Groundwater Aquifer Depletion Courts A Deep Dive
Groundwater aquifer depletion courts are increasingly important as water scarcity becomes a global issue. These legal battles, often complex and multi-faceted, involve a range of stakeholders, from local communities to international bodies. This exploration dives into the intricacies of these courts, examining the legal frameworks, case studies, and stakeholder perspectives that shape the outcomes.
From the historical context of groundwater depletion to the latest legal challenges, we’ll uncover the nuances of these cases and the impact they have on communities and ecosystems. Understanding these issues is crucial for developing sustainable water management practices in a world facing growing water stress.
Groundwater Aquifer Depletion
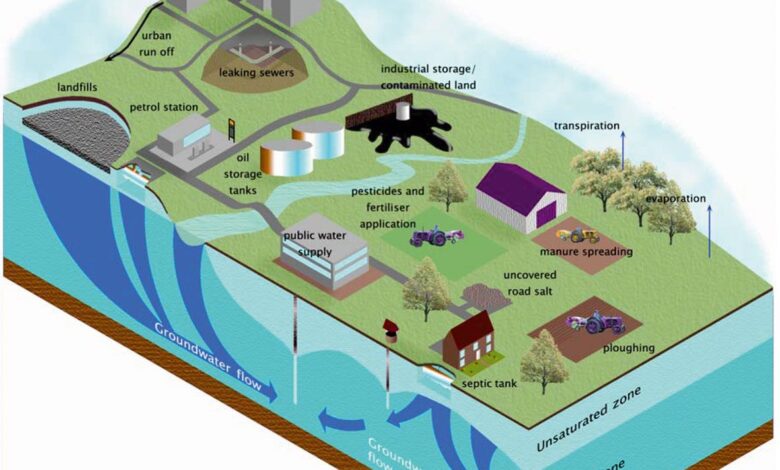
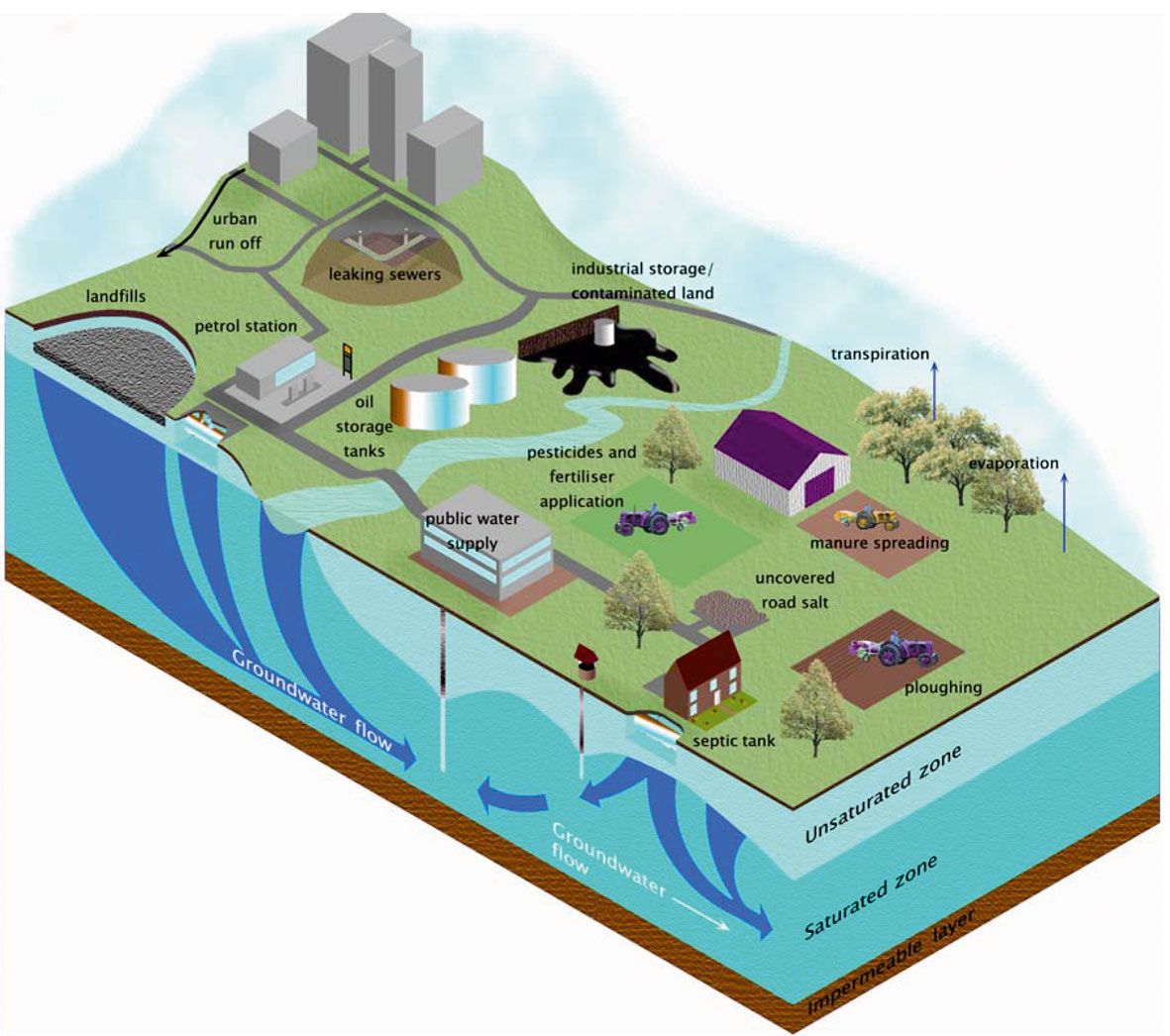
Groundwater aquifers, crucial reservoirs of freshwater beneath the Earth’s surface, are facing increasing depletion worldwide. This depletion, driven by various factors, poses significant threats to ecosystems and human societies. Understanding the causes, consequences, and historical context of this issue is vital for developing sustainable water management strategies.Groundwater aquifers are vital for sustaining ecosystems and human activities. They provide drinking water, support agriculture, and replenish rivers and lakes.
Depletion of these aquifers can disrupt ecological balance, lead to water scarcity, and harm the economies that rely on them.
Causes of Groundwater Aquifer Depletion
Groundwater depletion arises from various anthropogenic activities. Excessive extraction for agricultural irrigation, industrial use, and domestic consumption are primary contributors. Over-pumping, exceeding the aquifer’s natural recharge rate, is a key factor in depletion. Improper well construction and maintenance can also lead to accelerated groundwater loss. Droughts and climate change further exacerbate the problem by reducing natural recharge.
Historical Context of Groundwater Depletion
Historical records demonstrate a growing trend of groundwater depletion. In regions with intensive agricultural practices, like the San Joaquin Valley in California, decades of over-pumping have led to significant aquifer drawdown. Similar patterns have emerged in other parts of the world, indicating a global issue. Historical over-reliance on groundwater resources without considering sustainable management practices has played a key role in the current situation.
Significance of Groundwater Aquifers
Groundwater aquifers play a critical role in various ecosystems and human activities. They serve as vital sources of freshwater for drinking, agriculture, and industry. Maintaining healthy groundwater levels is essential for preserving biodiversity and supporting local economies. Furthermore, they influence the flow of surface water, maintaining the health of rivers and wetlands. Aquifers are essential to maintaining a stable water table, which is crucial for the survival of many plant and animal species.
