
Moon Landing NASA, Odysseus, Intuitive Machines
Moon landing NASA Odysseus Intuitive Machines explores the fascinating journey of lunar exploration, from the historic Apollo missions to the cutting-edge endeavors of modern companies like Intuitive Machines. This journey delves into the technological marvels, political implications, and the potential for future lunar outposts, examining the roles of NASA’s Odysseus program and the innovative strategies of Intuitive Machines. We’ll unravel the past, present, and future of lunar exploration, examining the challenges and triumphs that lie ahead.
The moon landing marked a pivotal moment in human history. The subsequent Apollo missions pushed the boundaries of space travel, laying the groundwork for future exploration. Now, private companies like Intuitive Machines are building upon this legacy, developing new technologies and approaches to lunar operations. The potential for resource utilization and the establishment of a sustained human presence on the moon is a significant driving force behind these endeavors.
This exploration will delve into the specifics of these ambitious projects and the collaborative efforts needed to achieve them.
Historical Context of Lunar Missions
The quest to reach the moon captivated humanity, igniting a fierce competition and a relentless pursuit of technological advancement. This journey, driven by the ambition to explore the unknown and understand our place in the cosmos, shaped our understanding of science, engineering, and the human spirit. The monumental achievement of the Apollo missions continues to inspire awe and wonder, reminding us of the potential within human ingenuity.The Apollo program, a cornerstone of the Space Race, was not merely a scientific endeavor but a symbol of national pride and a testament to the power of collaboration.
The race to the moon, fueled by Cold War tensions, propelled unprecedented advancements in various fields, demonstrating the remarkable progress achievable through focused determination.
NASA’s Odysseus mission, partnered with Intuitive Machines, is fascinating, especially with the recent focus on lunar exploration. While these robotic missions pave the way for future human endeavors on the moon, it’s a stark reminder of the unpredictable nature of our world when we consider the recent disappearance of a couple on a boat near Grenada, couple missing boat grenada.
Hopefully, they are found safely, and the focus can return to the exciting prospect of future moon missions by NASA and its partners.
Timeline of NASA Lunar Missions
The journey to the moon wasn’t a single event but a culmination of numerous missions, each building upon the successes and lessons learned from previous attempts. A chronological overview reveals the gradual progress and evolving capabilities that ultimately led to the historic Apollo 11 landing.
- Pioneer program (1958-1960): Early probes aimed to understand the lunar environment, gathering data on the lunar surface composition, and paving the way for future missions. These initial missions provided crucial insights into the challenges of space travel and lunar exploration.
- Ranger program (1961-1965): This program used robotic probes to take high-resolution images of the lunar surface. The program aimed to provide detailed images of landing sites, enabling scientists to plan future missions with greater precision. The successful close-up images of the lunar surface provided valuable data for future Apollo missions.
- Surveyor program (1966-1968): These robotic missions were crucial for testing the feasibility of soft landings on the moon. Surveyor probes performed surface experiments, including deploying scientific instruments and collecting samples, demonstrating the feasibility of a safe landing and laying the groundwork for the Apollo program’s crewed landings.
- Apollo program (1968-1972): The Apollo program, encompassing a series of crewed missions, culminated in the historic moon landing. Each mission built upon the previous one, increasing crew size, mission duration, and complexity of tasks. This program showcased human ingenuity and the power of international collaboration in achieving seemingly impossible goals.
Role of NASA’s Apollo Program in the Space Race
The Apollo program was a direct response to the Soviet Union’s advancements in space exploration. The competition for space supremacy spurred the United States to accelerate its space program, resulting in a rapid development of technologies and a surge in scientific breakthroughs.
NASA’s Odysseus mission, powered by Intuitive Machines, is fascinating, but I’m also really interested in the current housing market near NYC. The lunar exploration is cool, but the rising prices in places like Brooklyn and Queens are making it hard for families to afford a home. The complexities of lunar surface exploration, much like the complexities of the NYC housing market, show us how different factors impact the human experience, whether on Earth or on the Moon.
Ultimately, the ambition of Intuitive Machines and NASA’s moon landing efforts is quite inspiring, and I hope their success leads to more possibilities on Earth, too. housing market near nyc is a complex situation, but still fascinating to observe.
- Space Race Context: The Space Race was a geopolitical competition between the United States and the Soviet Union, primarily focused on achieving milestones in space exploration. The moon landing was a significant victory for the United States in this competition, demonstrating its technological and scientific prowess.
