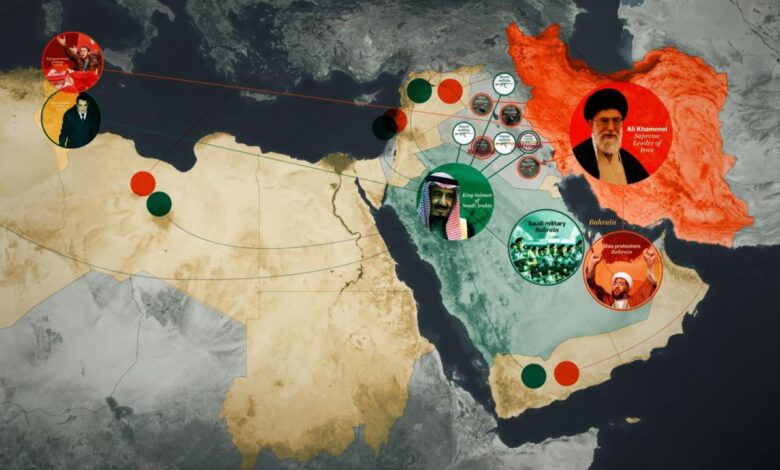
Iran War Middle East A Complex History
Iran war middle east is a deeply complex issue, stretching back through decades of conflict and shifting alliances. This post delves into the historical context, examining the roots of the tensions, the current state of affairs, regional impacts, international responses, and potential future scenarios. We’ll explore the key players, their motivations, and the economic and social consequences of these conflicts.
From the Iran-Iraq War to contemporary disputes, this exploration will illuminate the multifaceted nature of the conflicts in the Middle East involving Iran. We’ll examine the historical context, current issues, and the profound impact on the region and the world.
Historical Context of Conflict: Iran War Middle East
The Middle East, a region steeped in ancient history and diverse cultures, has witnessed countless conflicts throughout the ages. The relationship between Iran and its neighbors has been particularly fraught with tension, shaped by shifting power dynamics, religious differences, and competing geopolitical ambitions. Understanding this complex historical context is crucial to grasping the current state of affairs and the potential for future instability.The interplay of historical events and personalities has profoundly impacted the region’s trajectory.
The ongoing tensions in the Middle East surrounding the Iran war are complex and multifaceted. While global politics plays a significant role, it’s interesting to note that the career of a star like Chita Rivera, as detailed in chita rivera key moments career , highlights the broader human element amidst these geopolitical struggles. Ultimately, these conflicts impact the lives of individuals and ripple through society in ways that are often overlooked, and the Iran war is no exception.
From ancient empires to modern nation-states, the struggle for dominance and influence has been a defining characteristic of the Middle Eastern landscape. The legacy of these historical interactions continues to resonate in the present, shaping the political and social realities of the region.
Past Conflicts Involving Iran
Iran’s history is intertwined with the rise and fall of numerous empires in the Middle East. From the Achaemenid and Sasanian empires to the modern Islamic Republic, Iran has played a significant role in shaping the geopolitical landscape of the region. This role has often been characterized by periods of conflict and cooperation with neighboring powers.
- The Iran-Iraq War (1980-1988): This devastating conflict, sparked by territorial disputes and ideological differences, had a profound impact on the entire region. The war highlighted the volatile nature of the Middle East and the destructive consequences of prolonged conflict. The war’s devastating human and economic cost profoundly shaped the regional landscape, impacting political alliances and international relations.
- The Iran-Soviet Relations (1941-1988): The relationship between Iran and the Soviet Union was marked by periods of cooperation and intense rivalry. The Soviet Union’s expansionist policies during the Cold War were met with resistance from Iran, leading to strained relations and heightened regional tensions. This period of competition also involved proxy wars and covert operations, influencing the balance of power in the region.
- Conflicts with Regional Powers (Historically): Conflicts between Iran and neighboring countries, including Iraq, Afghanistan, and other nations, have been influenced by a complex web of historical, religious, and political factors. The influence of foreign powers and internal conflicts within these countries also played a major role in escalating tensions. These conflicts often had significant implications for regional stability and international relations.
