
Birth Rates Baby Bust Explained
Birth rates baby bust is a pressing global issue. Falling birth rates across many countries are causing significant societal and economic concerns. This article explores the factors contributing to this decline, its impacts, and potential solutions. We’ll delve into historical context, economic pressures, and societal shifts that shape family planning decisions.
From historical examples to modern-day challenges, this in-depth look at birth rates baby bust will examine the complex interplay of factors driving this trend. We will investigate the potential consequences for workforce, healthcare, and economic growth. Finally, we will explore potential solutions and interventions.
Defining the “Baby Bust” Phenomenon
A baby bust, a period of significantly declining birth rates, presents a complex interplay of societal and economic forces. This phenomenon is not simply a temporary fluctuation but rather a sustained decrease in fertility rates, impacting population dynamics and resource allocation. Understanding the factors driving these declines is crucial for forecasting future trends and developing appropriate policies.Declining birth rates are characterized by a sustained drop in the number of live births per 1,000 women of childbearing age.
This drop is typically measured over several years, distinguishing it from short-term fluctuations. A key characteristic is the overall reduction in the rate of population growth, often leading to a smaller proportion of younger people in the population.Societal and economic factors significantly contribute to declining birth rates. Increased educational and career opportunities for women frequently lead to delayed childbearing or a choice to forgo parenthood altogether.
Rising living costs, including housing, childcare, and healthcare, also deter prospective parents from having children. Economic uncertainty and instability can further discourage families from starting families, as they perceive financial strain. Additionally, changing cultural norms and values, including a shift towards smaller family sizes, play a role.Historical examples of baby bust periods are evident in the post-World War I era in some countries.
The economic hardship and social upheaval following the war contributed to a period of low birth rates. Similarly, economic downturns, such as the Great Depression, have also been linked to reduced birth rates in several regions. The aftermath of major conflicts often leads to societal shifts that impact family structures and decision-making.The long-term implications of low birth rates are profound.
A shrinking workforce can strain social security systems and healthcare services. Reduced population growth can impact economic development and innovation. Changes in the age structure of the population necessitate adjustments in policies and infrastructure to maintain societal well-being.
The declining birth rates, often called a “baby bust,” are a complex issue with many contributing factors. While economic pressures play a role, the influence of corporations like Koch and Chevron, who often demonstrate deference to the Supreme Court, as seen in the koch chevron deference supreme court case, might also be impacting societal decisions affecting family planning.
Ultimately, the mystery of declining birth rates remains a multifaceted puzzle.
Comparison of Birth Rates Across Countries/Regions
Examining birth rates across different countries and regions over time reveals significant variations. This analysis offers insights into the interplay of demographic and socioeconomic factors. Understanding historical trends can help predict future population dynamics.
| Country/Region | Year | Birth Rate (per 1000 women) |
|---|---|---|
| United States | 1960 | 23.7 |
| United States | 1970 | 18.0 |
| United States | 1980 | 15.7 |
| United States | 1990 | 16.2 |
| United States | 2000 | 14.1 |
| United States | 2010 | 14.1 |
| Japan | 1960 | 25.3 |
| Japan | 1970 | 18.1 |
| Japan | 1980 | 13.5 |
| Japan | 1990 | 12.5 |
| Japan | 2000 | 10.1 |
| Japan | 2010 | 7.6 |
Note: Data for birth rates is illustrative and may vary depending on the source and methodology. The table shows general trends but does not capture nuances of regional variations within countries.
