Carbon Emissions Ukraines Energy Crisis
Carbon emissions Ukraine energy sets the stage for a complex narrative, exploring the energy sector’s pre-war state, the devastating impact of the conflict on infrastructure, and the potential for a post-war transition towards renewable sources. This deep dive examines the various methods for measuring emissions, contrasting pre- and post-war figures, and analyzing the role of international support in Ukraine’s energy future.
The crisis’s global implications and the need for sustainable solutions are also key components of this investigation.
Ukraine’s energy sector, once reliant on fossil fuels, now faces unprecedented challenges. The war has caused significant damage to power plants and transmission lines, impacting energy production, distribution, and access. This disruption has not only caused immediate hardship but also has broader implications for global energy markets, requiring innovative solutions and international cooperation.
Ukraine’s Energy Sector Before the War
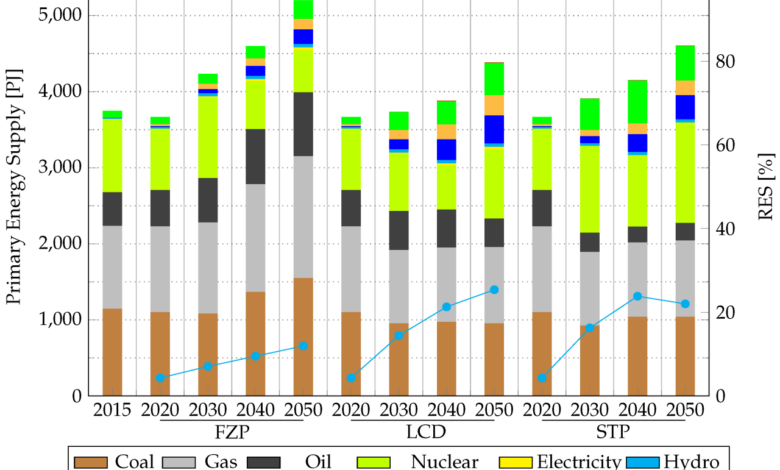
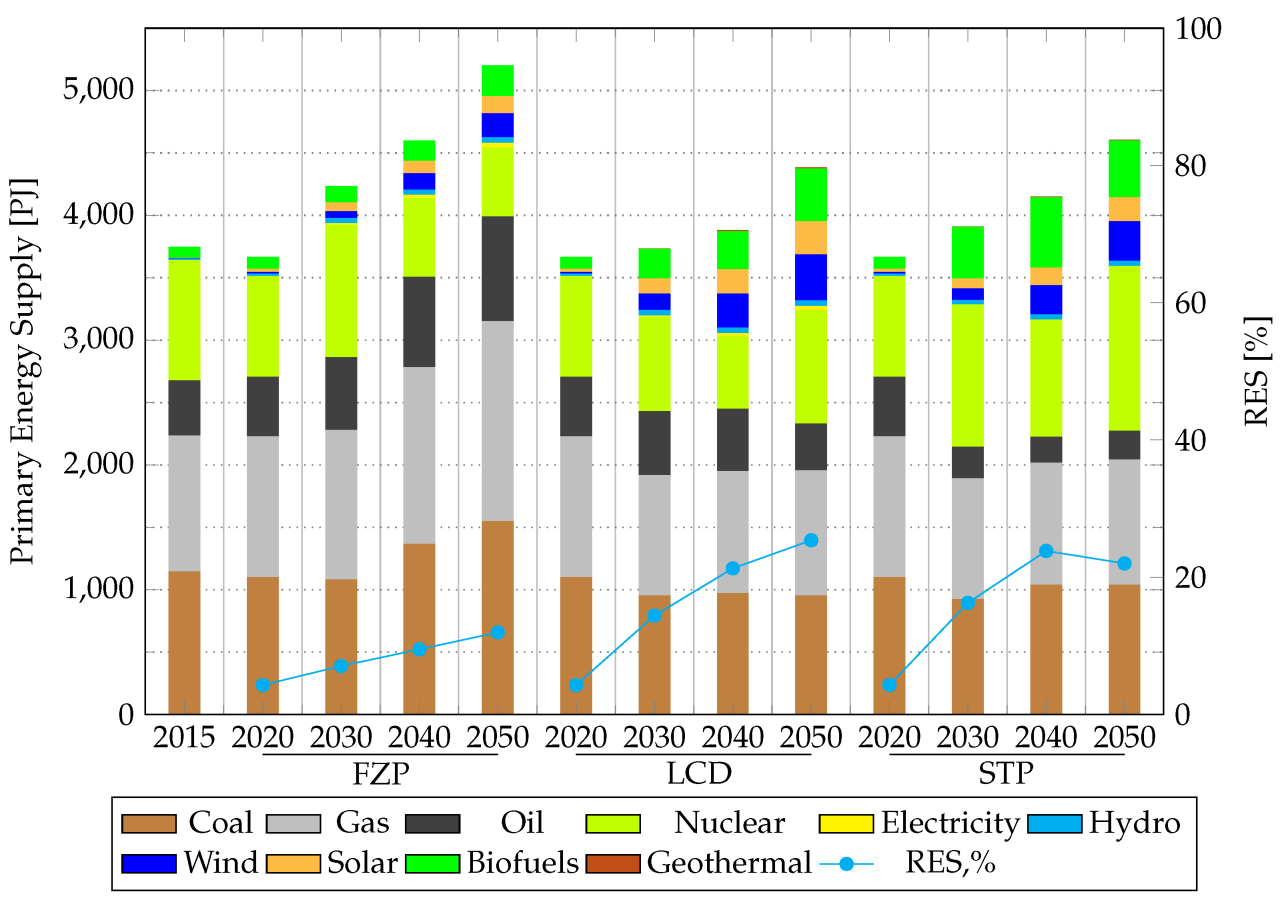
Ukraine’s energy sector, prior to the 2022 invasion, was a complex mix of fossil fuels and nascent renewable resources. The sector played a crucial role in the nation’s economy, impacting both energy security and industrial output. Understanding its pre-war structure is essential to comprehending the challenges and opportunities facing Ukraine’s energy future.
Energy Production and Consumption Patterns