- Technological Advancements: The Apollo program pushed the boundaries of rocketry, computing, and materials science. The development of powerful rockets like the Saturn V and advanced guidance systems were crucial for reaching the moon and returning safely. The creation of sophisticated life support systems for extended space travel also stemmed from this endeavor.
Technological Advancements Leading to the Moon Landing
The moon landing was a testament to the groundbreaking advancements in various fields. The sheer complexity of the mission demanded innovations in numerous technological areas.
NASA’s Odysseus mission, partnered with Intuitive Machines, is fascinating, but the recent tragedy at Disney World involving a guest with a severe allergy highlights a very different kind of mission: one of safety and precaution. The tragic lawsuit concerning the disney world allergy death lawsuit really makes you think about the responsibility of large organizations to ensure the well-being of their guests.
Ultimately, the meticulous planning and testing required for moon landing missions by NASA, and its partners like Intuitive Machines, show a similar commitment to safety in a different, but equally crucial, context.
- Rocketry: The development of the Saturn V rocket, a colossal launch vehicle, was pivotal for propelling the Apollo spacecraft to lunar orbit. Its power and reliability were essential for overcoming the immense gravitational forces required to achieve lunar orbit and return to Earth.
- Computing: The early digital computers were crucial for mission control and guidance. These systems processed vast amounts of data, tracked the spacecraft’s trajectory, and adjusted its course in real-time. The development of more powerful and sophisticated computing capabilities was critical to the success of the Apollo program.
- Materials Science: The extreme temperatures and vacuum of space required specialized materials that could withstand the harsh conditions. The development of heat-resistant materials for spacecraft and the creation of lightweight but strong alloys were crucial for the success of the mission.
Political and Societal Impact of the Moon Landing
The moon landing had a profound impact on global politics and society. It galvanized national pride, fostered international cooperation, and inspired generations to pursue scientific and technological careers.
- National Pride: The successful moon landing boosted national pride and confidence in the United States, serving as a significant triumph in the Space Race.
- Global Cooperation: The event fostered a sense of shared human endeavor, transcending political boundaries. International cooperation in space exploration became more common, showcasing the possibility of global collaboration in achieving monumental goals.
- Inspiration and Motivation: The moon landing inspired countless young people to pursue careers in science, technology, engineering, and mathematics (STEM). It highlighted the power of human ingenuity and the potential for achieving ambitious goals through focused effort.
Lunar Missions and Achievements
| Mission | Year | Achievements |
|---|---|---|
| Apollo 11 | 1969 | First crewed lunar landing |
| Apollo 12 | 1969 | Second crewed lunar landing |
| Apollo 17 | 1972 | Last crewed lunar landing |
NASA’s Odysseus Program
The Odysseus program, a proposed initiative, remains largely shrouded in speculation, with no concrete details officially released by NASA. While specific plans are still under development, its potential impact on lunar exploration and resource utilization is a topic of considerable interest within the space community. The program’s ambitious nature, coupled with the current surge in lunar exploration activities, positions it as a significant step towards future lunar endeavors.
Objectives and Scope
The potential objectives of the Odysseus program are likely to focus on establishing a sustainable lunar presence. This could include deploying advanced robotic systems for resource extraction, scientific research, and infrastructure development. The scope of Odysseus is likely to be broad, encompassing multiple phases of lunar exploration, from initial reconnaissance to long-term habitation.
Potential Connection to Lunar Resource Utilization
The Odysseus program’s potential connection to lunar resource utilization is substantial. The extraction and processing of lunar resources, such as water ice, could provide crucial elements for future lunar missions. These resources could be used for life support, propellant production, and even construction materials. This would greatly reduce the need to transport supplies from Earth, significantly decreasing mission costs and enabling more ambitious endeavors.
The program could pave the way for a self-sustaining lunar outpost.
Technological Innovations
The technological innovations planned for Odysseus are likely to be groundbreaking. Advanced robotic systems with enhanced autonomy and capabilities will likely be crucial. These systems could include specialized excavators, processing units, and transportation vehicles. The program will likely push the boundaries of robotic technology, focusing on improved navigation, remote operation, and adaptability in the harsh lunar environment.
Development in advanced materials science, designed for the extreme conditions of the lunar surface, will be critical.
Potential Challenges and Risks
The Odysseus program faces significant challenges. The harsh lunar environment, including extreme temperatures, radiation, and dust, poses significant risks to equipment and personnel. Ensuring the reliability and longevity of robotic systems in such a challenging environment is a major hurdle. Furthermore, the development of sustainable power sources and efficient resource utilization methods will be critical. The program’s high cost, coupled with the inherent uncertainties of space exploration, requires meticulous planning and risk assessment.