Exploring the Causes of Declining Birth Rates
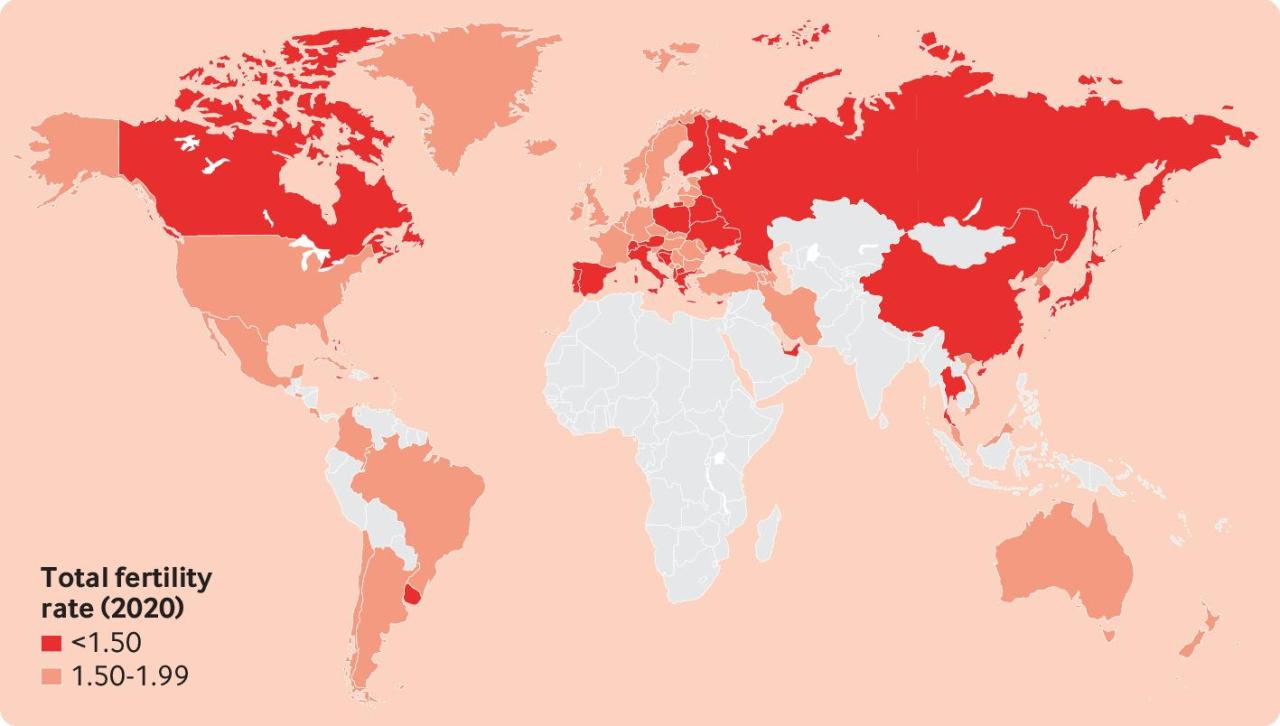
The global trend of declining birth rates is a complex phenomenon with far-reaching implications. Understanding the underlying factors is crucial for policymakers and individuals alike to address this issue effectively. Factors ranging from economic pressures to evolving societal norms play a significant role in shaping family planning decisions. This exploration delves into the multifaceted causes driving this demographic shift.The reasons behind declining birth rates are not singular, but rather a confluence of interconnected elements.
These factors often intertwine, creating a multifaceted challenge that requires a comprehensive approach to address. This analysis examines the significant roles of economic pressures, societal shifts, personal choices, and governmental support in shaping family size preferences.
The recent decline in birth rates, often called a “baby bust,” is a global phenomenon. It’s a complex issue with various contributing factors, including economic pressures and changing societal values. However, the implications of declining birth rates are increasingly linked to events like snow polo in St. Moritz, which is now increasingly affected by climate change, as reported in snow polo st moritz climate change.
This highlights how seemingly disparate events can be connected, and ultimately influence even something as fundamental as birth rates and population trends. Perhaps the changing climate is impacting people’s willingness to start families.
Economic Pressures and Family Planning
Economic hardship often leads to delayed or forgone parenthood. The rising cost of raising children, including childcare, education, and healthcare, is a significant deterrent for many couples. Housing costs, particularly in urban areas, can also make starting a family financially challenging. The fear of economic instability can impact decisions about having children, and the need for two incomes to meet expenses can lead to couples choosing to delay or forgo having children altogether.
