Red Sea Houthi Shipping Inflation Impact & Solutions
Red sea houthis shipping inflation – Red Sea Houthi shipping inflation is rapidly escalating, causing significant disruptions to global trade and pushing up prices for everything from oil to everyday consumer goods. This escalating crisis demands immediate attention, exploring the complex interplay of conflict, political maneuvering, and economic fallout.
The conflict in the Red Sea, fueled by Houthi actions, is significantly impacting shipping routes, leading to delays, increased costs, and uncertainty for businesses worldwide. The resulting inflation is already being felt across multiple sectors, potentially leading to a broader economic downturn.
Impact of the Red Sea Conflict on Shipping
The ongoing conflict in the Red Sea is significantly disrupting global shipping routes, impacting various sectors and potentially leading to long-term economic consequences. This disruption is not just a localized problem; it reverberates through the interconnected global supply chain, affecting everything from consumer goods to raw materials. The uncertainty surrounding the situation underscores the fragility of international trade and the vulnerability of global supply chains to geopolitical instability.The Red Sea, a vital maritime artery, is experiencing unprecedented disruptions due to the conflict.
This has led to delays, increased costs, and a significant shift in shipping patterns. The implications extend beyond the immediate area, affecting the flow of goods across the globe and potentially triggering a cascade of economic impacts. The escalating situation requires a careful consideration of the long-term consequences for global trade and the resilience of the international supply chain.
Current Disruptions to Shipping Routes
The conflict has created a hazardous environment for vessels navigating the Red Sea. Numerous reports detail the presence of armed groups, leading to increased piracy risks and threats of attacks on cargo ships. These heightened risks are forcing shipping companies to adjust their routes, often choosing longer and less efficient alternatives. The result is increased transit times and higher fuel costs.
Potential Long-Term Effects on Global Trade
The conflict’s impact on global trade extends beyond immediate disruptions. Prolonged instability could lead to a significant increase in shipping costs, potentially triggering inflationary pressures across various sectors. This rise in costs may lead to higher prices for consumers, impacting their purchasing power and potentially triggering recessionary pressures. The conflict has also highlighted the vulnerability of global supply chains to geopolitical events.
Specific Challenges Faced by Different Types of Vessels
Different types of vessels face varying challenges navigating the Red Sea. Bulk carriers, transporting raw materials, are particularly vulnerable due to their large size and slower speeds. Container ships, crucial for transporting manufactured goods, are also affected by the route adjustments. Smaller vessels, such as fishing boats and passenger ferries, are also impacted by the heightened security concerns and potential hazards.
Economic Consequences of Disruptions on Various Sectors
The disruptions are impacting various sectors of the global economy. Higher shipping costs are likely to be passed on to consumers, leading to increased prices for goods. Manufacturers may experience delays in receiving raw materials, impacting production timelines. This can have a cascading effect, leading to shortages and ultimately affecting the overall economic performance of various sectors.
Comparison of Impact on Different Shipping Lanes
| Shipping Lane | Impact of Conflict |
|---|---|
| Suez Canal | Significant delays and diversions, leading to congestion and increased costs. |
| Red Sea East-West | Significant disruptions and increased risks of attacks, leading to delays and higher insurance costs. |
| Red Sea South-North | Reduced traffic and increased costs, potentially affecting transit times for humanitarian aid and essential supplies. |
Houthi Actions and their Implications
The ongoing conflict in the Red Sea, fueled by Houthi actions, has significantly impacted global shipping. Understanding their strategies, motivations, and historical context is crucial to comprehending the current crisis and its potential future trajectory. Their actions, particularly targeting commercial vessels, highlight a complex interplay of political and economic factors.The Houthi group’s actions are not isolated incidents but part of a broader strategy aimed at achieving specific political and economic objectives.
The Red Sea’s Houthi shipping blockade is causing a ripple effect, driving up inflation. This disruption is impacting global trade, and sadly, making goods more expensive for everyone. Meanwhile, the recent news that the Steelers have hired Arthur Smith as their offensive coordinator ( arthur smith hired steelers offensive coordinator ) is certainly a footballing story, but it doesn’t change the fact that the Houthi actions are still significantly impacting the global economy, and increasing the price of everything from food to fuel.