Key Historical Figures and Events
Numerous historical figures and events have significantly shaped the relationship between Iran and other regional powers.
- Reza Shah Pahlavi: His modernization policies and efforts to assert Iranian independence often led to friction with neighboring countries and foreign powers, setting the stage for future conflicts. The historical relationship between Iran and foreign powers often involved complex interactions that were influenced by economic and political considerations.
- The 1979 Iranian Revolution: This revolution fundamentally altered Iran’s internal politics and foreign policy, leading to a shift in alliances and power dynamics in the region. The revolution’s impact on the Middle East and the world was profound, leading to a re-evaluation of existing political structures and relationships.
- The Rise of Radical Groups: The emergence of radical groups and their influence on Iranian foreign policy have complicated regional relationships. The rise of these groups further exacerbated tensions and altered the geopolitical landscape.
Evolving Geopolitical Landscape
The geopolitical landscape of the Middle East has been constantly evolving, and Iran’s role has been central to this transformation.
- The Cold War Era: The Cold War’s influence on the Middle East involved a complex interplay of regional actors and international powers. Iran’s position in this context was crucial, with its actions having significant implications for the balance of power in the region.
- Post-Cold War Era: The end of the Cold War led to significant shifts in the region’s power dynamics. Iran’s role in the post-Cold War era was marked by both cooperation and conflict, further shaping the region’s future.
The Iran-Iraq War: Historical Roots and Impact
The Iran-Iraq War was a protracted and devastating conflict with deep historical roots. It highlighted the complex interplay of factors that shaped the Middle East’s geopolitical landscape.
- Territorial Disputes: The war was, in part, a result of long-standing territorial disputes between Iran and Iraq. These disputes, rooted in historical rivalries, contributed significantly to the escalation of tensions.
- Ideological Differences: The ideological differences between the two countries also played a major role in escalating tensions and ultimately leading to war. These differences stemmed from differing political and religious viewpoints.
- Regional Implications: The Iran-Iraq War had far-reaching regional implications, influencing political alliances, economic stability, and regional power dynamics. The impact of the war was felt across the Middle East and beyond, affecting the geopolitical landscape.
Comparison of Middle Eastern Conflicts
| Conflict | Key Participants | Primary Causes | Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Iran-Iraq War | Iran, Iraq | Territorial disputes, ideological differences | Significant loss of life, economic devastation, regional instability |
| Arab-Israeli Conflicts | Arab nations, Israel | Territorial disputes, religious differences, political ideologies | Protracted conflicts, displacement of populations, regional tensions |
| Gulf War | Coalition forces, Iraq | Iraqi invasion of Kuwait | Military intervention, regional realignment |
Current Tensions and Issues
The Middle East, a region steeped in historical conflicts, continues to grapple with complex political and social issues. Iran, a significant player in the region, finds itself at the heart of many of these tensions. Recent events have exacerbated existing fault lines, leading to a heightened state of anxiety and uncertainty. Understanding the multifaceted nature of these conflicts requires a deep dive into the various contributing factors.The current geopolitical landscape in the Middle East is characterized by a complex interplay of regional and international actors.
Iran’s nuclear ambitions, its support for regional proxies, and its assertive foreign policy have sparked anxieties among its neighbors and beyond. This, coupled with long-standing historical grievances and cultural differences, creates a volatile mix. Examining the specific triggers and motivations behind these escalating tensions is crucial to comprehending the present situation.
Political and Social Issues Contributing to Tensions
Several political and social issues contribute to the current tensions in the Middle East, significantly involving Iran. These include regional rivalries, ideological differences, and the pursuit of strategic interests. The struggle for power and influence amongst various nations shapes the political landscape and fuels existing conflicts. Economic disparities and social inequalities also contribute to instability.