Societal Shifts and Family Size Preferences
Evolving societal norms and values have profoundly impacted family size preferences. Increased educational opportunities for women and changing gender roles have often resulted in a greater emphasis on personal fulfillment and career advancement. This often necessitates a shift in priorities, with individuals prioritizing personal pursuits over immediate family expansion. The rise of single-person households and cohabitation also contributes to the declining birth rate.
Women’s Empowerment and Educational Opportunities
Women’s empowerment, including access to education and employment opportunities, plays a crucial role in influencing family size decisions. Educated women tend to delay childbirth and have fewer children compared to those with limited educational attainment. Greater financial independence and career prospects often lead women to prioritize their careers and personal ambitions over traditional family structures. Access to family planning services and reproductive healthcare is also a crucial factor.
Government Policies and Support Systems
Government policies and support systems significantly influence family planning decisions. Countries with robust childcare subsidies, parental leave policies, and affordable housing initiatives often experience higher birth rates. These programs can help ease the financial burden of raising children and encourage individuals to start families. Furthermore, access to affordable healthcare and family planning services is essential.
Correlation Between Economic Indicators and Birth Rates
The following table illustrates the potential correlation between economic indicators and birth rates in a hypothetical European region. Note that this is a simplified example and does not account for all variables influencing birth rates.
| GDP per capita (USD) | Unemployment Rate (%) | Birth Rate (per 1000 people) |
|---|---|---|
| 25,000 | 5 | 10 |
| 30,000 | 6 | 9 |
| 35,000 | 7 | 8 |
| 40,000 | 8 | 7 |
| 45,000 | 9 | 6 |
Analyzing the Impact of Declining Birth Rates
Declining birth rates, a global phenomenon, are reshaping societies in profound ways. This shift isn’t merely a demographic trend; it’s a multifaceted challenge with significant implications for national economies, social structures, and individual well-being. The ripple effects of fewer births extend far beyond the immediate family unit, impacting the workforce, financial systems, and the very fabric of a nation.The consequences of declining birth rates are substantial and far-reaching.
Countries experiencing this trend face a complex web of interconnected challenges, affecting everything from economic growth to the future of social safety nets. Understanding these impacts is crucial for policymakers and individuals alike as they navigate the changing landscape of the 21st century.
Effects on a Nation’s Workforce
The declining birth rate translates directly into a shrinking pool of potential workers in the future. This reduced workforce has the potential to significantly impact labor markets, leading to shortages in key sectors. A smaller workforce can potentially slow economic growth, hinder innovation, and make it difficult to maintain productivity levels.
Impact on Social Security and Pension Systems
Social security and pension systems are directly tied to the ratio of working-age individuals to retirees. Lower birth rates mean fewer individuals entering the workforce to support a growing number of retirees. This demographic imbalance can strain existing systems, potentially requiring substantial reforms or increased contributions to ensure sustainability. For example, in Japan, the aging population and low birth rates have already put a considerable strain on the pension system, prompting government initiatives to address the issue.
Consequences for the Healthcare System
A smaller workforce also impacts the healthcare system. Fewer young people entering the workforce may lead to a shortage of healthcare professionals, potentially impacting the quality and accessibility of healthcare services. This is particularly concerning in sectors like nursing and medicine, where a substantial workforce is required to meet patient needs.
Impact on Economic Growth and Development
Declining birth rates can have a profound impact on economic growth and development. A smaller workforce can limit innovation, hinder productivity, and decrease overall economic output. This can be particularly detrimental to countries heavily reliant on a youthful workforce for economic activity. For instance, countries with strong manufacturing sectors and large populations of young workers may experience a significant slowdown in economic growth due to the reduced labor pool.