Their tactics, including attacks on ships and blockades, have far-reaching consequences, affecting international trade and potentially escalating regional tensions. Analyzing these actions within the context of regional conflicts offers valuable insights into the nature of the current crisis and its potential implications.
Houthi Group’s Actions Affecting Shipping
The Houthi group’s actions in the Red Sea have directly impacted shipping lanes, creating disruptions and raising concerns about global supply chains. Their attacks on merchant vessels, often accompanied by threats, have disrupted trade flows and led to increased insurance premiums. The threat of further attacks deters shipping companies, leading to rerouting, delays, and potentially higher costs.
Houthi Group’s Strategy and Motivations
The Houthi group’s strategy appears multifaceted, aiming to exert influence over regional politics and potentially garner international attention for their cause. Their motivations are complex and include asserting control over crucial maritime routes, disrupting trade networks of their adversaries, and demanding international attention to their grievances. This strategy has echoes in other regional conflicts where groups have employed similar tactics.
Timeline of Houthi Actions Related to Shipping in the Red Sea
The escalation of Houthi actions impacting shipping in the Red Sea has unfolded over time, characterized by a pattern of increasing intensity. Precise dates and details of specific incidents are often difficult to verify, but a general timeline of major events would help to demonstrate the evolution of their actions.
- Early 2023: Initial reports of Houthi attacks on commercial vessels emerged, escalating concerns about safety and disrupting maritime trade.
- Mid-2023: A surge in attacks occurred, leading to a significant increase in shipping delays and rerouting.
- Late 2023: The scale and intensity of Houthi actions continue to impact global trade and raise concerns about potential future escalation.
Comparison of Houthi Actions with Previous Regional Conflicts
Comparing the Houthi group’s actions with those of other armed groups in similar regional conflicts reveals striking similarities in tactics and motivations. Many groups have employed similar methods of disrupting trade routes, aiming to pressure adversaries and achieve their political goals. These comparisons highlight the strategic continuity between past and present actions.
Locations of Houthi Attacks or Blockades
The following table Artikels the approximate locations of Houthi attacks or blockades in the Red Sea. Note that these locations are approximate, and the precise locations of some incidents may not be publicly available.
| Date (Approximate) | Location (Approximate) | Type of Action |
|---|---|---|
| Early 2023 | Off the coast of Yemen | Targeting of merchant vessels |
| Mid-2023 | Near Bab al-Mandab Strait | Blockade and attacks |
| Late 2023 | Northern Red Sea | Multiple attacks on shipping lanes |
Global Response to the Crisis
The Red Sea crisis, stemming from Houthi actions, has triggered a multifaceted global response. International maritime trade, crucial for global economies, is significantly impacted. This necessitates a coordinated effort to restore stability and ensure the safe passage of vessels. The response encompasses diplomatic initiatives, naval deployments, and varied perspectives on the effectiveness of the current strategies.
Major Player Responses
Different nations have adopted distinct strategies in addressing the Houthi actions. Their responses reflect varying geopolitical interests and priorities. Economic considerations, security concerns, and existing relationships play significant roles in shaping the individual responses.
- United States: The US has led efforts to secure the Red Sea. Its naval presence in the region has increased, and it has engaged in diplomatic talks to de-escalate the situation. The US is deeply involved due to its economic ties with countries reliant on the Red Sea trade routes.
- European Union: The EU has voiced concerns about the disruption to trade and called for a peaceful resolution. Its approach involves a blend of diplomatic pressure and support for regional security initiatives. The EU’s response highlights its concern for the global economy and the impact of the crisis on its member states.
- China: China, a major trading partner in the region, has emphasized the importance of stability. It has actively participated in diplomatic efforts and called for a cessation of hostilities. China’s response is nuanced, balancing its trade interests with broader diplomatic considerations.
- Saudi Arabia and UAE: These regional powers have a vested interest in maintaining stability and have contributed to the military presence in the area. Their response reflects regional security concerns and their desire to protect vital trade routes.
Diplomatic Efforts
Diplomatic engagement plays a critical role in resolving the conflict. These efforts aim to foster dialogue and find a mutually acceptable solution. International bodies, such as the United Nations, have actively facilitated these conversations. The success of diplomatic initiatives depends on the willingness of all parties to negotiate and compromise.