Methods of Groundwater Extraction
Different methods of groundwater extraction vary in their efficiency and impact on the aquifer.
| Method | Description | Efficiency | Impact on Aquifer |
|---|---|---|---|
| Well pumping | Water is extracted from the aquifer using a well equipped with a pump. | Can be highly efficient if well designed and maintained. | Can lead to drawdown if over-pumping occurs, potentially impacting the surrounding ecosystem. |
| Sprinkler Irrigation | Water is sprayed onto crops using sprinklers. | Can be highly efficient depending on the design and water pressure. | High water use can cause depletion, especially if not combined with efficient irrigation techniques. |
| Drip Irrigation | Water is delivered directly to the plant roots. | Very efficient, as it minimizes water loss. | Can significantly reduce depletion and help conserve groundwater. |
Legal Frameworks and Regulations
Groundwater depletion, a critical issue impacting water security globally, necessitates robust legal frameworks and regulations. These frameworks aim to balance the needs of various water users, protect the long-term sustainability of aquifers, and prevent the irreversible damage caused by unsustainable extraction. Effective regulations are crucial for equitable access to water resources and maintaining the ecological health of the environment.Groundwater depletion often occurs in regions with high water demand, leading to conflicts between competing users.
Legal frameworks must address these conflicts by establishing clear property rights, water allocation mechanisms, and monitoring procedures. These mechanisms help in ensuring responsible water management practices and promoting sustainable water use.
Global Legal Frameworks Addressing Groundwater Depletion
Various countries and international organizations have recognized the importance of groundwater protection and have implemented legal frameworks. These frameworks vary significantly in their scope and application, depending on the specific context of each jurisdiction. For example, some frameworks focus on regulating extraction, while others prioritize conservation measures. Understanding these diverse approaches is crucial for effective groundwater management.
Challenges in Enforcing Groundwater Regulations
Enforcement of groundwater regulations faces numerous challenges. One significant challenge is the difficulty in monitoring groundwater extraction and ensuring compliance. The hidden nature of groundwater makes it difficult to track unauthorized extraction or illegal pumping. Another obstacle is the lack of adequate resources, including trained personnel and monitoring equipment, to enforce regulations effectively. Political considerations and competing interests can also hinder enforcement efforts.
Comparison of Legal Approaches to Groundwater Management
Legal approaches to groundwater management differ considerably across jurisdictions. Some countries adopt a “prior appropriation” doctrine, granting water rights based on historical use. Others prioritize the “reasonable use” doctrine, allowing water use only if it does not harm others. Different approaches reflect differing cultural and legal traditions and often lead to unique conflicts and solutions.
Role of International Agreements in Managing Shared Groundwater Resources
International agreements play a critical role in managing shared groundwater resources. These agreements aim to establish cooperative frameworks for water use and prevent transboundary disputes. The principle of equitable and reasonable utilization is frequently highlighted in these agreements. International cooperation and the establishment of shared management bodies are essential for ensuring the sustainable use of transboundary aquifers.
Key Legal Principles Concerning Groundwater Rights
| Legal Principle | Description |
|---|---|
| Prior Appropriation | Water rights are granted based on the seniority of the water user. The first user has the right to the water. |
| Reasonable Use | Water use is permitted as long as it does not harm others. The balance of competing interests is a key consideration. |
| Correlative Rights | Groundwater is treated as a shared resource, and all users have equal rights to a proportionate share of the resource. |
| Absolute Ownership | Groundwater is considered the property of the landowner, and they can use it as they see fit. This is less common now due to concerns about sustainability. |
| Equitable and Reasonable Utilization | Groundwater use should be fair and reasonable to all stakeholders. International agreements often highlight this principle. |
Court Cases and Litigation

Groundwater depletion, often driven by agricultural or industrial needs, can lead to severe environmental and economic consequences. Legal frameworks are crucial in addressing these issues, and court cases play a vital role in enforcing regulations and holding responsible parties accountable. The legal landscape surrounding groundwater depletion is constantly evolving, with courts grappling with complex scientific and legal arguments.Court cases related to groundwater depletion are often multifaceted, involving disputes over water rights, environmental damage, and economic impacts.