The recent baby bust in birth rates is a complex issue, and factors like economic anxieties play a significant role. However, the way parents choose to name and register their children, like the rules around “apellido bebe madre padre” apellido bebe madre padre , might also be contributing to the lower birth rates. Ultimately, understanding the motivations behind these choices is key to addressing the overall decline in birth rates.
Potential Consequences on Family Structures and Dynamics
The declining birth rate can lead to shifts in family structures and dynamics. Smaller families, or the absence of children, may result in changes in traditional family roles and responsibilities. It also affects the social support networks that families rely on, potentially impacting the emotional and practical well-being of individuals.
Potential Workforce Shortages
The declining birth rate presents a serious concern for several sectors. The shortage of skilled workers in key industries will have a substantial impact on productivity and economic growth.
| Sector | Projected Shortage | Potential Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Healthcare | Nurses, doctors, and other healthcare professionals | Reduced access to quality healthcare, increased wait times, and potential strain on the healthcare system. |
| Technology | Software engineers, data scientists, and other tech professionals | Slower technological advancements, decreased innovation, and potential loss of competitiveness in the global market. |
| Manufacturing | Skilled laborers and technicians | Reduced productivity, slower production rates, and potential difficulty in meeting consumer demand. |
| Education | Teachers and educators | Lower quality of education, reduced access to learning opportunities, and potential impact on future generations. |
Examining Potential Solutions and Interventions
Addressing declining birth rates requires a multifaceted approach encompassing various societal factors. The simple provision of financial incentives, while potentially impactful, is insufficient on its own. A comprehensive strategy must consider the interconnectedness of economic stability, social support systems, and individual aspirations. Ultimately, sustainable solutions must foster an environment where families feel supported and empowered to have children.
Potential Government Policies
Government policies play a crucial role in shaping societal attitudes towards family planning and childbearing. Effective policies aim to alleviate financial burdens, reduce childcare responsibilities, and promote a supportive environment for families. These policies can significantly impact birth rates by addressing the practical and emotional obstacles that prospective parents face.
- Financial Incentives: Offering financial incentives, such as tax breaks for families with children or subsidized childcare, can provide substantial relief to families struggling with the financial demands of raising children. This approach has proven effective in some countries, demonstrating the tangible impact of financial support on birth rates. For example, the French government’s “baby bonus” has been credited with a slight increase in birth rates.
The recent baby bust in birth rates is a fascinating trend, and it’s interesting to see how these demographic shifts might play out in the political landscape. The results of the New Hampshire Democratic primary, for example, demonstrating shifting voter preferences , could offer some clues. Perhaps the declining birth rate is connected to these shifts in political leaning, or maybe it’s a completely separate societal trend.
Regardless, it’s a complex puzzle with plenty of moving pieces, and understanding the factors behind the baby bust is more important than ever.
- Childcare Subsidies and Access: Improved access to affordable and high-quality childcare is vital for enabling parents to pursue careers while also providing adequate care for their children. Subsidized or publicly funded childcare can lessen the economic strain and allow parents to work without the constant worry of childcare costs. Countries with robust childcare infrastructure often experience higher birth rates.
- Parental Leave Policies: Generous parental leave policies that provide paid time off for both parents can empower families to care for their newborns without compromising financial stability. This support can help parents adjust to the significant changes brought on by the arrival of a child and foster a stronger family bond. Extensive parental leave has been correlated with increased birth rates in some European nations.
Impact of Financial Incentives and Support Systems
Financial incentives, when implemented strategically, can be a powerful tool for encouraging higher birth rates. These incentives can directly reduce the financial burden of raising children, thereby making parenthood more accessible and attractive. For example, the provision of child tax credits in the United States has demonstrated the potential of financial support to influence family decision-making.
- Impact on Lower-Income Families: Financial incentives are particularly beneficial for lower-income families, as they often face significant financial constraints when considering having children. These families are often most affected by economic downturns, and financial assistance can alleviate some of the stress associated with raising a family.
