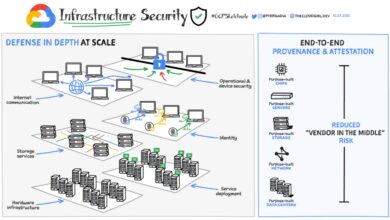
RISC-V China US Chip Security A Tightrope Walk
Risc v china united states chips security – RISC-V China United States chips security is a complex issue with global implications. This intricate web involves the rising adoption of the open-source RISC-V architecture, particularly in China, juxtaposed with the US government’s concerns about national security and export controls. The potential for both collaboration and competition between the two nations adds another layer of complexity to this already nuanced situation.
How will this new architecture shape the global semiconductor landscape, and what are the implications for trade relations between the US and China?
The emerging RISC-V architecture, designed for flexibility and customization, presents a powerful alternative to established architectures like ARM and x86. This open-source approach has attracted significant interest, especially in nations seeking to diversify their chip supply chains. However, the geopolitical implications of this adoption are undeniable, as the US government navigates its concerns about potential security risks and trade implications.
This discussion explores the factors driving this shift, examining the motivations behind adoption, the challenges posed by national security concerns, and the possible outcomes for the global chip industry.
RISC-V Architecture Overview
The RISC-V instruction set architecture (ISA) is gaining significant traction as an open-source alternative to established architectures like ARM and x86. Its open nature allows for customization and tailoring to specific needs, fostering innovation and competition in the semiconductor industry. This open-source model also encourages broader adoption and participation, potentially driving down costs and accelerating development cycles.The RISC-V ISA is designed with modularity in mind, allowing designers to select only the instructions needed for their application.
This flexibility is a key differentiator and caters to diverse requirements, from resource-constrained embedded systems to high-performance computing.
RISC-V Instruction Set Architecture
The RISC-V ISA is a modular and extensible architecture. This means it’s composed of several base ISAs, each with varying functionalities. This modular design allows for tailored implementations based on specific needs. The base instruction set is relatively small and simple, which translates to lower power consumption and potentially higher clock speeds in some cases. Furthermore, RISC-V offers a comprehensive set of extensions, including those for floating-point arithmetic, vector processing, and cryptography.
These extensions cater to a wide range of applications, from general-purpose computing to specialized domains like machine learning and signal processing.
Key Features and Benefits
RISC-V’s open-source nature is a key driver of its popularity. This openness allows developers to customize the architecture, create specialized extensions, and modify existing instructions to fit specific requirements. This contrasts with proprietary architectures, where modifications are often limited or require licensing fees. Moreover, the open-source nature fosters collaboration and innovation within the developer community, which accelerates the development of new tools, software, and hardware.
This collaborative environment has already resulted in a wide array of RISC-V-based processors and tools, signifying the architecture’s rapid adoption.
Comparison with Other Architectures
The following table presents a comparative analysis of RISC-V, ARM, and x86 architectures based on key performance metrics. It is important to note that specific implementations can vary significantly, affecting the actual performance.
| Metric | RISC-V | ARM | x86 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Power Consumption | Potentially lower, depending on implementation | Generally moderate | Generally higher, especially for high-performance implementations |
| Clock Speed | Potentially higher in specific low-power implementations | Generally high | Generally high, but varies significantly across implementations |
| Cost | Potentially lower due to open-source nature | Moderate, depending on licensing and implementation | Generally higher, especially for high-performance implementations |
| Customization | High, due to open-source nature | Moderate, with some licensing restrictions | Limited, proprietary architecture |
Potential Impact on the Global Semiconductor Landscape
The rise of RISC-V is expected to reshape the global semiconductor landscape. Its open-source nature and modularity could foster competition and innovation in processor design. This can lead to the emergence of specialized processors tailored to specific needs, potentially reducing reliance on a few dominant players in the industry. Furthermore, RISC-V’s adaptability to different applications could create new market opportunities for smaller companies, allowing them to compete more effectively with established players.