Previous lunar missions have experienced equipment failures, navigation issues, and other unexpected problems, which would need to be accounted for in the design and implementation phases.
Anticipated Timeline and Budget
| Phase | Description | Estimated Duration | Estimated Budget (USD Billions) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Phase 1: Reconnaissance and Site Selection | Initial robotic missions to identify suitable locations for resource extraction and infrastructure deployment. | 3-5 years | 2-3 |
| Phase 2: Resource Extraction and Processing | Development and deployment of advanced robotic systems for resource extraction and processing. | 5-7 years | 5-7 |
| Phase 3: Infrastructure Development | Establishment of a basic lunar infrastructure, including power generation and life support systems. | 7-10 years | 8-10 |
| Phase 4: Expansion and Sustainability | Expansion of the lunar base and development of self-sustaining operations. | Ongoing | Variable, dependent on mission requirements |
The table above provides a possible framework. Actual timelines and budgets will depend on technological advancements, funding availability, and unforeseen challenges. These figures are estimations and should be considered as potential ranges. The ongoing development of lunar resource utilization technologies and the experience gained from previous missions will significantly influence the feasibility and cost of the Odysseus program.
Intuitive Machines and Lunar Exploration
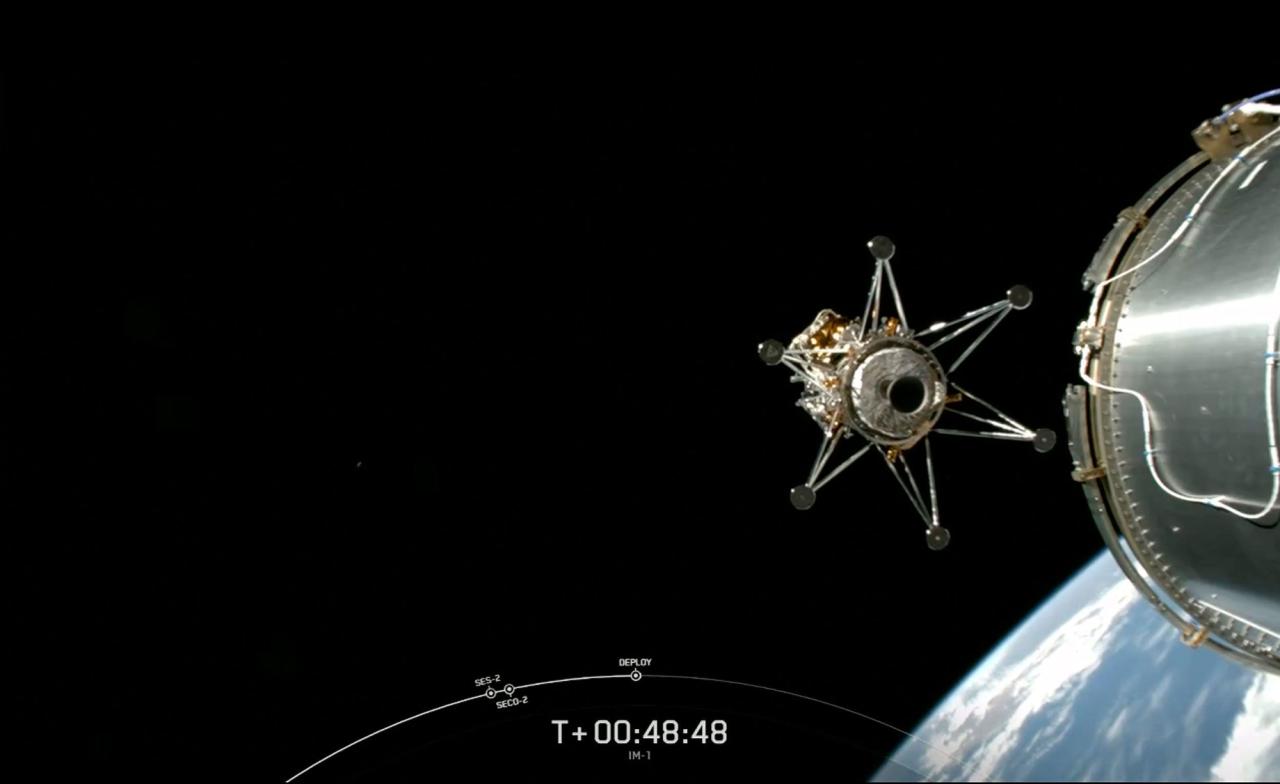
Intuitive Machines (IM) is a crucial player in the burgeoning private sector of lunar exploration. Their innovative approach to lunar missions, coupled with a focus on specific technologies, is reshaping the landscape of spacefaring endeavors. This company’s involvement signifies a shift towards a more collaborative and diverse approach to reaching the Moon, leveraging commercial ingenuity to augment traditional space agency efforts.IM’s involvement in lunar missions is driven by a commitment to developing and demonstrating cutting-edge technologies.
