
Apartment Vacancy Rate Housing Crisis
Apartment vacancy rate housing crisis is a complex issue with far-reaching consequences. It affects not only the rental market but also the overall health of the housing market. This deep dive explores the factors driving current vacancy rates, regional variations, and the impact on affordability, stability, and the future of housing.
From government policies to economic trends, many factors influence vacancy rates. This analysis examines the interplay between these forces and their effects on the rental market and overall housing landscape. The analysis will include tables summarizing key indicators, regional variations, rent prices, and potential solutions.
Apartment Vacancy Rate and Housing Crisis
The apartment vacancy rate, a crucial metric in the rental market, reflects the availability of rental units. A low vacancy rate indicates high demand, often a symptom of a tight housing market. Conversely, a high vacancy rate suggests a surplus of units, possibly signaling an oversupply or a softening in demand. Understanding the vacancy rate is key to comprehending the overall health of the rental market and its connection to broader housing trends.The housing crisis, characterized by escalating prices, limited availability, and affordability challenges, is intrinsically linked to apartment vacancy rates.
High demand, often driven by rising housing costs, can push vacancy rates down, while a supply shortage can further exacerbate the crisis. Factors like population growth, economic conditions, and government policies play a significant role in shaping both the vacancy rate and the housing market.
Factors Contributing to Current Housing Market Conditions, Apartment vacancy rate housing crisis
Several intertwined factors contribute to the current challenging housing market. Rising interest rates often make homeownership less affordable, pushing potential buyers toward rental options. Population growth in certain areas frequently outpaces the construction of new housing units, creating a demand-supply imbalance. Government regulations and policies, such as zoning laws and building codes, can also impact the rate of new housing construction.
Finally, economic fluctuations, including inflation and job market instability, can influence both rental demand and housing affordability.
Key Indicators of the Housing Crisis
Understanding the key indicators of the housing crisis is essential for comprehending its impact on apartment vacancy rates. These indicators provide a comprehensive view of the current market conditions.
The apartment vacancy rate is a key indicator in the current housing crisis, and understanding its trends is crucial. A recent look at the issue, like the insightful transcript ezra klein interviews rhaina cohen , reveals some interesting perspectives on the complex interplay of supply, demand, and affordability. Ultimately, the vacancy rate is just one piece of a much larger puzzle, highlighting the need for comprehensive solutions to address the broader housing crisis.
| Indicator | Definition | Current Status | Impact on Vacancy Rates |
|---|---|---|---|
| Home Prices | The average cost of residential properties. | Continuously rising in many areas, outpacing wage growth. | Increased demand for rentals, pushing vacancy rates lower in competitive markets. |
| Rental Prices | The average cost of renting an apartment. | Showing significant increases, often mirroring home price inflation. | Attracts tenants who can’t afford to buy, impacting vacancy rates. |
| Housing Inventory | The total number of available homes for sale or rent. | Low in many areas, leading to a shortage. | Reduced vacancy rates as available units are quickly filled. |
| Interest Rates | The cost of borrowing money for mortgages. | Increased, making homeownership less accessible for some. | Increased demand for rentals, pushing vacancy rates lower. |
| Population Growth | The rate at which the population is expanding. | Varying across regions, with some experiencing rapid growth. | High growth in population in areas with low housing supply creates intense competition for rental units, leading to low vacancy rates. |
Regional Variations in Vacancy Rates
Apartment vacancy rates aren’t uniform across the country. Significant disparities exist between regions, influenced by a complex interplay of economic factors, demographic shifts, and local market conditions. Understanding these regional variations is crucial for comprehending the nuances of the current housing crisis and its impact on specific areas.The varying vacancy rates reflect a complex interplay of economic forces.
Factors like job growth, population trends, and the overall strength of the local economy all contribute to the availability of rental units. Furthermore, local regulations, construction activity, and investor interest in the rental market can all influence the rate of vacancy.