The ongoing debate around RISC-V in China, the US, and chip security is fascinating. It’s a complex issue, but the recent political climate, particularly with the trump trial judge campaign , seems to be influencing how these nations approach chip development. Ultimately, the future of RISC-V in the global chip market remains uncertain, but the political landscape certainly plays a significant role.
China’s Semiconductor Industry: Risc V China United States Chips Security
China’s semiconductor industry is rapidly evolving, driven by a strong government push for self-sufficiency and a growing domestic market. Facing limitations imposed by geopolitical tensions and technological restrictions, China aims to reduce its reliance on foreign chipmakers while fostering innovation and developing indigenous capabilities. This pursuit has led to significant investments in research, development, and manufacturing facilities, positioning China as a formidable player in the global semiconductor landscape.China’s ambitions extend beyond mere replication.
The country is actively working on developing cutting-edge technologies and creating its own intellectual property, particularly in areas like RISC-V architecture. This strategic approach reflects a long-term vision to achieve technological independence and bolster its economic competitiveness.
Government Policies and Initiatives
China’s government actively promotes the development of its semiconductor industry through a combination of financial incentives, strategic partnerships, and regulatory support. These initiatives are designed to encourage domestic companies, attract foreign investment in specific areas, and foster technological advancements. For example, substantial government funding is allocated to research and development, with a particular focus on critical areas like advanced chip design, manufacturing processes, and materials science.
Specific policies include tax breaks, subsidies, and grants targeting the semiconductor sector.
Key Chinese Companies Involved in RISC-V Adoption
Several Chinese companies have begun adopting the open-source RISC-V architecture, recognizing its potential to reduce reliance on foreign designs. This shift allows these companies to customize and adapt the architecture to their specific needs, contributing to innovation and reducing dependence on established proprietary architectures. Examples include companies involved in developing embedded systems, networking equipment, and IoT devices, who see RISC-V as a way to achieve higher performance and lower costs.
China’s Strategic Goals Regarding Chip Independence and Security
China’s pursuit of chip independence and security is a multifaceted strategy. The ultimate goal is to reduce reliance on foreign suppliers, ensuring the availability and security of critical components for domestic industries. This strategy is driven by concerns about potential disruptions to supply chains and the need to control vital technologies for national security. The development of indigenous design capabilities is seen as crucial to achieve this goal.
Major Players in China’s Semiconductor Sector
| Company Name | Focus Area | Key Strengths |
|---|---|---|
| SMIC (Semiconductor Manufacturing International Corporation) | Foundry services | One of the largest semiconductor foundries in China, with a focus on advanced process nodes. |
| TSMC (Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing Company) | Foundry services | Although primarily a Taiwanese company, TSMC has a presence in China and plays a role in China’s semiconductor ecosystem. |
| Huawei | Telecommunications equipment, consumer electronics | Huawei is a major player in the Chinese tech sector, integrating chips into its products and developing in-house solutions. |
| BYD | Electric vehicles, battery technology | BYD is a significant player in electric vehicles, emphasizing in-house chip design and development for automotive applications. |
| JD.com | E-commerce | JD.com has expanded its involvement in the semiconductor space through investments and partnerships, aiming to improve supply chain resilience and product development. |
US Semiconductor Industry and National Security
The US semiconductor industry plays a critical role in the global economy and national security. Its dominance in chip design and manufacturing has long been a source of technological strength, but recent geopolitical shifts and the rise of competitors like China have prompted increased scrutiny of the sector’s vulnerability. This scrutiny has led to government intervention aimed at bolstering domestic capabilities and safeguarding national interests.
US Government Stance on Semiconductor Technology
The US government recognizes the strategic importance of semiconductor technology. The industry’s role in defense, communications, and countless consumer products necessitates safeguarding its domestic capabilities. This has manifested in various policies and initiatives, including subsidies for research and development, export controls, and investments in domestic manufacturing. The goal is to ensure a robust and secure supply chain for essential semiconductor components.
US Export Control Regulations
US export control regulations aim to manage the flow of sensitive semiconductor technology to foreign entities, particularly those perceived as posing a national security risk. These regulations are complex and subject to frequent revisions, encompassing various categories of semiconductors, design tools, and associated technologies. These controls have significant implications for the development and deployment of RISC-V, particularly in countries with close relationships to, or with interests in, adversarial nations.