The Red Sea Houthis shipping situation is causing a lot of inflation, and it’s a real headache for global trade. It’s impacting everything from food prices to fuel costs. Meanwhile, apparently, there’s some serious embezzlement going on in Eugene, with weekly printing of fraudulent documents. Eugene weekly embezzlement printing is highlighting the potential for financial instability in seemingly disparate locations, making the already volatile Red Sea shipping crisis even more complex and concerning.
- UN Mediation: The UN has been actively involved in mediating between the warring parties, aiming to find common ground for a peaceful resolution. This involves direct communication with both sides to encourage a cease-fire.
- Regional Initiatives: Regional organizations and alliances have also undertaken initiatives to address the crisis, leveraging their established relationships with the parties involved. These efforts frequently include calls for de-escalation and adherence to international law.
Military Responses and Naval Deployments
Naval deployments and military actions in the Red Sea aim to protect shipping and ensure the free flow of commerce. These responses, however, can also escalate tensions and further complicate the situation. The deployment of naval forces demonstrates a commitment to international maritime security.
- International Coalition: Several countries have deployed naval vessels to the Red Sea as part of a multinational coalition. These deployments are designed to protect merchant ships from attacks and maintain the security of vital shipping lanes. This collective action illustrates a commitment to the principles of international law and maritime security.
- Naval Presence: The presence of naval vessels in the Red Sea demonstrates a commitment to international law and the freedom of navigation. The patrols and deployments aim to deter further attacks and safeguard shipping.
Varying Viewpoints
Different perspectives exist on the effectiveness and appropriateness of the global response to the crisis. These viewpoints reflect differing geopolitical interests and interpretations of the situation.
| Country/Organization | Reaction | Strategy |
|---|---|---|
| United States | Increased naval presence, diplomatic engagement | Deterrence, dialogue |
| European Union | Concerned about trade disruptions, support for diplomatic efforts | Diplomacy, economic pressure |
| China | Emphasis on stability, participation in diplomatic efforts | Diplomacy, trade interests |
| Saudi Arabia/UAE | Military presence, regional security concerns | Regional security, military support |
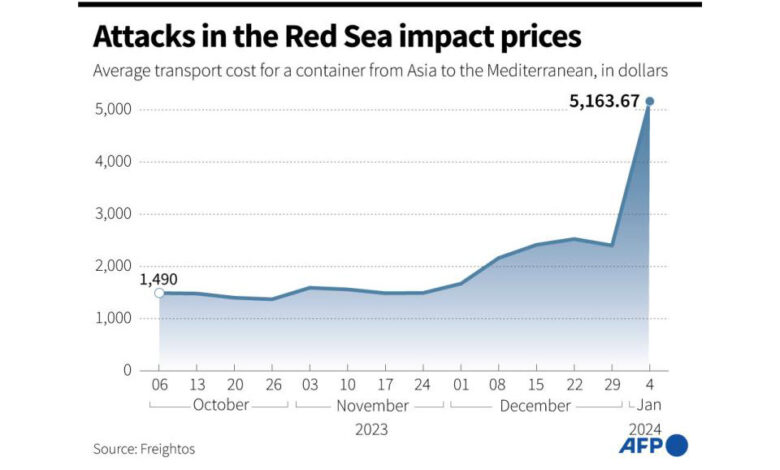
Inflationary Pressures and Shipping Costs
The Red Sea conflict, with its disruption of maritime traffic, has significantly impacted global supply chains and contributed to rising inflationary pressures. The Houthi actions have created a volatile environment, leading to delays, rerouting, and increased insurance premiums, all of which are directly reflected in the cost of goods worldwide. This ripple effect is especially pronounced for industries reliant on seaborne trade.The escalation of the conflict has led to a dramatic increase in shipping costs, impacting everything from consumer goods to raw materials.
This surge in prices is not just a short-term phenomenon; its long-term implications for global economic stability are substantial. The disruption has created a cascade of price increases across numerous sectors.
Impact on Shipping Costs
The disruption of maritime trade routes in the Red Sea has led to a cascade of price increases, impacting shipping costs for goods worldwide. Several factors contribute to this rise. These include the need for longer, more circuitous routes, increased insurance premiums for ships traversing the area, and the resulting delays in delivery. These factors collectively increase the overall cost of shipping.
