacted Hong Kong’s economy, leading to decreased tourism, business closures, and a decline in investor confidence.
What is the current status of Hong Kong’s political landscape post-unrest?
The political landscape has shifted significantly. A tightening of control by the Chinese government has altered the balance of power and limited avenues for dissent.