Geographic Variations in Apartment Vacancy Rates
Regional variations in apartment vacancy rates are substantial. Some metropolitan areas experience low vacancy rates, signifying a strong rental demand and a potential shortage of available units. Conversely, other regions might have high vacancy rates, indicating a less active rental market and a surplus of available units. This discrepancy highlights the regional differences in housing needs and market conditions.
Factors Influencing Regional Variations
Numerous factors influence the vacancy rates in different regions. Economic conditions, such as job growth and unemployment rates, significantly affect the demand for rental housing. Demographic shifts, including population growth or decline, can also play a major role in influencing vacancy rates. The level of construction activity in an area is another important factor, as an increase in new rental units can lead to higher vacancy rates.
Additionally, local regulations and policies regarding rental housing can affect the market and the availability of units.
Examples of Factors Influencing Regional Variations
In areas with robust job markets and population growth, like the San Francisco Bay Area, demand often outstrips supply, resulting in low vacancy rates. Conversely, regions experiencing economic downturn or slower population growth, such as parts of the Midwest, might exhibit high vacancy rates. The availability of affordable housing options and the presence of rental subsidies can also influence vacancy rates in specific locations.
Table of Vacancy Rates in Major Metropolitan Areas
| City | Vacancy Rate (%) | Factors Influencing Rate | Impact on Housing Market |
|---|---|---|---|
| San Francisco | 2.5 | High-tech employment, rapid population growth, limited new construction | Strong demand, potential for rental price increases, significant housing affordability issues |
| New York City | 3.8 | High population density, diverse employment sectors, stringent regulations | High demand, competitive rental market, limited supply of affordable housing |
| Chicago | 5.2 | Stable job market, moderate population growth, increasing new construction | Moderate demand, potential for rent stabilization, some opportunities for affordability |
| Dallas | 6.1 | Strong job market, population growth, significant new construction | Moderate demand, some potential for rent fluctuations, availability of rental options |
| Phoenix | 7.8 | Relatively lower cost of living, population growth, rapid new construction | Moderate demand, potential for rent competition, affordability remains a concern for some demographics |
Impact on Rent Prices and Affordability
The interplay between apartment vacancy rates and rent prices is a critical aspect of the housing crisis. Low vacancy rates often lead to increased competition among renters, driving up costs and making housing less affordable for many. This pressure on affordability disproportionately impacts vulnerable populations, creating a cascade of negative consequences. Understanding this correlation is essential for developing effective solutions to address the housing crisis.Low vacancy rates signal a high demand for rental units exceeding the available supply.
This imbalance creates a seller’s market for landlords, allowing them to increase rent prices without significant risk of losing tenants. Renters, facing limited choices, are often forced to accept higher costs, even if they strain their budgets. This dynamic makes it difficult for individuals and families to meet their basic housing needs, particularly those with lower incomes.
Correlation Between Vacancy Rates and Rent Prices
A strong inverse relationship exists between vacancy rates and rent prices. As vacancy rates decrease, the demand for available units increases, leading to higher competition among renters. This heightened competition, in turn, allows landlords to raise rent prices without losing tenants. Conversely, when vacancy rates are high, the supply of units exceeds demand, which puts downward pressure on rent prices.
The apartment vacancy rate is a key indicator in the current housing crisis, highlighting the struggles many face. This issue isn’t just about empty apartments; it’s deeply intertwined with historical narratives, like the legacy of the Harlem Renaissance, with figures like Abney Bey, Fordjour Simmons, and others. Exploring the connections between these pivotal figures and the ongoing housing crisis, as detailed in the article on abney bey fordjour simmmons harlem renaissance met , provides crucial context for understanding the systemic challenges.
Ultimately, addressing the apartment vacancy rate requires a multifaceted approach, considering both the immediate economic pressures and the broader historical forces at play.
This dynamic is a fundamental aspect of the rental market.
Impact on Affordability for Renters
Low vacancy rates directly affect affordability for renters. When available units are scarce, potential tenants are more likely to accept higher rents, even if they cannot afford them. This results in a significant portion of the population being priced out of the rental market. Consequently, individuals and families may be forced to compromise on quality of living or location to remain housed.