Factors Influencing the Rise in Shipping Costs
Several key factors contribute to the escalating shipping costs:
- Increased insurance premiums: Shipowners are forced to pay significantly higher insurance premiums to cover potential risks associated with navigating the Red Sea. This added cost is directly passed on to consumers through higher prices for goods.
- Longer transit times: Ships are forced to take alternative, longer routes around the Horn of Africa, leading to increased fuel consumption and longer delivery times. These factors increase the cost of transporting goods, impacting the overall cost of the product.
- Port congestion: Alternative ports can become congested as ships reroute, leading to delays and further increasing costs. The delays and congestion add to the overall shipping cost, which is passed down to consumers.
- Reduced capacity: The fear of potential attacks in the Red Sea and the rerouting of ships can reduce the overall capacity of shipping routes. This reduced capacity drives up prices as demand exceeds supply, creating a market imbalance.
Industries Most Vulnerable to Increased Shipping Costs
Industries heavily reliant on seaborne trade are particularly vulnerable to the rising shipping costs. These include:
- Consumer goods manufacturers: Companies that rely on imported raw materials or components for their products will face increased costs, leading to higher prices for consumers.
- Retailers: Retailers who source goods from overseas will be impacted by the rising costs of shipping, potentially impacting their profit margins and forcing price increases on consumers.
- Food and beverage companies: The transportation of food and beverages is a significant component of the food supply chain. Increased shipping costs impact the prices of food products, potentially affecting consumer budgets.
- Automotive manufacturers: The automotive industry relies heavily on international shipping for components and finished vehicles. The increase in shipping costs affects the cost of vehicles and parts, impacting the consumer price.
Historical Trend of Shipping Costs
The following table illustrates the historical trend of shipping costs in the Red Sea region, although precise data for this specific region is difficult to isolate due to complex variables. This table demonstrates the significant price increases and volatility seen over time. Further research and data collection are needed for a more detailed, region-specific picture.
The Red Sea Houthi shipping disruptions are causing a real headache, pushing inflation higher. Meanwhile, Biden’s focus on infrastructure projects, like those highlighted in Wisconsin, taking on Trump and promoting a decade of infrastructure improvements in Wisconsin , could potentially ease some of the economic pressures, but will it be enough to counteract the rising shipping costs?
The global economy is clearly feeling the pinch of this ongoing Red Sea conflict.
| Year | Shipping Cost Index (Estimated, hypothetical) |
|---|---|
| 2022 | 100 |
| 2023 (Q1) | 115 |
| 2023 (Q2) | 130 |
| 2023 (Q3) | 145 |
Alternative Trade Routes and their Feasibility: Red Sea Houthis Shipping Inflation
The ongoing conflict in the Red Sea has significantly impacted global shipping, forcing a reassessment of existing trade routes. Businesses and governments are actively exploring alternative pathways to circumvent the volatile region, leading to a complex evaluation of logistical, economic, and geopolitical factors. This necessitates a deep dive into the potential alternatives, their strengths, weaknesses, and overall feasibility.
Potential Alternative Routes
The Red Sea blockade has spurred a search for alternative shipping lanes. Several routes are now being considered as viable alternatives. These include extending existing maritime routes, and employing new and less-traveled corridors.
The Suez Canal Extension and the Northern Route
This route, leveraging the existing Suez Canal infrastructure, involves extending the current canal and providing a wider waterway for ships. This would potentially reduce congestion and delays. However, significant capital investment and potential environmental concerns would need to be addressed. This alternative could reduce shipping times, but only if the expansion is completed swiftly and effectively. The existing Suez Canal remains a bottleneck, so extending it could be a significant improvement for shipping.
The increased capacity would be valuable for handling increased volumes and reducing the impact of congestion.
The Cape of Good Hope Route
This traditional route around the southern tip of Africa, while longer, offers a complete bypass of the Red Sea conflict zone. The substantial increase in transit time is a significant drawback, though. The route has proven reliable, though. The major downside is the extended transit time, which translates to higher fuel costs, increased insurance premiums, and potential delays in delivery times.