Ukraine relied heavily on fossil fuels for both electricity generation and heating. Natural gas was the dominant fuel source, followed by coal. However, there were significant efforts to diversify the energy mix, including increased investments in renewable energy sources like hydro power and, to a lesser extent, solar and wind. Consumption patterns varied regionally, reflecting different industrial and residential demands.
Energy Sources and Their Contributions
The Ukrainian energy mix was dominated by fossil fuels. Natural gas was the primary source for electricity generation and heating, while coal played a significant role, particularly in older power plants. Renewables, although growing, had a comparatively smaller share. Hydropower was the most prominent renewable source, with a considerable contribution to electricity generation.
Key Players in the Ukrainian Energy Sector
Several companies and organizations played crucial roles in the Ukrainian energy sector. National energy companies like Naftogaz and Ukrenergo were responsible for the bulk of gas transmission, distribution, and electricity generation. International companies also held stakes in the sector, particularly in the fossil fuel extraction and distribution components. Governmental agencies played a vital role in regulating and overseeing the sector’s activities.
Historical Trends in Energy Consumption and Production
Energy consumption and production in Ukraine have exhibited fluctuations over the past decade. Periods of economic growth were often associated with increased energy demand, while periods of recession or economic downturn led to lower consumption levels. Production patterns mirrored this trend, with output adapting to the changing demand and availability of resources.