The regulations affect the ability of US companies to freely share designs, technology, and know-how.
Role of US Companies in the Global Semiconductor Supply Chain
US companies are integral to the global semiconductor supply chain. They dominate design, manufacturing, and distribution of advanced chips. Their presence in numerous countries and their influence in establishing industry standards ensure a degree of global control and influence over the technology. However, this intricate network of relationships and dependencies also creates potential vulnerabilities if not managed carefully.
The reliance on specific US companies can create bottlenecks or expose the global supply chain to risks.
The RISC-V chip architecture is heating up the debate about China, the US, and global chip security. It’s a complex issue, like trying to recreate Gordon Ramsay’s culinary precision in a kitchen with faulty equipment. Gordon Ramsay’s next-level chef approach demands impeccable technique, just as the race to dominate chip technology requires robust security measures. Ultimately, the competition over RISC-V chips will undoubtedly shape the future of global technology and the security landscape.
US Government Funding and Support for Semiconductor Research and Development, Risc v china united states chips security
The US government has significantly increased its funding and support for semiconductor research and development in recent years. This reflects a growing recognition of the sector’s strategic importance. These initiatives are aimed at fostering innovation, strengthening domestic capabilities, and mitigating reliance on foreign suppliers.
The US-China chip war is heating up, with RISC-V gaining traction as a potential alternative to traditional designs. This competition isn’t just about tech; it’s also about national security. Meanwhile, the stunning spectacle of snow polo in St. Moritz, a tradition deeply intertwined with the alpine environment, starkly highlights the impacts of climate change, as seen in snow polo st moritz climate change.
Ultimately, the race to develop secure and reliable chip technology has global implications, much like the delicate balance of the natural world we’re witnessing in the Alps.
| Program | Funding (estimated) | Focus Area |
|---|---|---|
| CHIPS Act | Billions of dollars | Funding for domestic semiconductor manufacturing facilities and research. |
| National Semiconductor Technology Center | Millions of dollars | Supporting fundamental research and development of advanced semiconductor technologies. |
| Various government agencies (e.g., NSF, DARPA) | Multiple funding sources | Supporting specific research projects, materials science, and advanced chip designs. |
RISC-V Adoption in China and the US
The rise of RISC-V as an open-source instruction set architecture (ISA) presents a compelling opportunity for both China and the US. Its open nature allows for customization and potential cost savings, attracting interest from various sectors. However, the geopolitical landscape and differing regulatory environments introduce complexities in its adoption. This analysis delves into the motivations, challenges, and potential consequences of RISC-V adoption in these two key players in the global semiconductor industry.
Motivations for RISC-V Adoption
China and the US have distinct motivations for embracing RISC-V. For China, a crucial factor is the desire to reduce reliance on foreign semiconductor technologies. This is driven by concerns about potential supply chain disruptions and technology restrictions. The open nature of RISC-V also provides a platform for developing customized chips tailored to specific needs. In contrast, the US is drawn to RISC-V’s potential to foster innovation and competition in the semiconductor sector, diversifying supply chains and countering potential threats.
Regulatory Environments for RISC-V Adoption
The regulatory landscape significantly impacts RISC-V adoption. China’s regulatory environment is characterized by increasing emphasis on domestic semiconductor development, with incentives and support for indigenous innovation. However, stringent export controls and security reviews may also apply. The US, on the other hand, maintains a more market-driven approach, although national security concerns influence regulatory decisions, potentially leading to export restrictions or security audits.
Security Concerns
Security is a paramount concern for both countries. RISC-V’s open-source nature raises concerns about potential vulnerabilities that could be exploited. China may be particularly wary of foreign entities gaining access to its proprietary designs or sensitive data. Similarly, the US may face concerns about potential backdoors or malicious code introduced into RISC-V designs. The need for robust security protocols and rigorous vetting processes is paramount for both nations.