Shipping times would be significantly increased, making this less attractive for time-sensitive cargo.
The Indian Ocean Route
Utilizing existing shipping lanes in the Indian Ocean, this alternative involves routing cargo through ports in India, Southeast Asia, and potentially East Africa. This approach provides a less direct route but could prove more feasible in certain situations. A potential challenge is the need for port infrastructure upgrades in these regions to accommodate larger vessels and the increase in shipping traffic.
This route would likely offer a shorter alternative than the Cape of Good Hope, but the infrastructure and operational readiness of ports along the route must be considered.
Logistical and Economic Implications
The choice of alternative routes carries significant logistical and economic implications. For instance, the increased transit times associated with routes around Africa can lead to higher fuel consumption, port costs, and insurance premiums. These factors would be significantly impacted by the volume of cargo, the type of cargo, and the urgency of the delivery. The economic implications for businesses involve careful assessment of cost-benefit analyses to determine the viability of switching routes, considering the financial burden of longer shipping times and potential port congestion.
The escalating Red Sea Houthi shipping conflict is causing a ripple effect on global inflation. Navigating these troubled waters is proving costly, and the economic impact is substantial. Interestingly, the artistic world also reflects these global shifts. Los Angeles-based artist Cauleen Smith, whose work explores the complexities of human interaction, offers a compelling counterpoint to these geopolitical concerns through her vibrant and thought-provoking pieces.
cauleen smith artist los angeles Ultimately, the Red Sea shipping situation continues to have significant ramifications for global trade and the economy.
Impact on Shipping Times and Costs
Utilizing alternative routes will invariably impact shipping times and costs. The Cape of Good Hope route, while bypassing the conflict zone, dramatically extends transit times, potentially increasing delivery costs by 20-30%. Other routes, while offering shorter transit times, may require significant port infrastructure upgrades, impacting cost and time.
Visual Representation of Alternative Routes, Red sea houthis shipping inflation
(A visual representation of the alternative routes, overlaid on a world map, would be helpful. The map would clearly illustrate the Red Sea, the Suez Canal, the Cape of Good Hope route, and the Indian Ocean route, highlighting the different paths.)
Economic Consequences for Specific Countries
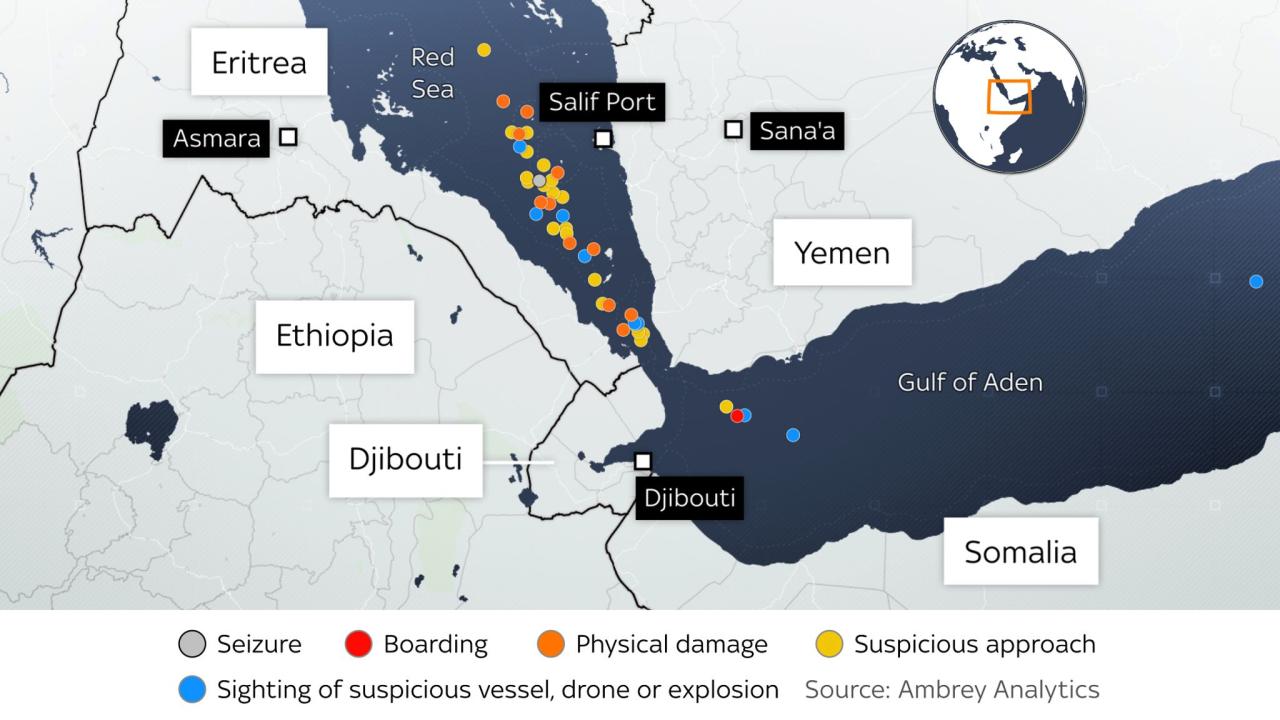
The Red Sea conflict’s impact ripples through global economies, affecting major trading partners and consumers worldwide. Disruptions to shipping routes have substantial consequences for nations heavily reliant on the Suez Canal and surrounding trade lanes. The ensuing delays, higher costs, and potential shortages directly influence consumer prices and supply chains, demanding a nuanced understanding of the economic repercussions across different regions.
Impact on Major Trading Partners
Major trading partners, particularly those located along the Indian Ocean and the Mediterranean, face substantial economic headwinds. The disruption of supply chains and the escalation of shipping costs directly translate to increased import prices for essential goods. This, in turn, exerts upward pressure on consumer prices and can trigger inflationary spirals within national economies.