The ongoing tensions in the Middle East, particularly concerning the Iran war, are a complex issue. It’s easy to get caught up in the geopolitical dramas, but sometimes a fun distraction can help put things in perspective. Have you seen the recent news about the Godzilla Oppenheimer Heron Boy movie? godzilla oppenheimer heron boy might just be the weird, wonderful, and surprisingly insightful pop culture commentary we need right now.
Ultimately, though, the Iran war situation remains a serious issue with far-reaching consequences.
Recent Events Escalating Tensions
Recent developments have significantly escalated tensions. These include heightened rhetoric from various parties, military exercises, and specific incidents that have raised concerns about the possibility of wider conflict. Analyzing these events and their impact on the region is essential for understanding the current state of affairs. Examples of these events include cross-border skirmishes, cyberattacks, and accusations of interference in domestic affairs.
Role of External Actors
External actors play a significant role in the current conflicts. These actors, often with their own interests in the region, can exacerbate existing tensions or attempt to mediate conflicts. Their actions and motivations can be complex and often shrouded in ambiguity. The involvement of external actors can directly or indirectly affect the course of events and the outcomes of conflicts.
For example, the supply of arms and military support to various factions can escalate conflicts, while diplomatic efforts aim to de-escalate them.
Perspectives of Countries Involved
Different countries involved in the conflicts have varying perspectives. These perspectives are shaped by their own national interests, historical grievances, and ideological viewpoints. Analyzing these perspectives provides a more comprehensive understanding of the underlying dynamics. For example, some countries may view Iran’s actions as a threat to regional stability, while others may see them as a response to perceived threats.
The perspectives of the involved parties are often presented in a way that aligns with their national interests and priorities.
Economic Factors Fueling Conflicts
Economic factors are significant contributors to the ongoing conflicts. Competition for resources, particularly oil and gas, has been a recurring theme in the region. Economic disparities and grievances also play a significant role. The pursuit of economic power and influence further complicates the situation. For example, the control of vital resources like oil and gas can become a source of conflict and tension between countries.
Actors Involved in Current Conflicts
| Actor | Role | Motivation |
|---|---|---|
| Iran | Regional power, supporter of proxies | Preservation of regional influence, expansion of its sphere of influence |
| Saudi Arabia | Regional rival, staunch opponent of Iran | Preservation of regional dominance, countering Iranian influence |
| United States | External power, involved in regional security | Maintaining regional stability, countering perceived threats |
| Israel | Regional power, concerned about Iranian influence | Protecting national security, countering Iranian nuclear ambitions |
| Various regional proxies | Armed groups, militias | Fulfilling the agendas of their respective sponsors, securing local power |
Regional Impacts
The conflicts involving Iran have profound and multifaceted impacts extending far beyond the immediate battlefield. These repercussions reverberate through regional economies, political landscapes, and humanitarian efforts, creating a complex web of interconnected challenges. The ripple effects are felt by neighboring countries and the international community, highlighting the importance of understanding the broader consequences of these conflicts.The intricate interplay of political maneuvering, economic pressures, and humanitarian crises shapes the regional landscape, making it crucial to examine the diverse impacts across various facets of life.
This analysis delves into the humanitarian crises, refugee flows, economic consequences, and the broader implications for regional stability, trade, and political dynamics.
Humanitarian Crises and Refugee Flows
The conflicts have triggered significant humanitarian crises, particularly in the form of displacement and loss of life. Millions have been forced to flee their homes, seeking refuge in neighboring countries, creating a complex refugee situation. The strain on resources and infrastructure in host nations often exceeds their capacity, leading to potential instability and further challenges. For example, the Syrian civil war, while not directly linked to Iran’s conflict, created a massive refugee crisis, significantly impacting neighboring countries like Lebanon and Jordan.
These situations often necessitate international assistance to address the immediate needs and long-term solutions for affected populations.