Collaboration and Competition
Collaboration between the US and China in RISC-V development could foster innovation and accelerate progress. Joint research and development efforts could lead to improved security and performance. However, competition remains a significant factor, especially in the context of national security concerns. Each country might prioritize its own needs and interests, potentially leading to divergent development paths.
Potential Benefits and Drawbacks of RISC-V Adoption
| Country | Potential Benefits | Potential Drawbacks |
|---|---|---|
| China | Reduced reliance on foreign technology, fostering domestic innovation, customized chips for specific needs, potential cost savings. | Security concerns related to open-source nature, potential for vulnerabilities, stringent regulatory requirements, export controls. |
| US | Fostering innovation and competition in the semiconductor sector, diversifying supply chains, countering potential threats, potential for collaboration. | National security concerns related to foreign access to designs, potential vulnerabilities in open-source designs, regulatory hurdles. |
Global Chip Security Concerns
The global semiconductor industry faces mounting security concerns, driven by the increasing complexity and interconnectedness of modern chips. Vulnerabilities in these components can have far-reaching consequences, impacting everything from national security to economic stability. Understanding these threats and implementing robust mitigation strategies is crucial for maintaining trust and resilience in the global technological ecosystem.The reliance on sophisticated integrated circuits for critical infrastructure and everyday devices makes chip security paramount.
A single vulnerability can have cascading effects, potentially compromising sensitive data, disrupting essential services, or even enabling malicious actors to gain unauthorized access to systems. This necessitates a proactive approach to identify, assess, and address these vulnerabilities before they can be exploited.
Potential Risks of Relying on Specific Chip Architectures
Specific chip architectures, while offering performance advantages, can introduce vulnerabilities if not designed with security in mind. Proprietary designs, especially those used in sensitive applications, might lack transparency and independent verification, potentially leading to unforeseen vulnerabilities. A lack of scrutiny can also allow vulnerabilities to remain unaddressed for extended periods, increasing the risk of exploitation.
The RISC-V chip architecture is heating up the debate in China and the US, particularly regarding security concerns in the semiconductor industry. A fascinating parallel exists in the world of art with the innovative work of Cauleen Smith, a Los Angeles-based artist, whose vibrant and thought-provoking pieces explore the very nature of human connection. This dynamic interplay of innovation and security underscores the complex interplay of technology and creativity in the modern world.
The implications of RISC-V in the global chip race, and the potential for conflict, remain significant.
Importance of Open-Source Hardware in Ensuring Security
Open-source hardware (OSH) fosters collaboration and scrutiny, making it easier to identify and address potential vulnerabilities. The collaborative nature of open-source development allows multiple developers to review the design, potentially uncovering vulnerabilities that would remain hidden in a proprietary design. This enhanced scrutiny contributes to a more secure and resilient overall system.
Role of International Standards and Regulations in Promoting Chip Security
International standards and regulations play a critical role in promoting a standardized approach to chip security. These frameworks provide guidelines and best practices, ensuring a level playing field for developers and promoting a common understanding of security protocols. This facilitates a more consistent and secure approach to chip design, production, and implementation across different countries and industries. Standardized methodologies also facilitate efficient vulnerability detection and reporting.
Potential Chip Vulnerabilities and Mitigation Strategies
| Potential Chip Vulnerability | Mitigation Strategy |
|---|---|
| Supply Chain Attacks: Malicious actors introducing compromised components into the supply chain. | Robust supply chain security measures, including rigorous vendor vetting, enhanced authentication procedures, and diverse sourcing strategies. |
| Side-Channel Attacks: Exploiting information leakage from unintended channels, such as power consumption or electromagnetic emissions. | Employing techniques like masking and randomization to reduce the leakage of sensitive information. This includes designing hardware with reduced power consumption, employing countermeasures to protect against electromagnetic emissions, and using advanced cryptographic techniques. |
| Hardware Trojans: Malicious code embedded within the chip design itself. | Thorough design reviews, independent verification, and advanced security testing methodologies. These can include formal verification techniques, as well as specialized hardware scanning tools, and advanced security auditing. |
| Software Vulnerabilities in Chip Drivers/Firmware: Exploitable weaknesses in the software controlling the chip. | Implementing robust software development life cycle (SDLC) practices, rigorous testing, and timely security patches. This includes code reviews, penetration testing, and proactive vulnerability management. |
Impact on Global Trade
The rise of RISC-V as an open-source instruction set architecture (ISA) presents both opportunities and challenges for global trade, particularly between the US and China. The potential for standardization and collaboration around this architecture could foster new partnerships, but the sensitive nature of semiconductor technology and the existing geopolitical tensions create a complex environment. This section will explore the potential impacts on trade relations, focusing on potential trade disputes, the role of international organizations, and the crucial role of intellectual property rights.