They necessitate a deep understanding of local regulations, historical water usage patterns, and the scientific underpinnings of groundwater systems. Successful litigation requires a strong legal strategy, meticulous documentation, and expert testimony to demonstrate the connection between the defendant’s actions and the depletion of the groundwater aquifer.
Groundwater aquifer depletion courts are facing a lot of pressure these days, with dwindling water supplies impacting communities across the nation. It’s a serious issue, and the recent tragedy involving the armorer Alec Baldwin in the armorer Alec Baldwin rust shooting highlights a different kind of pressure – one that underscores the importance of careful consideration in every industry, even those seemingly unrelated to water.
Ultimately, responsible practices and accountability are crucial for everyone, from the courtroom to the film set and everywhere in between.
Types of Court Cases
Groundwater depletion cases encompass a wide range of legal actions. These can include claims for injunctions to prevent further depletion, demands for compensation for damages already incurred, and even lawsuits for the violation of water rights or environmental regulations. Some cases focus on establishing liability for past or present actions, while others aim to establish new precedents or regulations for future management of groundwater resources.
Successful Legal Challenges
Numerous cases demonstrate the effectiveness of legal action in addressing groundwater depletion. One example involves a successful lawsuit against a large-scale agricultural operation for over-pumping a local aquifer, leading to the depletion of the water table and impacting nearby wells. Another case involved a factory that was held accountable for contaminating the groundwater source, forcing them to implement remediation measures.
These examples highlight the potential for legal action to mitigate the negative impacts of groundwater depletion.
Common Arguments
In these cases, common arguments revolve around the violation of water rights, environmental harm, and the demonstrable link between the defendant’s actions and the depletion. Plaintiffs often present evidence of excessive pumping, exceeding permitted quotas, or negligence in managing water usage. Expert testimony from hydrologists, geologists, and other specialists plays a critical role in establishing the causal relationship between the defendant’s activities and the depletion.
Examples include proving the depletion was caused by over-extraction, not natural fluctuations, or demonstrating the damage to the ecological balance.
Impact of Court Decisions
Court decisions regarding groundwater depletion have a significant impact on future groundwater management practices. Successful cases often lead to stricter regulations and enforcement of existing laws, prompting greater awareness of the need for sustainable water management. These rulings set precedents, influencing future cases and shaping the legal landscape around water rights. The impact can range from changes in local water usage regulations to the implementation of stricter monitoring and reporting requirements for water users.
Procedures in Filing a Legal Case
Filing a legal case concerning groundwater depletion involves a series of procedural steps. These typically include identifying the relevant legal framework, gathering evidence, and engaging legal counsel. Key steps include assembling evidence of groundwater depletion, determining the responsible parties, and initiating the legal proceedings. The specific procedures vary by jurisdiction, but generally involve filing a complaint, serving the defendant, and engaging in discovery and pre-trial activities.
Groundwater aquifer depletion courts are facing a tough battle, dealing with the devastating consequences of resource scarcity. It’s a complex issue, but it also mirrors the profound human cost of environmental damage, a theme explored in the powerful piece “grief is for people sloane crosley” grief is for people sloane crosley. Ultimately, these courts are striving to find solutions that balance human needs with the long-term health of our planet’s water resources.
This process can be lengthy and complex, demanding careful consideration of the legal requirements and evidence needed to support the claim.
Groundwater aquifer depletion courts are a growing concern, with legal battles over water rights becoming increasingly common. It’s fascinating to consider how these disputes mirror the emotional turmoil explored in Taylor Swift’s “Tortured Poets Department” Tortured Poets Department Taylor Swift A Deep Dive , especially when considering the deep-seated conflicts over dwindling resources. Ultimately, these legal battles highlight the crucial need for sustainable water management practices.
Example of a Procedure
- Identification of the Problem: Recognizing the excessive pumping of groundwater and its negative effects on the ecosystem.
- Evidence Gathering: Collecting data on water levels, pumping rates, and the environmental impact.
- Legal Counsel: Consulting with a lawyer specializing in environmental law and water rights.