Economic Consequences
The conflicts have substantial economic consequences, both directly and indirectly. Trade disruptions, sanctions, and decreased investment often cripple regional economies, impacting livelihoods and hindering development. Sanctions imposed on Iran, for example, have restricted access to international markets and financial systems, causing severe economic hardship. These sanctions also create a domino effect on neighboring countries reliant on trade with Iran.
Reduced economic activity can lead to unemployment, inflation, and social unrest.
Impact on Regional Stability, Iran war middle east
The conflicts significantly affect regional stability. Tensions, distrust, and proxy wars often escalate the risk of further conflicts, creating an environment of uncertainty and instability. The complex interplay of regional actors, including Iran, often creates volatile situations, threatening to destabilize the entire region. The history of proxy conflicts in the Middle East demonstrates the profound impact of these conflicts on regional stability.
Impact on Regional Trade and Economic Development
Regional trade and economic development are often hampered by conflict. Disruptions to supply chains, insecurity, and uncertainty regarding the future often discourage investment and limit economic growth. Reduced trade and investment flows can have a cascading effect, impacting economic development and the overall well-being of the region.
Impact on Regional Political Landscapes
The conflicts shape and reshape regional political landscapes. The rise of new political alliances, the strengthening of existing ones, and the emergence of new power dynamics are common occurrences in such situations. For example, the conflicts often influence the political alignment of neighboring countries, which in turn impacts the regional political order.
Table of Impacts on Different Countries
| Country | Humanitarian Impact | Economic Impact | Political Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Syria | Massive displacement, loss of life, strain on neighboring countries | Destruction of infrastructure, economic decline, decrease in trade | Rise of political factions, shift in regional alliances |
| Iraq | Refugee influx, internal displacement, loss of life | Economic disruption, decreased oil production, sanctions | Weakening of government, rise of extremist groups |
| Lebanon | Increased refugee burden, strain on resources, economic hardship | Reduced trade, decrease in investment, increased inflation | Political instability, social tensions |
| Jordan | Increased refugee burden, strain on resources, economic hardship | Reduced trade, decrease in investment, increased inflation | Political instability, social tensions |
International Relations and Responses

The conflicts involving Iran have deeply impacted international relations, prompting varied responses from the global community. These responses are often complex and multifaceted, influenced by geopolitical considerations, economic interests, and ideological differences. The international community’s approach to the situation is not uniform, with countries employing different strategies and exhibiting varying degrees of engagement.International actors have attempted to address the complexities of the conflicts through diplomatic efforts, sanctions, and other forms of pressure.
The effectiveness of these strategies, however, is often debatable, and their impact can be seen as both positive and negative, depending on the specific context and the perspectives of those involved.
International Community’s Response
The international community’s response to conflicts involving Iran has been characterized by a mix of diplomatic engagement, economic sanctions, and military deterrence. Different nations have employed diverse approaches, often based on their individual national interests and security concerns. The level of engagement varies significantly, with some countries taking a more proactive role in mediation and conflict resolution, while others remain more reserved.
Role of International Organizations
International organizations, such as the United Nations, have played a limited but significant role in mediating or resolving conflicts involving Iran. Their efforts have often focused on promoting dialogue and de-escalation, although their success has been mixed. The UN Security Council, for instance, has imposed sanctions on Iran in response to concerns about its nuclear program, but these actions have been met with varying degrees of support and opposition from member states.
The ongoing tensions in the Middle East, particularly concerning Iran’s role, are complex. Recent developments like the Israel-Hamas conflict and the critical hostage situation, highlighted in the latest ceasefire talks here , are undeniably impacting the region. However, Iran’s influence remains a significant factor in the larger geopolitical landscape of the Middle East.
Approaches of Different Countries
Different countries have adopted diverse approaches to address the conflicts involving Iran. Some nations, primarily those with strong economic interests in the region, have employed economic sanctions to pressure Iran’s government. Others have prioritized diplomatic engagement, seeking dialogue and negotiation to resolve outstanding issues. The specific approach often depends on the country’s own foreign policy priorities, regional alliances, and economic ties with the region.