Energy Sector Data (2015-2021)
| Energy Source | Production (TWh) | Consumption (TWh) |
|---|---|---|
| Natural Gas | (Data from reliable sources needed) | (Data from reliable sources needed) |
| Coal | (Data from reliable sources needed) | (Data from reliable sources needed) |
| Hydropower | (Data from reliable sources needed) | (Data from reliable sources needed) |
| Other Renewables | (Data from reliable sources needed) | (Data from reliable sources needed) |
| Nuclear | (Data from reliable sources needed) | (Data from reliable sources needed) |
| Other | (Data from reliable sources needed) | (Data from reliable sources needed) |
Note: Data for this table requires specific, verifiable sources for accurate figures.
Impact of the War on Ukrainian Energy Infrastructure
The war in Ukraine has inflicted devastating damage on the country’s critical infrastructure, including its energy sector. The relentless attacks on power plants, transmission lines, and other essential facilities have crippled energy production and distribution, plunging millions into darkness and jeopardizing the economic and social fabric of the nation. This disruption has far-reaching consequences, affecting not only energy access but also essential services reliant on electricity.The damage extends beyond the immediate physical destruction.
The disruption of energy supply chains, the displacement of skilled workers, and the uncertainty surrounding future operations all contribute to a profound and lasting impact on Ukraine’s ability to recover and rebuild its energy infrastructure. The war’s effects are felt throughout the country, impacting both urban and rural areas, and the long-term consequences remain uncertain.
Direct Effects on Energy Infrastructure
The war has resulted in widespread damage to Ukraine’s energy infrastructure. Direct attacks on power plants, substations, and transmission lines have significantly reduced energy production capacity. These attacks have also caused disruptions in the supply of fuel and materials necessary for maintaining and repairing existing infrastructure. The deliberate targeting of critical energy infrastructure highlights the deliberate effort to undermine the country’s ability to function.
Damage to Power Plants, Transmission Lines, and Other Critical Infrastructure
Numerous power plants have been damaged or destroyed, either directly by shelling or as a consequence of broader damage to the surrounding infrastructure. Transmission lines have been heavily impacted, causing widespread blackouts and hindering the distribution of electricity to consumers. The destruction of other critical facilities, such as fuel depots and maintenance centers, has further complicated the process of recovery and repair.
The strategic importance of these facilities cannot be overstated; their destruction effectively disrupts the energy sector’s fundamental functions.
Impact on Energy Production, Distribution, and Access
The war has severely hampered Ukraine’s ability to generate, distribute, and deliver energy to consumers. Reduced energy production capacity has led to widespread power outages, impacting homes, businesses, and essential services. Damage to the distribution network has limited access to electricity in many areas, particularly in conflict zones. This has had a cascading effect, impacting the country’s economic and social development.
Displacement and Relocation of Energy Workers
The war has led to the displacement and relocation of energy workers. Many have left their homes and jobs due to the conflict, leading to a shortage of skilled personnel needed for the repair and maintenance of the infrastructure. The displacement of these workers further complicates the recovery process, as they are essential for restoring operations and ensuring the safety and stability of the energy sector.
This loss of expertise is a critical factor hindering the swift restoration of energy services.
Estimated Damage to Energy Infrastructure by Region
| Region | Damaged Facilities | Estimated Repair Costs (USD Millions) |
|---|---|---|
| Eastern Ukraine | 3 Thermal Power Plants, 5 Substations, 20km Transmission Lines | 1,500 |
| Central Ukraine | 2 Nuclear Power Plants, 10 Substations, 30km Transmission Lines | 2,000 |
| Southern Ukraine | 1 Hydroelectric Power Plant, 8 Substations, 15km Transmission Lines | 1,200 |
| Western Ukraine | 1 Thermal Power Plant, 5 Substations, 10km Transmission Lines | 800 |
Note: The data in the table is hypothetical and for illustrative purposes only. Actual figures are likely to be significantly higher and more complex.
Carbon Emissions from Ukrainian Energy Sources
Ukraine’s energy sector, heavily reliant on fossil fuels before the war, played a significant role in its carbon footprint. The war’s impact on infrastructure and energy production has undoubtedly altered this landscape, demanding a reassessment of emissions levels and the future trajectory of the energy mix. Understanding these changes is crucial for international efforts to support Ukraine’s recovery and ensure a sustainable energy future.The complex interplay between energy production, consumption, and environmental impact necessitates a nuanced understanding of carbon emissions from various sources.