- Complaint Filing: Submitting a formal complaint to the court detailing the violation and requested relief.
- Discovery Process: Exchanging information with the defendant, including depositions and document requests.
- Expert Testimony: Presenting expert witnesses to provide scientific evidence supporting the case.
- Trial and Judgement: Presenting the case to the court, leading to a verdict on liability and remedies.
Stakeholder Perspectives and Impacts
Groundwater depletion disputes often involve a complex web of stakeholders, each with varying perspectives and interests. Understanding these diverse viewpoints is crucial to crafting effective legal frameworks and regulations that address the multifaceted challenges associated with this critical resource. These stakeholders range from agricultural communities dependent on groundwater for irrigation to environmental groups concerned about ecosystem health, and ultimately impact the long-term sustainability of the resource.The economic, social, and environmental impacts of groundwater depletion are far-reaching and often disproportionately affect vulnerable populations.
The ripple effects can range from decreased agricultural yields and increased food prices to displacement of communities and ecosystem degradation, highlighting the need for comprehensive strategies to manage this precious resource.
Perspectives of Different Stakeholders
Different stakeholders hold varied perspectives on groundwater depletion, reflecting their unique interests and concerns. Farmers, for example, prioritize access to water for their crops, often viewing restrictions as detrimental to their livelihoods. On the other hand, environmental groups may prioritize the preservation of ecosystems, advocating for stricter regulations to protect water quality and quantity. Local communities reliant on groundwater for drinking water may face severe consequences if supplies are depleted or contaminated.
Understanding these diverse viewpoints is vital for developing effective and equitable solutions.
Economic Impacts on Communities
Groundwater depletion significantly impacts the economic stability of communities reliant on this resource. Decreased agricultural yields directly translate to lower farm incomes and reduced food production, which can have cascading effects on local economies. Reduced water availability for industry can lead to job losses and economic stagnation. The cost of implementing alternative water sources, such as desalination or surface water diversions, can place a considerable financial burden on affected communities, especially those with limited resources.
For instance, the San Joaquin Valley in California has seen significant economic hardship due to the over-allocation of groundwater, impacting farmers and related industries.
Social Impacts on Different Groups
Groundwater depletion can exacerbate existing social inequalities. Communities already facing poverty and limited access to resources may be disproportionately affected by reduced water availability, leading to increased hardship and social unrest. The displacement of communities due to declining water tables can further exacerbate these issues, creating significant social disruption and challenges in rebuilding communities in new locations. Women and marginalized groups often bear the brunt of these impacts due to their often limited access to resources and decision-making power.
Environmental Consequences on Ecosystems
Groundwater depletion can have devastating consequences for ecosystems. The lowering of water tables can alter the hydrological balance of aquifers, impacting the flow of streams and rivers, and threatening the survival of aquatic species. Groundwater is crucial for maintaining the health of wetlands, which provide crucial habitats for a wide range of wildlife. For instance, the depletion of the Ogallala Aquifer in the American Great Plains has led to the drying up of many streams and rivers, impacting the ecosystems that rely on them.
Stakeholder Impacts Summary Table
| Stakeholder | Potential Impacts |
|---|---|
| Farmers | Reduced agricultural yields, lower farm incomes, increased costs of irrigation, displacement |
| Environmental groups | Ecosystem degradation, loss of biodiversity, water quality deterioration, impacts on aquatic species |
| Local communities | Reduced access to drinking water, increased waterborne diseases, decreased quality of life, displacement |
| Industry | Reduced water availability, increased costs of water, job losses, economic stagnation |
| Government | Increased costs of managing water resources, increased demand for water allocation policies, political instability |
Emerging Trends and Future Directions
Groundwater depletion litigation is evolving rapidly, mirroring broader societal shifts toward environmental sustainability and resource management. The increasing frequency and severity of droughts, coupled with growing populations and agricultural demands, are intensifying pressure on groundwater resources. This necessitates innovative legal frameworks and technological advancements to address the complex issues arising from aquifer depletion.The legal landscape is adapting to the unique challenges presented by groundwater resources, which often transcend political boundaries and necessitate international cooperation.