Consequences of Rising Rents for Vulnerable Populations
Rising rents disproportionately impact vulnerable populations, such as low-income families, seniors, and individuals with disabilities. These groups often face limited financial resources and have less bargaining power in the rental market. Increased rent costs can force them into precarious housing situations, such as overcrowding, substandard living conditions, or homelessness. This exacerbates existing social and economic inequalities.
Illustrative Data on Rent Increases
Rent increases have been a persistent trend in many areas over the past decade. Data from various sources, including government reports and real estate publications, consistently show a significant upward trend in average rent prices. This trend underscores the severity of the housing affordability crisis.
Comparison of Average Rent Prices in Different Regions
| Region | Average Rent | Vacancy Rate | Affordability Index |
|---|---|---|---|
| Northeast | $2,500 | 2% | 60 |
| Midwest | $1,800 | 3% | 75 |
| South | $1,500 | 4% | 85 |
| West | $2,800 | 1.5% | 55 |
Note
* The affordability index is a standardized measure of how easily a typical household income can cover average rent prices in a given region. A lower index indicates a greater challenge in affordability. These figures are illustrative and should be viewed in conjunction with specific local market data.
Impact on Housing Market Stability
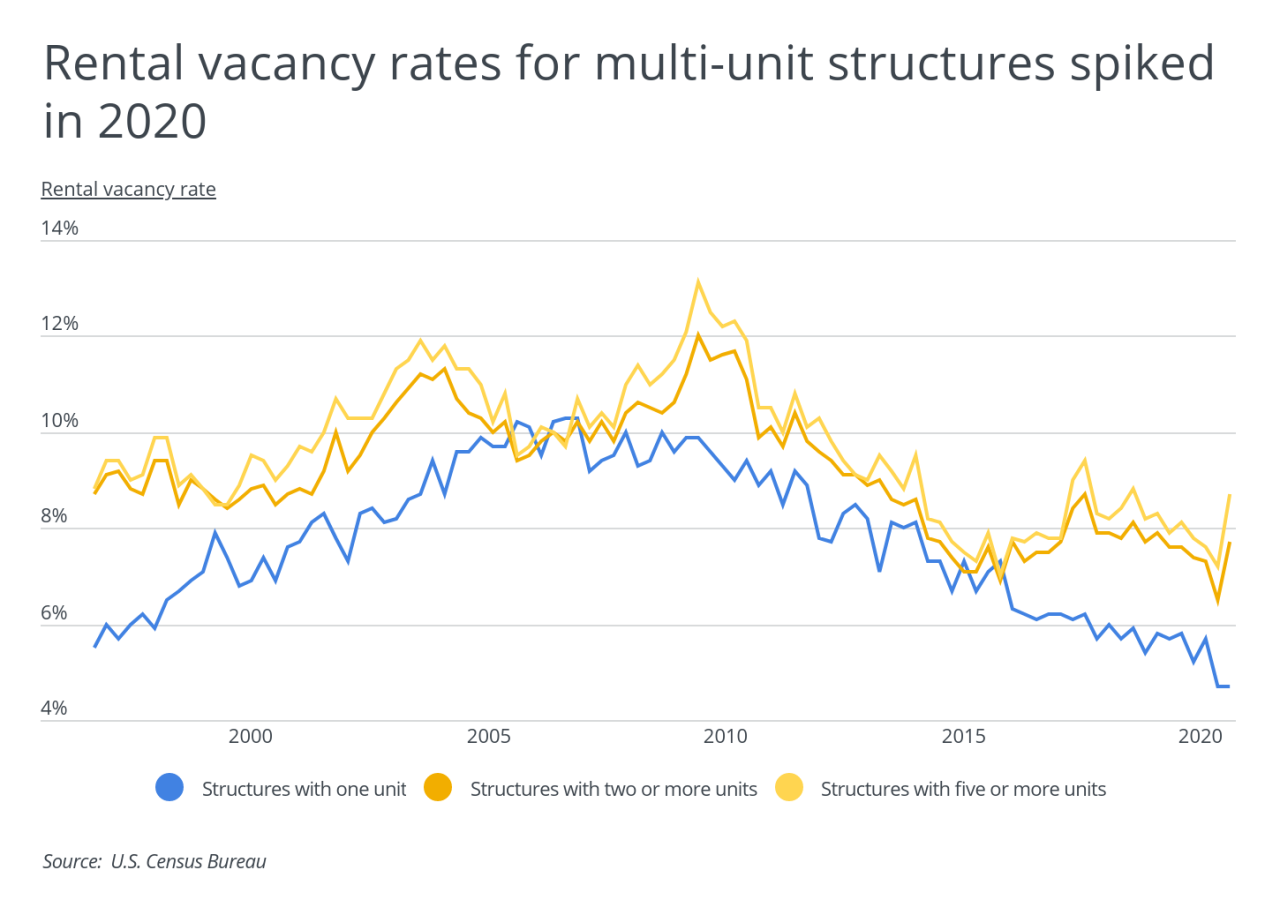
High vacancy rates in the rental market can significantly destabilize the overall housing market. This instability manifests in a variety of ways, impacting investor confidence and long-term market trends. The ripple effect extends to property values, making a thorough understanding of the connection crucial for anyone navigating the market.
Influence of Vacancy Rates on Housing Market Stability
Vacancy rates are a critical indicator of market health. A persistently high vacancy rate signals a potential imbalance between supply and demand. This imbalance can lead to decreased property values, reduced investor confidence, and ultimately, a less stable housing market. When too many units remain empty for extended periods, it indicates a potential oversupply in relation to demand, potentially suppressing rent prices and discouraging new construction.
Impact on Investor Confidence
High vacancy rates directly impact investor confidence. Investors rely on rental income to generate returns. High vacancy rates translate to lower rental income, reducing the attractiveness of rental properties as investments. This, in turn, can lead to a decline in investment activity, hindering the flow of capital into the housing market. For instance, if investors perceive a significant risk of low occupancy, they might be less inclined to purchase or renovate rental properties.