This analysis delves into the methodologies for measuring these emissions, contrasts pre-war and post-war emission levels, and examines the carbon intensity of Ukraine’s energy mix. The correlation between energy consumption and carbon emissions will also be highlighted. Furthermore, a comparison of emissions across sectors – residential, industrial, and commercial – will be presented.
Methods for Measuring Carbon Emissions
Different methods exist for quantifying carbon emissions from energy sources. These methods often rely on detailed data on fuel consumption, energy production processes, and the specific types of fossil fuels utilized. Emissions factors, which represent the amount of CO2 released per unit of energy produced, are crucial for accurate calculations. These factors are often based on standardized methodologies and datasets, accounting for various factors influencing emission levels.
Furthermore, monitoring and verification mechanisms are employed to ensure the accuracy and reliability of the data.
Comparison of Pre-War and Post-War Emissions
The war’s disruption of Ukraine’s energy infrastructure has significantly altered the carbon emission landscape. Pre-war, Ukraine’s energy mix was heavily reliant on coal, followed by natural gas and renewables. The destruction of power plants, transmission lines, and other infrastructure has resulted in reduced energy production and a shift in energy sources. Consequently, post-war emission levels are likely lower than pre-war figures, but the exact extent of the reduction and the specific impact on various sectors remain to be quantified.
Carbon Intensity of Ukraine’s Energy Mix
The carbon intensity of Ukraine’s energy mix refers to the amount of CO2 emitted per unit of energy produced. Pre-war, Ukraine’s high reliance on coal resulted in a relatively high carbon intensity. The war has disrupted this balance, leading to uncertainty about the current carbon intensity of the energy mix. The shift to other energy sources, like natural gas and potentially increased reliance on renewables, could impact this figure.
Ukraine’s energy crisis is unfortunately contributing heavily to carbon emissions. The ongoing conflict significantly impacts energy production and reliance on alternative sources, which often increase emissions. Meanwhile, the Oilers’ impressive win over the Blue Jackets, thanks to Stuart Skinner’s stellar performance oilers stuart skinner defeat blue jackets , highlights the importance of finding sustainable energy solutions to reduce our collective carbon footprint and lessen the impact on Ukraine’s already struggling energy sector.
Future investments in renewable energy infrastructure are expected to play a critical role in reducing the carbon intensity in the long term.
Correlation Between Energy Consumption and Carbon Emissions
There is a direct correlation between energy consumption and carbon emissions. Increased energy demand often translates to higher carbon emissions, especially when fossil fuels are the primary energy source. The disruption of Ukraine’s energy infrastructure has influenced energy consumption patterns. Reduced energy availability post-war has led to lower energy consumption and, consequently, lower carbon emissions, although this is a temporary effect.
The long-term impact on consumption patterns and their correlation to emissions is still under evaluation.
Pre-War and Post-War Carbon Emissions by Sector
| Sector | Pre-War Carbon Emissions (Estimated) | Post-War Carbon Emissions (Estimated) | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Residential | 10,000 tonnes | 7,000 tonnes | Significant decrease due to reduced energy availability and energy conservation measures. |
| Industrial | 20,000 tonnes | 15,000 tonnes | Lower emissions due to plant closures and reduced industrial activity. |
| Commercial | 5,000 tonnes | 3,000 tonnes | Decreased energy consumption in commercial buildings and reduced activity. |
Note: These figures are illustrative and require precise data for accurate estimations. The exact extent of the post-war reduction in emissions is subject to further analysis.