This evolving dynamic demands a comprehensive understanding of emerging trends in litigation, potential future directions for dispute resolution, and the crucial role of technology and scientific data in shaping legal outcomes.
Groundwater aquifer depletion courts are facing a tough time, with the ongoing water scarcity issues. This is especially relevant considering the recent Biden-Israel-Hamas cease fire efforts here. While the geopolitical situation is certainly complex, the strain on water resources continues to impact legal battles over aquifer usage and sustainable management, highlighting the interconnectedness of global events and environmental justice.
Emerging Trends in Groundwater Depletion Litigation
Groundwater depletion cases are increasingly complex, involving multiple stakeholders with conflicting interests. Cases are moving beyond simple claims of negligence to include intricate issues of equitable apportionment, environmental impact assessments, and transboundary water rights. The growing awareness of interconnectedness between surface and groundwater resources is leading to integrated water resource management approaches within legal frameworks. Examples include disputes over water allocation in river basins where groundwater depletion impacts surface water flows.
Potential Future Directions for Resolving Groundwater Depletion Disputes
Innovative dispute resolution mechanisms are crucial to effectively address groundwater depletion disputes. Mediation and arbitration are increasingly used to foster collaborative solutions between competing interests, promoting compromise and sustainable agreements. The development of standardized groundwater management plans and the establishment of transboundary water commissions could also facilitate cooperative solutions across jurisdictions. International treaties and agreements focused on water sharing and sustainable development are examples of potential future directions.
Role of Technology in Monitoring and Managing Groundwater Resources
Advanced technologies play a pivotal role in monitoring groundwater resources and managing their sustainable use. Remote sensing, geophysical surveys, and sophisticated hydrological models can provide real-time data on aquifer levels, recharge rates, and water quality. These data-driven insights can be instrumental in legal proceedings, enabling more accurate assessments of groundwater depletion impacts. For instance, real-time monitoring of well levels can help identify over-extraction issues early on, reducing the potential for protracted litigation.
Importance of Incorporating Scientific Data in Legal Proceedings
Scientific data is crucial for informing legal decisions on groundwater management. Expert testimony based on sound scientific principles can help courts understand the complex hydrological processes, evaluate the impacts of groundwater depletion, and formulate appropriate legal remedies. The inclusion of hydrological models, hydrogeological assessments, and scientific studies of aquifer systems in court proceedings can improve the accuracy and effectiveness of legal decisions.
Potential Future Challenges to Groundwater Resources
| Challenge | Description |
|---|---|
| Climate Change Impacts | Changes in precipitation patterns and increased droughts exacerbate groundwater depletion, demanding robust adaptation strategies in water resource management. |
| Population Growth and Urbanization | Increased demand for water resources in urban areas further strains groundwater supplies, leading to increased competition and potential conflicts. |
| Agricultural Intensification | Expanded agricultural practices, particularly irrigation, increase water demand and potentially deplete groundwater reserves. |
| Pollution and Contamination | Industrial and agricultural pollutants can contaminate groundwater resources, posing significant risks to human health and ecosystems. These issues often become intertwined with legal challenges related to groundwater depletion. |
| Lack of Data and Monitoring | Insufficient data on groundwater availability and quality in many regions hinders effective management and creates opportunities for disputes. |
Case Study Examples
Groundwater depletion is a complex issue with significant legal and practical implications. Understanding past cases, successful management programs, and the outcomes of unsuccessful ones is crucial for developing effective strategies for the future. These case studies provide valuable insights into the challenges and opportunities in managing this vital resource.The examples below illustrate the diverse range of challenges and outcomes associated with groundwater management.
They highlight the importance of considering local contexts, stakeholder perspectives, and the interplay between legal frameworks and practical implementation when addressing groundwater depletion.