Their mission goals extend beyond simple surface surveys; they aim to advance lunar resource utilization and establish a more sustainable presence on the lunar surface. This marks a departure from the traditional, government-led approach, showcasing the growing importance of private sector partnerships in space exploration.
NASA’s Odysseus mission with Intuitive Machines, aiming for a moon landing, is seriously cool. Thinking about the vastness of space and robotic exploration, it got me digging through my music library. I found this awesome playlist featuring SZA, Norah Jones, and AG Cook – perfect for those late-night moon gazing sessions. playlist sza norah jones ag cook Seriously, it’s a great listen while you ponder the future of lunar exploration and the intricacies of the Odysseus mission.
Role of Intuitive Machines in Lunar Exploration
Intuitive Machines is a pioneering private spaceflight company focused on lunar exploration. Their primary role involves deploying and operating robotic spacecraft on the lunar surface. This includes conducting scientific research, gathering data, and ultimately, facilitating the establishment of a sustainable lunar presence. IM is not merely an explorer; it’s a facilitator, laying the groundwork for future endeavors.
Current and Planned Lunar Missions
IM has several lunar missions currently underway or planned. These missions often include deployments of robotic landers, or small rovers, to the lunar surface. These vehicles are designed for specific tasks, ranging from surface reconnaissance and sample collection to resource assessment. The successful execution of these missions often paves the way for further exploration and utilization of lunar resources.
Technologies Utilized by Intuitive Machines
IM leverages advanced technologies across various stages of its lunar missions. Their spacecraft employ sophisticated navigation systems for precise landing, communication protocols for efficient data transfer, and specialized sensors for comprehensive data collection. These technologies are crucial for successful lunar operations, demonstrating a commitment to cutting-edge engineering.
Comparison to Other Lunar Exploration Efforts
IM’s approach to lunar exploration contrasts with traditional space agency missions in its emphasis on private sector innovation and commercial partnerships. While NASA and other governmental agencies remain key players, IM represents a growing trend toward a more collaborative and diversified approach to space exploration. This shift is seen in the increasing number of private companies vying for a stake in lunar operations.
The inclusion of diverse actors in lunar endeavors introduces a broader range of perspectives and approaches.
Comparison Table: Intuitive Machines Missions vs. Others
| Company | Mission Type | Primary Objectives | Technologies |
|---|---|---|---|
| Intuitive Machines | Robotic Lander Deployments | Lunar surface exploration, resource assessment | Advanced navigation, communication, sensors |
| NASA (Artemis Program) | Crewed Missions | Establishing human presence on the Moon | Advanced life support, habitats |
| SpaceX | Commercial Cargo Missions | Delivering cargo to the ISS and lunar surface | Reusable rockets, advanced propulsion |
Lunar Surface Operations and Resource Utilization
The Apollo missions marked a monumental achievement in human history, demonstrating our capacity to reach the lunar surface. However, the potential of the Moon extends far beyond a historical landmark. Understanding how to operate on and utilize lunar resources is crucial for future missions, including extended stays and establishing a permanent presence. This opens doors to lunar outposts, scientific research, and even launching space missions from the Moon itself.
Potential for Lunar Surface Operations, Moon landing nasa odysseus intuitive machines
The Moon presents a unique opportunity for establishing surface operations. The low gravity, lack of atmosphere, and unique geological composition offer advantages for various activities. These operations could range from setting up temporary bases for scientific experiments to constructing larger, more permanent outposts. The availability of resources on the lunar surface will be key to supporting these operations.
Lunar Resource Utilization for Future Missions
Utilizing lunar resources is critical for sustainability in space exploration. Bringing materials from Earth for every mission is not only costly but also impractical for long-term ventures. Lunar resources like regolith, water ice, and minerals can be processed into crucial materials, including rocket propellants, construction materials, and life support systems. This concept of in-situ resource utilization (ISRU) is vital for future space missions.