Impact on Consumer Prices in Various Regions
The conflict’s effects on consumer prices are not uniform. Regions heavily reliant on imported goods, such as those in Africa and parts of Asia, are experiencing significant price increases. These increases are felt in various sectors, from food and energy to manufactured goods. Increased costs for raw materials and finished products directly impact the retail prices consumers pay, leading to reduced purchasing power.
Impact on Supply Chains of Specific Goods
The disruption in shipping affects numerous supply chains, with noticeable consequences for goods such as oil, agricultural products, and manufactured components. Oil prices, for example, are influenced by the availability of vessels to transport it from the Middle East. Agricultural goods, such as grains and fruits, may experience shortages and price hikes if transit times lengthen or ports become congested.
The production of manufactured goods, which rely on global component sourcing, may also be affected, leading to delays and price increases.
Financial Implications for Countries Heavily Reliant on Red Sea Trade
Countries that rely heavily on Red Sea trade routes face substantial financial implications. Increased shipping costs directly translate into higher import costs, potentially impacting national budgets and reducing disposable income. The disruption also affects export earnings, as companies face increased shipping costs, which could result in reduced profitability. These financial repercussions can lead to reduced foreign investment and economic stagnation.
Comparative Table of Economic Consequences
| Region | Impact on Import Prices | Impact on Consumer Prices | Impact on Supply Chains | Financial Implications |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| East Africa | Significant increase in import prices for essential goods | Higher prices for food, fuel, and other consumer goods | Disruptions in food imports, leading to potential shortages | Reduced purchasing power, impact on national budgets |
| South Asia | Increased costs for raw materials and manufactured goods | Rising prices for essential commodities and consumer products | Disruptions in the supply of raw materials and finished goods | Strain on import-dependent industries and reduced economic growth |
| European Union | Moderate increase in import prices for certain goods | Impact on prices of specific goods, depending on import reliance | Disruptions in the supply chain for some goods | Indirect impact on the overall economy, particularly for businesses heavily reliant on Red Sea trade |
Impact on Specific Industries
The Red Sea conflict’s impact extends far beyond headlines and geopolitical anxieties. It directly affects global supply chains, particularly for vital commodities and consumer goods, leading to significant disruptions and price increases. This section will detail the impact on key industries, comparing their vulnerabilities, and examining potential mitigation strategies.
Oil and Energy Sector
The disruption of shipping lanes in the Red Sea has a direct impact on oil and energy markets. Reduced oil tanker traffic leads to higher insurance costs and longer transit times. This, in turn, affects the availability of refined products, increasing prices for consumers and businesses. For instance, a substantial increase in shipping costs for crude oil can be seen as a direct result of this conflict.