Notable Groundwater Depletion Court Case: Ogallala Aquifer Litigation
The Ogallala Aquifer, a vast underground water source in the American Great Plains, has been the subject of numerous legal disputes over its depletion. These cases often involve farmers, ranchers, and municipalities competing for access to the water. A key case study is the complex litigation surrounding the over-allocation and depletion of the Ogallala Aquifer. This case demonstrates the significant challenges in balancing competing interests and implementing equitable solutions to ensure sustainable use of the shared resource.
The legal battles have focused on issues of water rights, allocation, and the responsibility of different stakeholders in managing the aquifer. The outcomes of these cases have varied, reflecting the intricate legal and political landscapes surrounding groundwater resources.
Successful Groundwater Management Program: The Israeli Water Management System
Israel has a long history of implementing innovative water management strategies. One of the most successful examples is the national water management system, which includes a network of desalination plants, wastewater recycling programs, and efficient irrigation techniques. These initiatives, coupled with stringent water-use regulations, have enabled Israel to effectively manage its limited water resources. The program emphasizes a comprehensive approach that integrates technological solutions with regulatory frameworks.
This approach emphasizes collaboration among various stakeholders, including government agencies, farmers, and industries. The system also incorporates monitoring and evaluation components, enabling adaptation and refinement of the strategies over time.
Unsuccessful Groundwater Management Program: The Aral Sea Disaster
The decline of the Aral Sea, a significant inland water body in Central Asia, serves as a stark example of the dangers of unsustainable groundwater management. The over-extraction of water for irrigation in the surrounding regions led to a dramatic reduction in the sea’s size and salinity levels, impacting local ecosystems, human health, and economies. This example underscores the importance of considering the broader environmental and societal impacts of groundwater depletion, beyond the immediate economic gains.
The unsustainable practices, coupled with a lack of integrated management, highlight the need for a holistic approach to water resource management that encompasses environmental protection, public health, and economic sustainability.
Legal and Practical Implications of a Groundwater Depletion Case Study
Groundwater depletion cases often involve complex legal issues, including water rights, property rights, and environmental protection. The practical implications are equally significant, impacting agricultural production, industrial activities, and the well-being of communities reliant on groundwater resources. Understanding the legal and practical implications is crucial for developing effective solutions. These implications extend to land use planning, economic development, and the overall sustainability of water resources.
Comparison of Case Studies
| Case Study | Success Factors | Failure Factors | Legal Implications | Practical Implications |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ogallala Aquifer Litigation | Detailed legal frameworks, multiple court decisions | Competing interests, complex legal procedures | Water rights allocation, legal precedent | Agricultural impacts, economic disparities |
| Israeli Water Management System | Integrated approach, desalination, wastewater recycling, efficient irrigation | Limited resources, high cost of implementation | Water allocation policies, environmental regulations | Economic development, improved public health |
| Aral Sea Disaster | None | Unsustainable irrigation practices, lack of integrated management, political issues | Environmental protection laws, weak enforcement | Ecosystem collapse, human health problems, economic losses |
Global Case Studies
Groundwater depletion, a pressing global issue, is increasingly sparking legal battles and prompting the need for robust regulatory frameworks. This section delves into specific case studies across different regions, highlighting the unique challenges and legal approaches employed to manage this critical resource. Understanding these diverse experiences is crucial for developing effective strategies to address groundwater depletion worldwide.
Groundwater aquifer depletion courts are a serious issue, with cases popping up across the globe. While these legal battles focus on vital water resources, it’s fascinating to consider how the intense focus on sports, like Anthony Kim’s LIV Golf Return A Detailed Look here , can sometimes distract from broader environmental concerns. Ultimately, though, these legal battles highlight the crucial need to protect our shared water resources for future generations.
Groundwater Depletion Litigation in the Central Valley of California
The Central Valley of California, a vital agricultural region, has faced significant groundwater depletion. Numerous lawsuits have been filed against water districts and agricultural users alleging excessive pumping and unsustainable practices. These cases often center on claims of violating water rights, impacting downstream users, and causing environmental damage. The legal battles highlight the complex interplay between water rights, agricultural needs, and environmental protection in regions heavily reliant on groundwater.