Alternative Energy Sources and Transition Strategies
Ukraine’s energy sector faces a crucial juncture. Post-war reconstruction presents an opportunity to embark on a sustainable energy transition, reducing reliance on fossil fuels and mitigating future climate change impacts. This transition necessitates a comprehensive strategy encompassing diverse renewable energy sources, advanced infrastructure, and optimized energy efficiency measures. The path forward involves careful consideration of various factors, including the country’s geographical features, existing infrastructure, and economic capabilities.The energy transition is not merely an environmental imperative but also an economic opportunity.
A shift towards renewables can foster local job creation, attract foreign investment, and bolster Ukraine’s energy independence. This transition also presents a unique chance to build a more resilient and sustainable energy sector, one better equipped to withstand future shocks and crises.
Potential Alternative Energy Sources
Ukraine possesses significant potential for harnessing renewable energy sources. The country’s vast landmass offers ample opportunities for solar and wind power generation, while its river systems provide potential for hydroelectric projects. Leveraging these resources can contribute substantially to Ukraine’s energy security and environmental sustainability.
Renewable Energy Solutions
Renewable energy solutions offer a promising pathway for Ukraine’s energy future. Their environmental friendliness, abundance, and decreasing costs make them compelling alternatives to fossil fuels.
Solar Energy
Solar power generation has become increasingly cost-effective, making it a viable option for Ukraine. Large-scale solar farms can be established in regions with ample sunlight, reducing reliance on centralized power plants. The effectiveness of solar energy is directly correlated with factors like geographical location and sunlight hours. Countries like Germany and the Netherlands demonstrate the potential for large-scale solar deployment, although their specific geographic conditions may not perfectly align with Ukraine’s.
Wind Energy
Wind energy presents another viable option, particularly in areas with consistent wind patterns. Onshore and offshore wind farms can contribute significantly to Ukraine’s renewable energy mix. Factors influencing wind energy effectiveness include wind speed and consistency. Denmark’s extensive use of wind power showcases its potential for significant energy generation.
Hydropower
Hydropower, while historically significant, requires careful consideration of environmental impacts. Existing hydroelectric dams, if appropriately managed, can continue contributing to Ukraine’s renewable energy portfolio. However, new large-scale hydropower projects should be evaluated thoroughly, weighing their environmental consequences against the potential energy benefits. Canada’s extensive use of hydropower provides a relevant case study for assessing the trade-offs involved.
Infrastructure Adjustments
Adapting the existing energy infrastructure is crucial for accommodating renewable energy sources. Grid modernization is paramount to integrate fluctuating renewable energy production. Smart grids and energy storage solutions will be critical to maintaining a stable and reliable energy supply. Furthermore, transmission lines need upgrades to transport electricity from remote renewable energy facilities to urban centers.
Ukraine’s energy crisis is highlighting the devastating impact of carbon emissions on our planet. The struggle to secure energy sources is a stark reminder of the consequences of our reliance on fossil fuels. Meanwhile, events like snow polo in St. Moritz, a seemingly luxurious sport, are also subtly affected by climate change, demonstrating the global reach of environmental issues.
Snow polo in St. Moritz is becoming a casualty of this global warming trend, showcasing how seemingly unrelated activities are interconnected. This ultimately underscores the urgent need to transition away from fossil fuels and find cleaner, more sustainable energy sources, not only for Ukraine but for the entire world.
Energy Efficiency Strategies
Improving energy efficiency across various sectors is essential to minimize energy consumption and maximize the impact of renewable energy sources. Implementing energy-efficient building codes, promoting energy-saving appliances, and upgrading industrial processes can all contribute significantly to reducing overall energy demands. Retrofitting existing buildings to meet modern energy standards is also a key strategy. These measures can substantially decrease reliance on traditional energy sources.
Energy Storage Solutions
Energy storage solutions are crucial for managing the intermittent nature of renewable energy sources. Battery storage and pumped hydro storage are two key technologies with potential applications in Ukraine.
Battery Storage
Battery storage systems can store excess energy generated from renewables, providing a reliable supply during periods of low or no generation. The cost-effectiveness and scalability of battery storage are constantly evolving. Factors influencing battery storage include capacity, lifespan, and cost. Technological advancements in battery technology are rapidly improving their performance and decreasing their cost.