The ongoing conflict in the Middle East, particularly concerning Iran, is a complex issue with far-reaching consequences. While global attention often focuses on geopolitical tensions, it’s important to remember that these conflicts can significantly impact daily life, especially in the region. In contrast, initiatives like President Biden’s push for a renewed infrastructure decade in Wisconsin, as detailed in this CNN article , highlight a different kind of struggle for progress.
Ultimately, the challenges in the Middle East, and the responses to them, continue to be crucial topics demanding attention and effective solutions.
Potential Consequences of Inaction or Intervention
The consequences of international inaction or intervention in conflicts involving Iran can be significant and far-reaching. Inaction could potentially embolden Iran’s actions and lead to further regional instability, while intervention could exacerbate tensions and trigger broader conflicts. These potential consequences underscore the need for careful consideration and a balanced approach to addressing the situation.
Strategies Employed by Major Powers
Major powers, including the United States, Russia, and China, have employed distinct strategies in dealing with the Iranian conflicts. The US has primarily relied on sanctions and military deterrence, while Russia has focused on maintaining diplomatic ties and leveraging its economic influence. China has pursued a more balanced approach, engaging in diplomacy while also seeking economic opportunities in the region.
Comparison of Foreign Policies
| Country | Foreign Policy Focus | Key Strategies | Examples |
|---|---|---|---|
| United States | Containing Iran’s influence and promoting regional stability | Sanctions, military presence, support for regional allies | Imposing sanctions on Iranian oil exports, military exercises in the region |
| Russia | Maintaining regional stability and expanding economic influence | Diplomacy, arms sales, economic partnerships | Negotiations with Iran, military cooperation agreements |
| China | Expanding economic interests and avoiding direct confrontation | Trade, investment, diplomatic engagement | Increasing trade with Iran, infrastructure projects |
Possible Future Scenarios
The volatile dynamics surrounding Iran’s role in the Middle East present a complex web of potential future scenarios. The interplay of regional ambitions, international pressures, and internal Iranian developments will significantly shape the trajectory of the conflicts and their consequences. Understanding these potential paths is crucial for anticipating the challenges and opportunities that lie ahead.The future trajectory of conflicts in the Middle East, particularly those involving Iran, hinges on a multitude of intertwined factors.
These include the evolving regional power dynamics, the shifting international alliances, and the internal political and social shifts within Iran itself. The outcomes will not only affect the stability of the region but also have significant implications for global security and energy markets.
Potential Outcomes and Their Impacts
The future of the Middle East involving Iran is likely to be characterized by a range of possible outcomes, each with its own set of consequences. These scenarios will not be mutually exclusive, and the reality will likely be a complex combination of factors.
- Escalation of Regional Conflicts: Continued tensions and proxy wars between Iran and its regional rivals could escalate into direct military confrontation. This scenario could lead to a significant humanitarian crisis, further destabilization of the region, and a potential spillover effect on neighboring countries. The 2006 Lebanon War, where Hezbollah, backed by Iran, clashed with Israel, serves as a precedent for the potential for regional conflict escalation.
- Negotiation and De-escalation: A negotiated settlement, potentially facilitated by international actors, could lead to a reduction in tensions and a de-escalation of hostilities. However, trust-building and implementation of agreements would be crucial for long-term success. The Iran nuclear deal (JCPOA), though ultimately unsuccessful, demonstrated the possibility of diplomatic solutions.
- Internal Iranian Instability: Significant internal political and social unrest within Iran could lead to regime change or a shift in its foreign policy. This scenario could bring about uncertainty in the region, affecting the balance of power. The Arab Spring uprisings in several countries are examples of how internal political instability can trigger significant regional changes.
- Regional Cooperation: Despite the existing tensions, regional cooperation, including joint initiatives on economic development and security, could create opportunities for de-escalation. The potential for such cooperation is significant, but overcoming historical distrust and political differences would be crucial. The Shanghai Cooperation Organisation (SCO) offers a potential model for regional cooperation, though its effectiveness in addressing complex conflicts remains to be seen.