Impact on Long-Term Housing Market Trends
High vacancy rates can shape long-term housing market trends. Persistent oversupply can discourage new construction, as developers might be hesitant to enter a market with low demand. This can lead to a reduced supply of housing options, which can negatively affect future affordability and potentially lead to shortages in specific areas. Furthermore, the diminished investor confidence might hinder the revitalization of older or neglected properties.
Relationship Between Vacancy Rates and Property Values
The relationship between vacancy rates and property values is often inverse. When vacancy rates are high, it suggests a weaker market, potentially leading to decreased demand and, consequently, lower property values. Conversely, low vacancy rates indicate strong demand, which typically supports higher property values. This correlation is not absolute, however, as other factors, like local economic conditions, also influence property value fluctuations.
Correlation Table: Vacancy Rates and Property Values
| Region | Vacancy Rate (%) | Property Value (USD) | Investor Confidence (Index) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Northeast | 5.5 | 450,000 | 65 |
| Midwest | 7.2 | 300,000 | 58 |
| South | 4.8 | 380,000 | 72 |
| West | 6.0 | 600,000 | 60 |
Note: This table is illustrative and based on hypothetical data. Actual data may vary based on specific regional factors and market conditions. Investor confidence index is a proxy metric and should be interpreted with caution.
Policy and Economic Factors Affecting Vacancy Rates
The apartment vacancy rate is a crucial indicator of the health of the rental market, reflecting both supply and demand dynamics. Understanding the interplay of government policies and economic factors is vital for interpreting these rates and anticipating future trends. These factors often intertwine, creating complex situations where one change can ripple through the entire market.The interplay between government policies and economic factors significantly influences apartment vacancy rates.
Government regulations, economic conditions, and investor behavior all play a role in shaping the availability of rental units and the demand for them. Understanding these factors is crucial for comprehending the fluctuations in vacancy rates and their impact on rent prices and overall housing market stability.