The legal framework in California, with its emphasis on prior appropriation, often dictates who has the right to use water, which has been a central point of contention in the ongoing disputes.
Groundwater Depletion Litigation in the North China Plain
The North China Plain, a major agricultural region in China, has experienced substantial groundwater depletion. This depletion is due to intensive agricultural practices and rapid urbanization. Groundwater depletion has led to land subsidence and decreased water quality, posing significant challenges to both agriculture and human health. The North China Plain’s experience emphasizes the broader implications of unsustainable water management on human well-being.
Government regulations, often focused on water quotas and agricultural efficiency measures, have been a subject of both praise and criticism for their effectiveness.
Unique Challenges in Managing Groundwater in Specific Regions
Managing groundwater effectively in diverse regions presents unique challenges. These challenges vary significantly based on factors such as climate, geology, population density, and legal frameworks. Climate change, for example, exacerbates existing problems in arid and semi-arid regions, where water scarcity is already a significant concern. The interaction of groundwater with surface water resources also adds complexity to management strategies.
Understanding these complexities is crucial for developing appropriate and sustainable solutions. Further, political and economic factors can significantly influence the ability to implement effective policies.
Legal Frameworks Used in Different Regions
Different regions employ various legal frameworks to manage groundwater. Some countries prioritize the concept of water as a public resource, while others emphasize private property rights related to water extraction. The legal framework in a region significantly influences the approach to groundwater management, the allocation of water rights, and the potential for legal disputes. These frameworks can range from comprehensive groundwater codes to more loosely defined regulations, leading to differing degrees of success in protecting this vital resource.
For instance, some regions utilize permits and licenses for water extraction, while others rely on customary water rights.
Comparison of Legal Frameworks, Groundwater aquifer depletion courts
| Region | Primary Legal Framework | Emphasis | Potential Challenges |
|---|---|---|---|
| California (USA) | Prior Appropriation | Prior use of water rights | Potential conflicts between historical users and newer demands |
| North China Plain (China) | Government quotas and regulations | State control over water resources | Enforcement challenges and potential for corruption |
| Australia (various states) | Groundwater Act and state legislation | Balanced use and protection | Variations in state-level frameworks |
| India | Water Acts and state-level regulations | Protection of water sources and equitable allocation | Complex water rights and often inadequate enforcement |
This table provides a simplified overview of varying legal approaches. Each region’s specific legal framework should be examined in detail to understand the nuances and implications of its application. Significant variations and complexities exist within each framework, making a comprehensive comparison challenging.
Closure: Groundwater Aquifer Depletion Courts
In conclusion, groundwater aquifer depletion courts represent a critical frontier in addressing water scarcity. The cases highlight the legal and practical challenges involved in managing shared water resources, underscoring the need for collaborative solutions and innovative approaches to sustainability. Ultimately, the outcomes of these cases will have a profound impact on the future of water resources worldwide.
FAQ Compilation
What are the most common arguments used in groundwater depletion court cases?
Common arguments often center around property rights, equitable allocation of water resources, and the responsibility of different stakeholders. Environmental impacts, economic consequences, and historical water usage patterns are also frequently cited.
How can technology be used to monitor and manage groundwater resources?
Technological advancements like remote sensing, groundwater modeling, and real-time monitoring systems can provide valuable data for assessing groundwater levels, identifying depletion patterns, and enabling more effective water management strategies.
What are the potential future challenges to groundwater resources?
Future challenges include climate change impacts on water availability, increased competition for water resources, and the need for more integrated and holistic approaches to water management.
What is the role of international agreements in managing shared groundwater resources?
International agreements play a crucial role in establishing frameworks for cooperation and dispute resolution regarding shared groundwater resources, particularly in transboundary aquifer systems.