- Impact on Career Choices: Improved access to childcare and parental leave can significantly influence career choices for both parents. Parents are more likely to pursue education and careers if they feel supported in their family roles. This can contribute to a more stable and prosperous society.
Public Awareness Campaigns
Public awareness campaigns can play a critical role in fostering a more supportive environment for families and promoting the benefits of parenthood. These campaigns can challenge societal stereotypes, highlight the positive aspects of family life, and offer guidance to prospective parents.
- Promoting Positive Perceptions: These campaigns can help to change perceptions about having children and emphasize the positive aspects of family life. They can help break down stereotypes about parental roles and encourage a wider range of people to consider parenthood.
- Addressing Societal Pressures: Public awareness campaigns can also address societal pressures and expectations that may be deterring individuals from having children. They can provide resources and information to help prospective parents navigate the challenges of parenthood.
Promoting Family-Friendly Workplaces
Family-friendly workplaces can contribute significantly to the well-being of employees and their families. Such workplaces often demonstrate a clear understanding of the importance of work-life balance, which can encourage individuals to have children.
- Flexible Work Arrangements: Flexible work arrangements, such as remote work options or flexible hours, can empower parents to manage their work and family responsibilities more effectively. This can significantly ease the burden of childcare and parental responsibilities, fostering a more family-centric workplace culture.
- Supporting Parents: Implementing policies that support parents, such as providing on-site childcare facilities or offering generous parental leave, can create a supportive environment where employees feel valued and appreciated.
Improving Access to Childcare and Parental Leave
Improving access to affordable and high-quality childcare is critical for enabling parents to balance work and family responsibilities. Similarly, extended parental leave policies can provide crucial support to new parents as they adjust to the responsibilities of parenthood.
- Childcare Availability: Expanding access to affordable and high-quality childcare facilities can help reduce the financial burden and time constraints on parents. This can empower parents to pursue their career aspirations while also providing the necessary care for their children.
- Parental Leave Policies: Increasing the duration and accessibility of parental leave policies can provide essential support to new parents. This can foster a more supportive environment for new families and encourage a higher birth rate.
Government Policies for Increasing Birth Rates (Example Table)
| Country | Policy | Intended Impact |
|---|---|---|
| France | “Baby Bonus” | Increased financial support for families with children. |
| Sweden | Extensive parental leave | Increased support for parents adjusting to parenthood. |
| South Korea | Financial incentives, childcare subsidies | Reduce financial burden of child rearing. |
| Germany | Child allowance, parental benefits | Encourage higher birth rates through financial incentives. |
Illustrative Examples of Societal Responses

Declining birth rates are a global phenomenon prompting various societal responses. Countries are exploring diverse strategies to address this demographic shift, recognizing its potential impact on economic growth, social structures, and the future of their populations. These responses range from government policies to social support systems, reflecting a complex interplay of economic, social, and cultural factors.Governments worldwide are actively engaging in initiatives to counteract the trend of falling birth rates.
These strategies encompass a spectrum of approaches, from financial incentives to improved parental support systems, aiming to encourage families to have more children. Different countries have implemented varying approaches, leading to a mixed bag of results. Examining these examples can offer valuable insights into effective strategies and potential pitfalls.
Government Policies Implemented to Increase Birth Rates
Various countries have introduced policies to incentivize higher birth rates. These policies aim to ease the financial burden of raising children, promote work-life balance, and enhance the overall quality of life for families. Examples include subsidized childcare, parental leave programs, and tax benefits for families with children.
The recent dip in birth rates, often called a “baby bust,” is a complex issue with various contributing factors. Understanding these factors is crucial, and the political landscape plays a significant role. For example, the upcoming Nevada caucus primary, with its potential impact on the future of the country, offers a unique opportunity to examine the interplay of political strategy and demographics.
A deeper dive into the complexities of the political climate can be found in this Nevada caucus primary explainer. Ultimately, these political developments, along with economic and social trends, all contribute to the ongoing discussion about declining birth rates.