Potential Trade Disputes
The adoption of RISC-V by both US and Chinese companies could lead to disputes over intellectual property, especially if a specific design or enhancement is deemed proprietary by one nation. For example, a US company might claim that a particular RISC-V core developed by a Chinese company infringes on a US patent. Conversely, a Chinese company could argue that a US company’s RISC-V implementation uses a standard component that’s part of the open-source architecture.
These disputes could escalate into trade barriers or restrictions, potentially impacting the broader global chip supply chain.
Role of International Organizations in Managing Trade Disputes
International organizations, such as the World Trade Organization (WTO), play a critical role in mediating trade disputes. The WTO’s dispute settlement mechanism provides a framework for resolving trade conflicts, including those involving intellectual property rights and technology transfer. Their involvement in adjudicating RISC-V-related disputes could be essential in preventing escalations and ensuring a fair playing field for all participants.
Intellectual Property Rights in RISC-V Chips
Intellectual property rights are paramount in the development and deployment of RISC-V chips. While RISC-V is open-source, the modifications, optimizations, and extensions made to the base architecture are often proprietary. This creates a situation where the underlying RISC-V ISA is freely available, but specific implementations may be protected by patents or copyrights. Understanding and enforcing these rights will be crucial to avoid disputes and ensure innovation.
Potential Scenarios of Global Chip Supply Chain Disruptions
The global chip supply chain is intricate and highly interconnected. Disruptions can have significant ripple effects across various industries. The adoption of RISC-V may introduce new vulnerabilities, particularly if it’s not widely adopted across the supply chain.
| Scenario | Description | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Increased US-China Tensions | Heightened geopolitical tensions between the US and China could lead to restrictions on technology transfer and trade, potentially affecting the development and deployment of RISC-V chips. | Disruptions in the flow of materials and components, and possibly a decline in the pace of innovation. |
| Intellectual Property Disputes | Disagreements over intellectual property rights related to RISC-V implementations could escalate into trade disputes. | Imposition of tariffs or trade restrictions on specific RISC-V chip products. |
| Standardization Issues | Lack of standardized design practices within the RISC-V community could lead to incompatibility issues between different chips, potentially causing problems for supply chains. | Increased costs and delays in chip production and integration, and a possible shift to alternative architectures. |
| Cybersecurity Concerns | The open-source nature of RISC-V could introduce new vulnerabilities to the supply chain, if not carefully managed. | Increased risk of cyberattacks and data breaches, possibly impacting critical infrastructure. |
Future Trends and Implications
The future of RISC-V hinges on its ability to adapt to evolving technological landscapes and address the security concerns inherent in complex systems. This section examines potential trends in RISC-V’s development, the impact of emerging technologies, and the long-term implications for the global economy and security. The adoption of RISC-V is poised to significantly alter the chip design landscape, creating both opportunities and challenges.The increasing demand for specialized processors for artificial intelligence, machine learning, and other emerging applications is likely to drive further innovation in RISC-V architecture.
The ongoing debate around RISC-V, China, and the US chip security landscape is fascinating. A crucial aspect is the potential impact of the upcoming Taiwan election, specifically the Democratic Progressive Party’s (DPP) stance on these issues. Taiwan election democratic progressive party results could significantly influence the geopolitical dynamics surrounding semiconductor technology. Ultimately, the RISC-V movement and the US-China chip rivalry remain complex and uncertain, with many factors at play.