Factors Influencing the Course of Conflicts
Various factors will influence the trajectory of conflicts involving Iran in the Middle East. These factors will intertwine and interact in complex ways, shaping the future of the region.
- International Relations: The involvement and actions of major global powers, such as the United States, Russia, and China, will play a significant role in shaping the dynamics. These powers have diverse interests and strategic objectives, which can either escalate or de-escalate conflicts. The role of international actors is crucial in setting the stage for future developments.
- Internal Iranian Dynamics: The internal political and social situation in Iran, including leadership transitions and shifts in public opinion, will significantly affect the country’s foreign policy. Internal developments can drastically shift the regional landscape.
- Regional Power Dynamics: The interplay of regional powers, such as Saudi Arabia, Turkey, and Israel, will also significantly influence the outcome of the conflicts. These powers have competing interests and alliances that can either exacerbate or mitigate tensions.
Potential Implications for Global Stability and Security
The future conflicts in the Middle East, involving Iran, could have significant implications for global stability and security.
- Energy Security: Disruptions in the Middle Eastern energy supply, potentially resulting from conflicts, could have a significant impact on global energy markets and economic stability. Disruptions to oil production and transportation routes can trigger global price fluctuations and economic instability.
- Refugee Crisis: Escalated conflicts could lead to large-scale refugee flows, placing a strain on neighboring countries and international aid organizations. Regional conflicts can create large-scale refugee movements and humanitarian crises.
- International Relations: The outcome of these conflicts could lead to shifts in global alliances and geopolitical dynamics. These shifts can impact global security and trade relations.
Table of Potential Outcomes and Impacts
| Potential Outcome | Possible Impacts |
|---|---|
| Escalation of Regional Conflicts | Humanitarian crisis, regional destabilization, spillover effects, potential for wider war |
| Negotiation and De-escalation | Reduced tensions, de-escalation of hostilities, potential for long-term stability |
| Internal Iranian Instability | Uncertainty in the region, shift in foreign policy, potential for regional power vacuum |
| Regional Cooperation | De-escalation, economic development, enhanced regional security |
Illustrative Examples
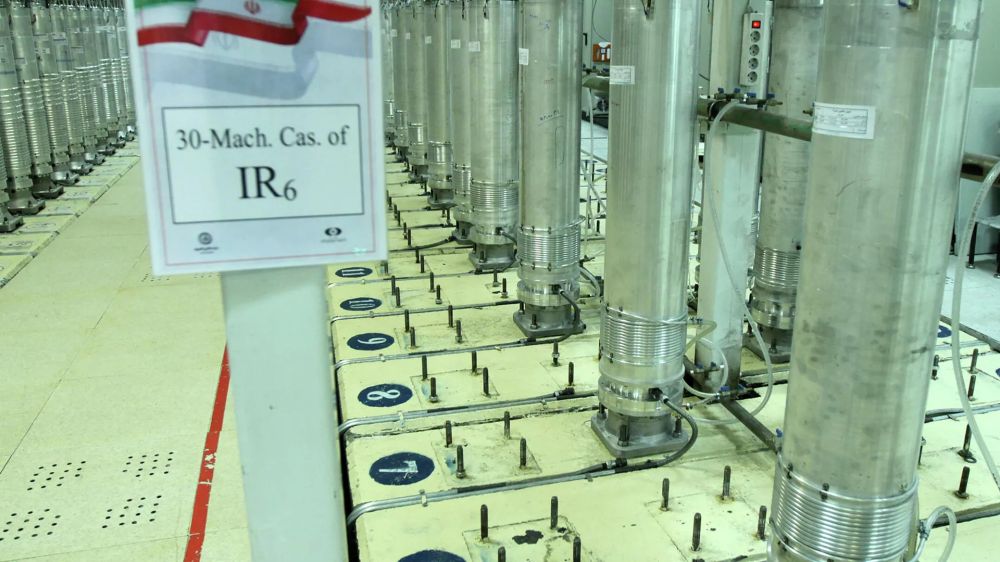

The Middle East’s intricate web of conflicts often involves Iran, creating a complex tapestry of regional and international relations. Examining specific conflicts provides valuable insights into the motivations, actors, and outcomes, shedding light on the enduring tensions and the potential for future instability. These examples highlight the interplay of political, economic, and social factors that shape the region’s trajectory.