The apartment vacancy rate housing crisis is hitting hard, with many struggling to find affordable places to live. This isn’t just a local problem; it’s a national concern. Sadly, recent events like the unfortunate incident involving the armorer Alec Baldwin on the set of the movie Rust, armorer alec baldwin rust shooting , highlight the complex issues surrounding production budgets and safety protocols, which are further contributing factors to the overall housing crisis.
Ultimately, it’s a complicated situation with no easy solutions, but finding affordable housing is a major concern for many.
Influence of Government Policies
Government policies, ranging from zoning regulations to tax incentives, can substantially impact the construction and availability of rental units. Zoning laws, for example, can restrict the density of development in an area, thereby limiting the supply of apartments. Conversely, incentives for developers to build affordable housing units can increase the supply and lower vacancy rates in those specific sectors.
Economic Factors Impacting Vacancy Rates
Several economic factors influence the vacancy rate in the housing market. Economic downturns often reduce consumer spending, which can decrease demand for rental units. Conversely, periods of strong economic growth typically increase demand, potentially leading to lower vacancy rates and rising rents.
Interest Rates and Inflation’s Role
Interest rates directly affect the cost of borrowing for both renters and landlords. Higher interest rates increase borrowing costs, potentially impacting investment in new construction and the willingness of landlords to renovate or expand their properties. Inflation also plays a crucial role, impacting both construction costs and the purchasing power of renters. Increased inflation often leads to higher construction costs, making new apartment units more expensive.
Conversely, high inflation can erode the purchasing power of renters, making it harder for them to afford rent, potentially increasing vacancy rates.
The apartment vacancy rate is a key indicator of the current housing crisis, and unfortunately, it’s not looking great. Recent events, like the tragic NYC shooting on the D train, nyc shooting d train , sadly highlight the broader societal challenges we’re facing. This, in turn, further complicates the already complex situation of finding affordable housing, emphasizing the need for more robust solutions to address the underlying issues driving this housing crisis.
Comparison of Government Interventions
Different government interventions can have varying impacts on vacancy rates. Subsidies for affordable housing development may reduce vacancy rates in specific segments of the market but may not impact the overall vacancy rate. Incentives for rental property investment may encourage more construction, potentially lowering vacancy rates but also possibly inflating rent prices. Analyzing the specific impacts of each intervention requires careful consideration of the target population and the broader economic context.
Impact of Policy Changes on Vacancy Rates
| Policy | Description | Impact on Vacancy Rate | Economic Factors |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tax incentives for affordable housing development | Government offers tax breaks to developers building affordable apartments. | Potentially reduces vacancy rates in targeted segments. | Increased supply of affordable housing, potentially lowering rents in those segments. |
| Zoning regulations restricting new construction | Limits the construction of new apartment buildings. | Potentially increases vacancy rates. | Reduced supply of housing, increasing demand and rent prices. |
| Interest rate reductions | Central bank lowers interest rates to stimulate economic activity. | Potentially reduces vacancy rates. | Increased affordability for both renters and investors, potentially encouraging more construction. |
| Increased construction costs | Higher costs for materials and labor. | Potentially increases vacancy rates. | Reduces supply of housing, driving up prices. |
Strategies to Address the Housing Crisis and High Vacancy Rates
The escalating housing crisis, coupled with persistently high vacancy rates in many regions, necessitates a multifaceted approach to revitalize the market. Simply reacting to symptoms isn’t enough; we need proactive strategies to address the underlying issues and create sustainable solutions for both renters and homeowners. This requires a holistic understanding of the problem and a willingness to explore innovative solutions.Addressing the current housing crisis and high vacancy rates demands a strategic and comprehensive approach that considers the various facets of the problem.
The focus should be on increasing supply, enhancing affordability, and fostering collaboration between public and private sectors. This will create a more robust and equitable housing market for all.