This evolution is crucial for ensuring that the architecture remains competitive and relevant in the face of ongoing advancements.
Potential Future Trends in RISC-V Development
RISC-V’s open-source nature allows for rapid customization and adaptation to diverse needs. This flexibility is a key driver of its potential growth. Several key trends are anticipated:
- Increased Customization and Specialization: RISC-V’s open-source nature facilitates the creation of specialized processors tailored to specific tasks, such as AI acceleration or high-performance computing. This adaptability is crucial for meeting the unique demands of emerging applications and will drive the growth of diverse RISC-V-based systems.
- Integration with Emerging Technologies: The integration of RISC-V with emerging technologies like quantum computing, neuromorphic computing, and edge computing will be critical for its future success. The architecture’s adaptability is a crucial factor in its ability to seamlessly integrate with these advancements.
- Enhanced Security Features: As reliance on embedded systems grows, security vulnerabilities become a critical concern. RISC-V architectures will likely incorporate advanced security features, such as hardware-based security modules and trusted execution environments, to mitigate these risks. This trend reflects the growing need for secure and reliable systems.
Impact of Emerging Technologies on RISC-V
Emerging technologies are rapidly transforming the landscape of computing and communications, which will profoundly affect the RISC-V architecture. These include:
- AI Acceleration: The increasing demand for AI processing power will necessitate specialized RISC-V processors optimized for AI tasks. This specialization will drive the development of efficient and powerful AI-specific architectures.
- Edge Computing: The rise of edge computing will lead to a greater demand for low-power, energy-efficient RISC-V processors. This will further drive the development of specialized architectures designed for edge devices.
- Quantum Computing: RISC-V could potentially play a role in the development of quantum computing hardware, particularly in areas like quantum simulation and algorithm development. This potential role is still largely unexplored but offers intriguing possibilities.
Potential Long-Term Implications for the Global Economy and Security
The adoption of RISC-V could have profound effects on the global economy and security landscape.
- Economic Diversification: The rise of RISC-V could lead to greater economic diversification in chip design and manufacturing, particularly in regions outside the traditional powerhouses of the semiconductor industry.
- Enhanced Security Posture: The adoption of RISC-V’s open-source nature and security-focused designs can foster greater trust in global supply chains, contributing to a more secure and reliable global infrastructure.
- Global Competition: The shift towards open-source architectures could lead to increased competition and innovation in the semiconductor industry, ultimately benefiting consumers and driving technological advancement.
Predictions about the Evolution of Chip Architecture and Security
Future chip architecture will likely see a greater emphasis on specialization, with processors optimized for specific tasks such as AI or edge computing. Security will become an integral part of the design process, moving beyond traditional software-based solutions to include hardware-based security measures.
“The evolution of chip architecture will be driven by the need for specialization and enhanced security.”
Closing Notes
In conclusion, the interplay of RISC-V, China, and the United States in the semiconductor industry is a dynamic and multifaceted issue. The potential for both collaboration and competition is significant, with the outcome depending heavily on how various stakeholders navigate the complexities of security concerns, trade relations, and intellectual property rights. The future of chip architecture and the global economy will undoubtedly be shaped by this evolution, highlighting the critical need for clear communication and cooperation to mitigate potential risks.
Essential Questionnaire
What are some potential security vulnerabilities in RISC-V chips?
RISC-V, like any other architecture, is susceptible to vulnerabilities. However, its open-source nature allows for faster identification and patching of potential flaws, but the lack of stringent standardization can also lead to inconsistencies in implementation and security protocols across different vendors. The specific vulnerabilities will depend on the implementation and use cases.
How might the US export controls affect the development of RISC-V chips in China?
US export controls on certain technologies could hinder China’s access to advanced components or tools necessary for the development of specific RISC-V chips. This could slow down the adoption of RISC-V and potentially limit its applicability for specific applications requiring advanced technology.
What role do international standards play in promoting chip security?
International standards provide a framework for security best practices and help ensure consistency in chip design and implementation. This can reduce the risk of vulnerabilities and promote interoperability, but achieving widespread adoption and enforcement of these standards can be challenging.