The ongoing tensions surrounding the Iran war in the Middle East are undeniably complex. Understanding the political landscape is crucial, and that includes the upcoming Nevada caucus primary, which is a vital step in the US presidential election process. A great resource to learn more about the intricacies of this process is the Nevada caucus primary explainer.
Ultimately, these internal US political debates, while seemingly far removed, have implications for the geopolitical climate and the Iran war.
The Iran-Iraq War (1980-1988)
This protracted conflict, fueled by territorial disputes, ideological differences, and regional power struggles, exemplifies the destructive potential of regional conflicts involving Iran. Iraq, under Saddam Hussein, initiated the war, aiming to curb Iranian influence and expand its own regional dominance. Iran, seeking to project its revolutionary ideology and defend its borders, fought fiercely.
- Key Actors: Iraq, led by Saddam Hussein; Iran, under Ayatollah Khomeini.
- Motivations: Iraq sought to control the Shatt al-Arab waterway and contain Iran’s revolutionary influence. Iran aimed to defend its borders and export its Islamic revolution.
- Geopolitical Context: The war occurred amidst the Cold War’s proxy conflicts and the rise of Islamic fundamentalism. The conflict destabilized the region and drew in various regional and international actors.
- Economic Implications: The war inflicted immense economic damage on both countries, leading to significant human and material losses. The war severely hampered economic development and led to international sanctions on both nations.
- Outcomes: The war resulted in millions of casualties and widespread devastation. It ended with no clear victor and left a legacy of deep-seated animosity between the two nations. The war crippled both economies, leading to years of recovery and further instability.
The Iran-Saudi Arabia Proxy Conflicts (2010-Present)
The competition between Iran and Saudi Arabia for regional influence has manifested in various conflicts and proxy wars, especially in Yemen, Syria, and Iraq. This competition often takes the form of supporting opposing sides in civil conflicts, thereby exacerbating regional tensions.
- Key Actors: Iran, supporting Shia militias; Saudi Arabia, backing Sunni groups.
- Motivations: Both countries are vying for regional dominance and fear the other’s influence. This competition often reflects broader ideological and sectarian divides.
- Geopolitical Context: The rise of Islamic State (ISIS) and the ongoing Syrian Civil War provided fertile ground for these proxy conflicts. Regional alliances and rivalries further complicated the situation.
- Economic Implications: The conflicts in Yemen and Syria have caused widespread humanitarian crises and significantly disrupted economic activity in the region. These conflicts have led to significant displacement and hindered economic growth in the targeted countries.
- Outcomes: The conflicts have destabilized Yemen, Syria, and other regions, creating humanitarian crises and fueling further instability. These proxy wars have demonstrated the destructive power of competition for regional influence.