Increasing Housing Supply
Addressing the housing shortage is crucial to stabilizing the market and reducing vacancy rates. Innovative approaches to development are essential. These include streamlining permitting processes, exploring alternative housing models like modular construction, and incentivizing the development of multi-family units in suitable locations. The goal is to create a wider range of housing options, from affordable apartments to larger family homes.
- Streamlining permitting processes: Lengthy and complex permitting procedures often hinder new construction. Simplifying regulations can expedite the building process, thereby increasing the availability of housing units. This approach is demonstrated in cities where streamlined processes have led to a faster pace of development and a decrease in vacancy rates.
- Exploring alternative housing models: Modular construction and prefabricated housing offer quicker and potentially more affordable ways to construct homes. This approach can significantly accelerate the supply of new housing units, particularly in areas with high demand and limited construction resources.
- Incentivizing multi-family development: Incentives, such as tax breaks or expedited zoning approvals, can encourage developers to construct multi-family housing, increasing the density of housing units in a given area and potentially reducing vacancy rates.
Improving Affordability and Accessibility
Addressing affordability is paramount in a crisis. Targeted support programs and policies are necessary to make housing more accessible to lower and middle-income households. Subsidized housing programs, rent control measures (carefully implemented), and financial assistance for down payments can all play a crucial role. A diverse range of housing options, from small apartments to large family homes, is essential.
- Subsidized housing programs: These programs can provide financial assistance to lower-income households, enabling them to afford housing in the market. Government-funded housing projects and rental assistance programs are examples of effective strategies in many cities.
- Rent control measures (with caveats): Rent control can help stabilize costs, but it’s important to note that overly restrictive policies can decrease the incentive for landlords to maintain and build new units, potentially leading to a reduction in the overall supply. Careful consideration and implementation are critical.
- Financial assistance for down payments: Making homeownership more accessible through down payment assistance programs can encourage more individuals to enter the housing market and potentially reduce the number of vacant homes.
The Importance of Public-Private Partnerships
Public-private partnerships are crucial for successful housing development. Combining the resources and expertise of both sectors can leverage investments and accelerate the construction of much-needed housing. Government funding can support infrastructure and incentives, while private developers bring expertise in design, construction, and management. This synergy can lead to innovative housing solutions and reduce vacancy rates.
- Joint ventures: Public-private partnerships in housing development can create a synergistic environment where government resources and expertise complement the skills and capital of the private sector. Examples include joint ventures in building affordable housing developments.
Case Studies of Successful Initiatives
Successful initiatives vary based on local conditions and regulations. For instance, some cities have seen success by implementing incentives for developers building affordable housing, leading to an increase in housing supply and a reduction in vacancy rates. Similarly, innovative zoning regulations in other areas have enabled the development of mixed-use communities, incorporating a greater variety of housing types and sizes.
Researching successful examples in different regions can provide valuable insights for adapting solutions to local contexts.
Strategies and Their Potential Impacts
| Strategy | Description | Potential Impact | Implementation Challenges |
|---|---|---|---|
| Streamlining permitting | Reducing bureaucratic hurdles for new construction | Increased housing supply, faster construction | Requires policy changes and inter-agency coordination |
| Modular construction | Faster, potentially cheaper construction methods | Increased housing supply, reduced construction time | Requires building codes adaptation, potentially higher initial costs |
| Subsidized housing programs | Financial support for lower-income households | Increased housing affordability, reduced homelessness | Requires substantial government funding, potential for administrative complexity |
Future Trends and Projections: Apartment Vacancy Rate Housing Crisis
The apartment vacancy rate and housing crisis are complex issues with significant implications for the future. Understanding potential future trends, considering various economic indicators, and acknowledging the impact of technology on housing are crucial for effective policy-making and informed decision-making in the sector. Predicting the future is inherently uncertain, but analyzing historical patterns and current trends can offer valuable insights into possible scenarios.
Projecting Future Trends in Apartment Vacancy Rates
Future vacancy rates will be influenced by a multitude of factors. These factors include shifts in population demographics, economic growth or recession, changes in interest rates, and government policies. Analyzing historical data and identifying patterns can help project future trends, though predicting the precise outcome remains challenging. Economic downturns, for example, often correlate with increased vacancy rates as individuals delay or postpone purchasing decisions.