The potential for further escalation, and the lack of alternative routes, means sustained pressure on energy prices. Moreover, the conflict’s uncertainty affects investment decisions, potentially leading to slower growth in the sector.
Consumer Goods Industry
The consumer goods sector faces a significant challenge. Many essential products, from electronics to clothing, rely on global supply chains. Delays in shipping, combined with rising freight costs, push up retail prices for consumers. The ripple effect is seen across various consumer goods categories, from food to appliances. This can be seen in the increase of costs for retailers to acquire products from overseas, and thus impacting the prices for consumers.
The impact on consumer purchasing power is an important concern, especially for lower-income households.
The escalating Red Sea Houthi shipping inflation is a serious concern, impacting global trade and supply chains. This geopolitical instability, however, is a tiny ripple compared to the larger waves of human rights struggles. The recent case of Olympic intersex athlete Maximila Imali, highlighted in this article olympic intersex maximila imali , reminds us of the larger issues of human rights and inclusion that often go unnoticed amidst economic crises.
Ultimately, the Red Sea Houthi shipping inflation, while impactful, is just one piece of a complex global puzzle.
Comparative Analysis of Industry Impacts
The oil and energy sector is highly vulnerable due to the critical nature of its commodities and the high value of shipments. Consumer goods are also significantly affected, but the impact is more diffused across various product categories. The intensity of the impact is dependent on the specific supply chain for each industry. For example, a country heavily reliant on imports for electronics will experience a higher impact compared to a country with significant domestic production.
Supply Chain Disruptions
The Red Sea conflict exemplifies the fragility of global supply chains. Delays in shipments, higher transportation costs, and potential port congestion all contribute to substantial disruptions. These disruptions are not limited to a single region or industry. The interconnectedness of global trade means that disruptions in one area can have cascading effects across the entire system. A prime example of this is the impact of a global chip shortage on various industries, which highlights the critical role of uninterrupted supply chains.
Mitigation Strategies
Several mitigation strategies can help affected industries. Diversifying supply chains, exploring alternative shipping routes, and investing in robust logistics planning can reduce vulnerability to future disruptions. Government support for industries facing challenges, along with proactive measures to minimize disruptions, are crucial.
Affected Industries and Challenges
| Industry | Specific Challenges |
|---|---|
| Oil & Energy | Increased insurance costs, longer transit times, reduced availability of refined products, higher prices for consumers and businesses, uncertainty affecting investment decisions. |
| Consumer Goods | Delays in shipments, rising freight costs, increased retail prices for consumers, impact on consumer purchasing power. |
| Manufacturing | Supply chain disruptions, higher production costs, delays in raw material supply. |
| Agriculture | Delayed or higher cost of importing fertilizers, impacting yields, potential food shortages. |
Final Wrap-Up
In conclusion, the Red Sea Houthi shipping inflation crisis underscores the interconnectedness of global trade and the devastating consequences of conflict. Alternative routes, diplomatic solutions, and industry adaptations are crucial to mitigating the long-term impact. The need for swift and decisive action is paramount to preventing further escalation and safeguarding global economic stability.
FAQ Compilation
What are the specific goods most vulnerable to increased shipping costs?
Industries heavily reliant on imported goods, like consumer electronics, clothing, and certain food products, are experiencing major price increases due to the rising shipping costs. Oil and energy sectors are also greatly impacted.
How do the Houthi’s actions compare to previous regional conflicts?
Analyzing the Houthi actions in relation to past regional conflicts reveals similarities in tactics and motivations. However, the scale and global implications of this conflict are unprecedented, with significant disruptions to international trade.
What are the most significant alternative trade routes?
Alternative routes, such as those through the Suez Canal or the Cape of Good Hope, are being considered, but each presents logistical and economic challenges, affecting transit times and costs. The feasibility of each route varies.
What is the current status of diplomatic efforts to resolve the conflict?
Diplomatic efforts are underway, but the progress is slow, hindered by differing viewpoints and political agendas. A lack of consensus makes reaching a resolution challenging.