- Subsidized childcare: Many European nations have implemented comprehensive childcare subsidies to reduce the financial strain on families. This makes childcare more affordable and accessible, encouraging parents to return to work or pursue further education, without the fear of high childcare costs impacting their family’s budget.
- Extended parental leave: Some countries offer generous parental leave, allowing parents more time to bond with their newborns and care for their children. This can positively influence family dynamics and increase the likelihood of having more children.
- Tax benefits for families with children: Many countries offer tax breaks or deductions for families with children. This aims to reduce the financial burden of raising a family, making it more attractive for families to have more children.
Social Support Systems Established to Help Families
In addition to government policies, various countries have established social support systems to provide assistance to families with children. These initiatives aim to alleviate the stresses of raising children and improve the overall well-being of families.
- Improved access to healthcare and education: Accessible and affordable healthcare and education are crucial for family well-being. Quality education empowers parents and children, while reliable healthcare ensures a healthy environment for raising families.
- Community support programs: Support programs for families can include community centers, playgroups, and parenting classes. These programs can provide social support, networking opportunities, and access to resources for parents.
- Increased availability of affordable housing: Affordable housing is vital for families. Housing costs often contribute to the decision to limit family size. Ensuring access to affordable housing can influence family planning decisions.
Effectiveness of Strategies Across Various Countries
| Country | Strategy | Success Indicators |
|---|---|---|
| France | Subsidized childcare, parental leave | Higher birth rate compared to some other European countries, but still below replacement level. |
| South Korea | Financial incentives, improved social support | Limited success in significantly increasing birth rates, despite substantial efforts. |
| Japan | Financial incentives, extended parental leave | Minimal impact on birth rates, indicating a need for broader societal changes. |
| Sweden | Extensive parental leave, subsidized childcare | High birth rate in comparison to other developed nations, demonstrating the effectiveness of comprehensive support systems. |
Example of a Public Awareness Campaign, Birth rates baby bust
Finland launched a public awareness campaign that emphasized the joys and benefits of having children. The campaign featured various media outlets, including television, radio, and social media, highlighting positive family experiences. The campaign focused on portraying diverse family structures and emphasizing the importance of children in society. It aimed to counter negative perceptions about having children and the challenges of raising a family.
Example of Economic Incentives
South Korea has offered various financial incentives, such as tax breaks and subsidies for childcare, to encourage higher birth rates. However, the success of these measures has been limited. This indicates that financial incentives alone may not be sufficient to address the complex factors influencing declining birth rates.
Conclusion
In conclusion, birth rates baby bust presents a multifaceted challenge requiring comprehensive solutions. The interconnectedness of economic pressures, societal norms, and personal choices underscores the need for nuanced approaches. By understanding the causes and consequences of declining birth rates, we can begin to develop effective strategies for fostering sustainable population growth and economic prosperity.
FAQ: Birth Rates Baby Bust
What are some common misconceptions about the baby bust phenomenon?
One common misconception is that the baby bust solely stems from economic hardship. While economic factors play a role, societal shifts, women’s empowerment, and access to education and employment opportunities also contribute significantly.
How do government policies influence birth rates?
Government policies, including financial incentives, childcare support, and parental leave, can significantly impact birth rates. However, the effectiveness of these policies varies depending on the specific context and societal factors.
What is the long-term impact of declining birth rates on the healthcare system?
Declining birth rates can lead to a shrinking workforce in the healthcare sector, potentially impacting the availability of healthcare professionals and services. This can also affect social security and pension systems.
Are there any examples of countries that have successfully addressed declining birth rates?
Some countries have implemented various strategies to encourage higher birth rates, including financial incentives, subsidized childcare, and improved parental leave policies. The success of these strategies is complex and depends on various factors. Analyzing the specific policies and their effectiveness in different countries can offer valuable insights.