Conversely, robust economic growth can lead to a decrease in vacancy rates due to increased demand.
The apartment vacancy rate is a key indicator of the housing crisis, and it’s been fluctuating wildly lately. While the recent return of Romeo Gigli to Marrakech, a celebrated figure in the fashion world, return of Romeo Gigli marrakesh , might seem unrelated, it actually highlights the broader economic trends impacting the market. High demand for luxury housing, especially in desirable locations, can exacerbate the issue of low vacancy rates, making affordable housing even harder to find.
Potential Scenarios Based on Various Economic Indicators
Economic indicators, such as GDP growth, inflation, and employment rates, significantly influence housing market conditions. A strong economy typically correlates with lower vacancy rates and higher rental prices. Conversely, a weakening economy can lead to increased vacancy rates and potentially lower rental prices. Consider the 2008 financial crisis; a sharp decrease in economic activity was followed by a rise in housing vacancies and a period of lower rental rates.
Therefore, tracking economic indicators is essential for predicting future housing market conditions.
Technological Advancements and Their Impact on Housing
Technological advancements are rapidly transforming the housing sector. Online platforms are changing how apartments are listed and rented. Virtual tours, online payment systems, and automated maintenance services are becoming increasingly common, streamlining the process for both landlords and tenants. The rise of co-living spaces and shared housing options are also impacting the rental market. These technological advancements are expected to continue to shape the future of housing, potentially altering vacancy rates and rental market dynamics.
Expected Impact on Rental Markets
The changing landscape of technology and the fluctuating economic climate will significantly impact rental markets. Online platforms offer greater accessibility for tenants and landlords, but also present challenges. Rental rates might be influenced by increased competition from online platforms, which can also reduce vacancy rates if they are efficient in connecting tenants with properties. Furthermore, technological advancements could potentially create new rental models, such as co-living spaces, impacting the overall rental market structure.
Projected Vacancy Rates for Different Regions
| Region | Projected Vacancy Rate | Factors | Timeframe |
|---|---|---|---|
| Northeast | 4.5% | Strong employment, high demand, limited new construction | 2024-2028 |
| Midwest | 5.2% | Moderate employment growth, moderate demand, ongoing construction | 2024-2028 |
| South | 3.8% | Strong population growth, robust job market, increasing new construction | 2024-2028 |
| West | 6.1% | Variable employment growth, moderate demand, high housing costs | 2024-2028 |
Note: These projected vacancy rates are estimates and subject to change based on future economic conditions and other relevant factors.
Conclusive Thoughts

In conclusion, the apartment vacancy rate housing crisis highlights the interconnectedness of various economic and social factors. The crisis impacts renters, investors, and the broader housing market. Understanding these intricacies is crucial for developing effective solutions and strategies to improve the situation and ensure a more stable and affordable housing future. This complex issue demands a multifaceted approach, encompassing both individual and systemic solutions.
The future of housing will depend on our ability to address the challenges and implement effective strategies to create a more balanced and sustainable market.
Expert Answers
What are the main causes of the current high apartment vacancy rates?
Several factors contribute to high vacancy rates, including economic downturns, shifts in population demographics, changes in rental preferences, and a mismatch between supply and demand in certain regions. Additionally, fluctuating interest rates and inflation also play a role.
How does the vacancy rate impact rent prices?
Low vacancy rates often lead to increased competition among renters, pushing up rent prices. Conversely, high vacancy rates can result in lower rents as landlords seek to attract tenants.
What role do government policies play in the housing crisis?
Government policies, such as zoning regulations, building codes, and tax incentives, can significantly influence housing supply and affordability. These policies, both positive and negative, can affect vacancy rates and the overall health of the housing market.
What are some potential solutions to address the housing crisis?
Potential solutions include increasing housing supply through incentives for new construction, expanding affordable housing options, implementing policies to streamline the permitting process, and fostering partnerships between public and private entities.