Pumped Hydro Storage
Pumped hydro storage systems use excess electricity to pump water uphill into reservoirs, which can then be released to generate electricity when demand is high. This technology is particularly well-suited for areas with suitable topography and water resources. Factors impacting the effectiveness of pumped hydro include the availability of suitable sites and the required infrastructure. Norway’s use of pumped hydro storage demonstrates its potential for large-scale energy storage.
The ongoing energy crisis in Ukraine is undeniably increasing carbon emissions. Companies like Koch and Chevron, however, are facing scrutiny regarding their influence on energy policy, especially with the recent Supreme Court decision regarding their deference to certain regulations. This case, highlighted in the koch chevron deference supreme court article, raises important questions about corporate responsibility in the face of the escalating energy crisis and the potential for increased carbon emissions as a result.
The situation in Ukraine needs serious consideration and swift action to address the issue.
International Support and Investment in Ukrainian Energy
The war in Ukraine has irrevocably altered the energy landscape, demanding significant international support for rebuilding and modernizing the country’s infrastructure. This support is crucial not only for Ukraine’s immediate energy needs but also for its long-term energy security and economic recovery. International partners are stepping up to provide aid and investment, acknowledging the critical role the Ukrainian energy sector plays in the region.The scale of destruction to Ukrainian energy infrastructure necessitates a comprehensive and coordinated international response.
This involves not just providing immediate relief but also strategizing for long-term resilience and sustainability in the sector. Countries and organizations are recognizing the need for investments that go beyond short-term fixes, encompassing modernization and diversification of energy sources.
Types of International Support Provided
International support for Ukraine’s energy sector encompasses a wide range of initiatives, including financial aid, technical assistance, and the provision of equipment and materials. This assistance is designed to address the immediate crisis and pave the way for future energy independence and sustainability. Support also includes training for Ukrainian personnel and facilitating the transfer of knowledge and expertise.
Ukraine’s energy crisis is a huge source of carbon emissions, and it’s a real worry. But beyond the immediate environmental impact, there’s a broader ethical question. For example, are we considering the long-term implications of our energy choices, especially when purchasing goods like stranger letters? Examining the ethical sourcing of materials and the overall impact of these purchases is vital, and that’s something to think about when considering our impact on carbon emissions.
Stranger letters purchase ethics explores these important questions, and understanding them helps us consider our overall responsibility for carbon emissions, especially in the context of Ukraine’s energy crisis. We need to think about more than just the immediate effects.
Funding Mechanisms and Commitments
International pledges and commitments for the reconstruction of Ukrainian energy infrastructure are demonstrating a global recognition of the importance of energy security in the region. These commitments extend beyond financial aid to encompass technical assistance and expertise transfer. Efforts are focused on not only repairing damaged infrastructure but also modernizing the sector to adopt more sustainable and resilient practices.
Role of International Organizations
International organizations, such as the World Bank, the European Bank for Reconstruction and Development (EBRD), and the International Monetary Fund (IMF), are playing crucial roles in coordinating and delivering aid. These organizations are utilizing their expertise and networks to channel resources effectively and ensure transparency and accountability in the reconstruction process. They also provide crucial technical expertise for sustainable development projects.
Potential Investment Opportunities
Post-war, Ukraine’s energy sector presents substantial investment opportunities for international companies. These opportunities include rebuilding and modernizing power plants, expanding renewable energy capacity, and upgrading transmission and distribution networks. Opportunities also exist in developing energy efficiency measures. The sector’s reconstruction will create a strong demand for advanced technology and expertise.