Table: Illustrative Examples of Conflicts in the Middle East
| Conflict | Years | Key Actors | Outcome Summary |
|---|---|---|---|
| Iran-Iraq War | 1980-1988 | Iran, Iraq | Millions of casualties, significant economic damage, no clear victor. |
| Iran-Saudi Arabia Proxy Conflicts | 2010-Present | Iran, Saudi Arabia (supporting opposing sides in conflicts) | Destabilization of Yemen, Syria, and other regions; humanitarian crises; economic disruption. |
| 2011 Iranian Protests | 2011 | Iranian government, protesters | Suppression of protests, significant political and social repercussions. |
Final Review
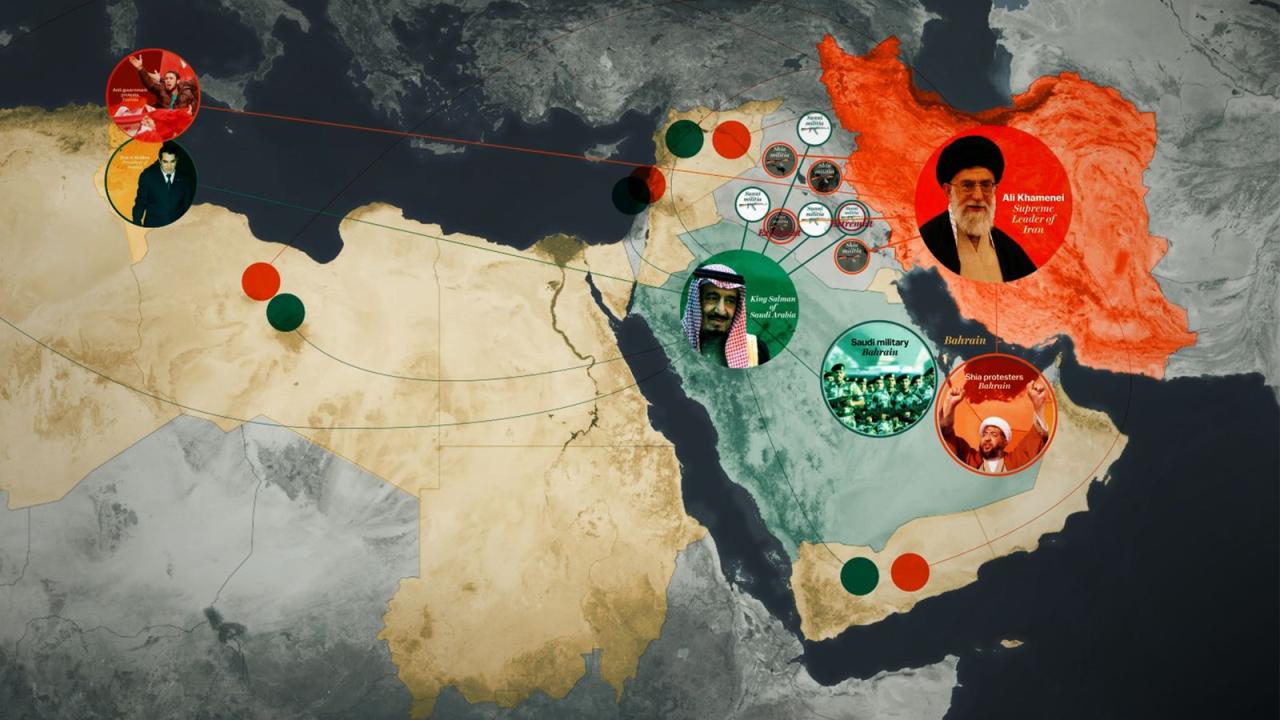
In conclusion, the conflicts involving Iran in the Middle East present a multifaceted challenge with deep historical roots. The interplay of geopolitical forces, economic factors, and the actions of various actors have shaped the current situation. The potential consequences for regional stability and global security are significant. Understanding the past, present, and potential futures of these conflicts is crucial for comprehending the complex dynamics of the region.
Question & Answer Hub
What are the key economic factors fueling the conflicts?
Resource competition, particularly oil and gas, plays a significant role. Economic sanctions imposed on Iran have also had a considerable impact on the region’s economic landscape, contributing to instability.
How do refugees impact the regional conflicts?
Mass refugee flows strain the resources and stability of neighboring countries, exacerbating existing tensions and contributing to humanitarian crises.
What is the role of international organizations in mediating the conflicts?
Various international organizations, such as the UN, have attempted mediation efforts, though with varying degrees of success. Their role is often complex and constrained by the political realities of the region.
What are some potential future scenarios for the conflicts?
Future scenarios range from continued conflict to potential de-escalation, depending on various factors including the actions of key actors and international responses. These outcomes will have significant implications for regional and global stability.