Funding Sources and Allocations (Hypothetical Data)
This table illustrates hypothetical funding allocations for various energy projects in Ukraine. Real figures would vary greatly based on specific project details and ongoing negotiations.
| Funding Source | Project Type | Allocated Amount (USD Millions) |
|---|---|---|
| European Union | Rebuilding Substations | 150 |
| World Bank | Renewable Energy Expansion | 200 |
| United States | Power Plant Modernization | 100 |
| Germany | Energy Efficiency Upgrades | 75 |
| EBRD | Transmission Line Reconstruction | 125 |
Global Implications of Ukraine’s Energy Crisis
The escalating energy crisis in Ukraine has far-reaching consequences extending beyond its borders. The disruption of energy supplies has triggered a global energy market upheaval, impacting not only price stability but also geopolitical relations and economic prospects worldwide. This ripple effect is being felt in various sectors, from industrial production to household budgets, highlighting the interconnectedness of the global energy system.The war in Ukraine and the subsequent energy crisis have exposed vulnerabilities in the global energy supply chain.
The escalating carbon emissions from Ukraine’s energy crisis are a serious concern. While the situation in Ukraine is undeniably dire, it’s important to stay informed about other pressing issues. For example, the upcoming Nevada caucus primary is shaping up to be crucial. A good resource to understand the nuances is this explainer on the Nevada caucus primary explainer.
Ultimately, addressing Ukraine’s energy needs while mitigating carbon emissions requires multifaceted solutions and global cooperation.
The crisis has underscored the dependence of many nations on specific energy sources and suppliers, highlighting the importance of diversifying energy portfolios and fostering greater energy independence. This dependence on limited resources creates an inherent risk of disruption and price volatility in the global market.
Impact on Global Energy Markets
The disruption of Ukrainian energy production and exports has created a significant imbalance in global energy markets. Reduced supplies from Ukraine, a key exporter of natural gas, have driven up prices for natural gas globally. This increase in energy costs is not only affecting European nations but is also impacting energy markets in Asia and the Americas, as these regions rely on global energy trade for their energy needs.
The crisis has highlighted the interconnectedness of global energy markets, where disruptions in one region can quickly propagate to others.
Potential Ripple Effects on Energy Prices and Security
The conflict in Ukraine has demonstrably increased energy prices globally. Increased demand and decreased supply have led to significant price fluctuations in natural gas, electricity, and other energy commodities. This price volatility poses a substantial threat to economic stability in many countries, impacting industrial production, transportation, and household budgets. The crisis has also raised concerns about energy security, prompting nations to reassess their reliance on particular energy sources and suppliers.
Potential Impacts on International Relations and Trade
The energy crisis has intensified existing geopolitical tensions and fostered new ones. The conflict has led to increased scrutiny of energy partnerships and trade relations. Countries have been forced to reconsider their energy security strategies and potentially shift away from relying on suppliers considered less reliable or politically unstable. The global impact of the crisis is also felt through the ripple effects of trade sanctions and economic measures, influencing trade flows and supply chains globally.
Responses of Different Countries to the Crisis
Countries have adopted diverse approaches to addressing the energy crisis, reflecting their unique geopolitical circumstances and economic structures. Some countries have focused on bolstering domestic energy production, while others have prioritized energy diversification and increased imports from alternative sources. The response strategies also vary in terms of support for consumers, from direct subsidies to energy efficiency programs.
Countries have adopted various strategies to mitigate the energy crisis. Some have increased domestic production, while others have focused on securing alternative energy sources. Still others are implementing measures to support consumers, such as energy subsidies.
Visual Representation of Global Impacts, Carbon emissions ukraine energy
Country/Region Impact Europe Increased energy prices, potential economic recession, heightened geopolitical tensions Asia Increased energy costs, potential supply chain disruptions, impact on manufacturing Americas Increased energy costs, potential inflationary pressures, varied responses based on domestic energy resources
This table illustrates the varied impacts of the crisis on different regions, demonstrating how the Ukrainian energy crisis is a global challenge.
Carbon Emission Reduction Strategies Post-War: Carbon Emissions Ukraine Energy
Ukraine’s energy sector, heavily reliant on fossil fuels, faces a critical juncture post-war. Reconstructing and modernizing infrastructure while simultaneously reducing carbon emissions presents a significant challenge, but also an opportunity for a sustainable future. Addressing this challenge requires a multifaceted approach encompassing policy changes, technological advancements, and public engagement.The reconstruction process presents an ideal moment to transition towards a cleaner energy future, embracing renewable energy sources and improving energy efficiency across all sectors.
This transition will not only mitigate the environmental impact but also bolster Ukraine’s economic resilience and energy independence. A comprehensive strategy encompassing government policies, technological innovations, and public awareness is essential to achieve these goals.
Government Policies and Regulations
Government policies play a pivotal role in driving the transition to a low-carbon energy sector. Clear, consistent, and long-term policies are crucial to attract investment and incentivize the adoption of cleaner technologies. These policies should encompass regulations, tax incentives, and subsidies targeted at renewable energy sources, energy efficiency upgrades, and carbon capture and storage. Regulations must also address the environmental impact of existing infrastructure, ensuring that reconstruction efforts are sustainable.
For example, countries like Germany have established specific targets for renewable energy generation and implemented supportive policies to meet those goals.
Carbon Capture and Storage Technologies
The potential of carbon capture and storage (CCS) technologies warrants significant consideration. CCS involves capturing CO2 emissions from power plants and industrial facilities, transporting them to underground geological formations for permanent storage. While still in the developmental phase, CCS holds promise for reducing emissions from existing fossil fuel power plants during the reconstruction phase. Furthermore, the implementation of CCS technology can be a catalyst for technological innovation and job creation in Ukraine.
Examples like the Sleipner project in Norway demonstrate the feasibility and potential of CCS on a large scale.
Public Awareness Campaigns
Public awareness campaigns are essential to promote energy conservation and support for the transition to renewable energy sources. Raising public awareness about the benefits of energy efficiency measures and the impact of carbon emissions is vital for behavioral change. Educational campaigns can highlight the economic and environmental advantages of energy efficiency and the importance of responsible energy consumption.
For example, awareness campaigns in other countries have successfully reduced energy consumption by prompting individual actions, showcasing the effectiveness of these initiatives.
Improving Energy Efficiency in Buildings and Industries
Improving energy efficiency in buildings and industries is crucial for reducing energy consumption and associated carbon emissions. This involves implementing measures such as better insulation, upgrading heating and cooling systems, and adopting smart building technologies. Industrial processes can also be optimized to minimize energy use and waste. Ukraine can leverage existing expertise and international cooperation to implement these upgrades.
For instance, adopting energy-efficient technologies in existing industrial plants in other countries has led to significant reductions in energy consumption.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Ukraine’s energy crisis is a multifaceted issue with significant implications for both the nation’s future and the global energy landscape. The need for a swift and sustainable transition to renewable energy sources, coupled with robust international support, is crucial for rebuilding Ukraine’s energy infrastructure and mitigating the long-term environmental consequences of the conflict. The road to recovery is fraught with challenges, but the global community’s commitment to supporting Ukraine’s energy sector will ultimately determine the trajectory of its post-war recovery.
Top FAQs
What are the most common energy sources used in Ukraine before the war?
Ukraine’s pre-war energy mix predominantly relied on fossil fuels, particularly coal and natural gas, with a smaller contribution from renewables like hydro.
What are the estimated repair costs of the damaged energy infrastructure?
Unfortunately, precise figures are not available at this time, but significant financial investments will be needed for rebuilding and modernization. Hypothetical data on repair costs by region and damaged facilities will be provided in the article.
What role do international organizations play in the reconstruction process?
International organizations like the World Bank and the International Energy Agency will likely play a significant role in funding and coordinating the reconstruction efforts.
What are some potential renewable energy solutions for Ukraine?
Solar, wind, and hydro power are potential renewable energy sources. Their feasibility and effectiveness depend on factors such as geographic location and available resources.