The development of efficient processing techniques is a critical area of research.
Challenges of Establishing and Maintaining Lunar Outposts
Establishing and maintaining lunar outposts presents significant challenges. The extreme temperatures, radiation exposure, and lack of atmosphere are just some of the environmental factors that must be overcome. Furthermore, the logistical hurdles of transporting equipment and personnel to and from the Moon are considerable. Developing robust and reliable infrastructure for power generation, communication, and life support is essential.
Simulating these conditions on Earth is crucial for mitigating these challenges.
Types of Resources Found on the Moon
The Moon’s surface holds a variety of resources. Regolith, the powdery lunar soil, is abundant and can be used for construction and radiation shielding. Water ice, trapped in permanently shadowed craters, holds the potential to be a source of drinking water, rocket propellant, and oxygen. Other minerals, including metals, can be used for various technological applications. Understanding the distribution and accessibility of these resources is vital for successful ISRU.
Potential Uses of Lunar Resources
| Resource | Potential Use |
|---|---|
| Regolith | Construction materials, radiation shielding, 3D printing materials |
| Water Ice | Drinking water, rocket propellant, oxygen, life support |
| Minerals | Metals for construction and technology, raw materials for processing |
These resources, when processed and utilized effectively, can revolutionize space exploration. By establishing lunar outposts, we can move towards a future where space missions are more sustainable and efficient.
The Moon Landing and its Legacy
The Apollo 11 moon landing, a pivotal moment in human history, transcended the realm of space exploration. It ignited a global fascination with the cosmos and spurred profound advancements in various fields, from technology to societal understanding. The echoes of that monumental achievement resonate even today, shaping our aspirations and driving continued exploration of the universe.
Lasting Impact on Scientific Advancements
The quest to reach the moon demanded unparalleled scientific breakthroughs. The development of sophisticated navigation systems, materials science for spacecraft construction, and computational power all saw significant progress. These advancements directly impacted terrestrial technologies, leading to innovations in fields like medicine, communication, and manufacturing. For instance, the heat-resistant materials developed for the spacecraft contributed to advancements in protective gear for firefighters and high-temperature applications.
The precision required in lunar landing procedures spurred the development of more accurate and reliable guidance systems used in various modern applications.
Effect on Space Exploration
The moon landing catalyzed a surge in space exploration. It demonstrated the feasibility of venturing beyond Earth’s orbit and inspired subsequent missions, including robotic probes to other planets and moons. The Apollo program, while ultimately ending, laid the groundwork for future space exploration endeavors, such as the Space Shuttle program and the International Space Station. This momentum continues to drive our exploration of the solar system and beyond.
Significance in International Cooperation
The moon landing stands as a testament to international cooperation. The United States, in collaboration with international partners, shared knowledge and resources to achieve this monumental task. This spirit of collaboration remains crucial in tackling global challenges, particularly in the realm of science and technology. The scientific data gathered during the Apollo missions, for example, was shared among participating nations, contributing to a collective understanding of space and the universe.
Societal and Cultural Impact
The moon landing’s impact on society and culture is undeniable. It fostered a sense of global unity and inspired generations of scientists, engineers, and astronauts. The images of astronauts on the lunar surface became iconic symbols of human ambition and achievement, capturing the imagination of people worldwide. The landing also fostered a deeper understanding of our place in the universe, encouraging a renewed sense of wonder and curiosity about the cosmos.
Summary Table: Long-Term Effects of the Moon Landing
| Area | Technological Impact | Societal Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Materials Science | Development of heat-resistant alloys and composites for spacecraft, leading to advancements in aerospace engineering and various industrial applications. | Increased public awareness of the potential of scientific research and technological innovation. |
| Computing and Data Processing | Advancements in computational power and data analysis techniques for spacecraft navigation and mission control, leading to more efficient and reliable systems in various sectors. | Inspired a new generation of computer scientists and engineers, driving the evolution of technology. |
| Communication and Navigation | Development of more sophisticated communication systems and navigation technologies, impacting global telecommunications and transportation. | Encouraged a sense of shared human endeavor and international collaboration in tackling scientific challenges. |
| Medical Research | Improved understanding of space medicine and its applications in terrestrial settings, leading to advancements in healthcare and medical equipment. | Fostered a sense of collective human achievement and inspired new generations to pursue careers in science and engineering. |
Future Lunar Exploration: Moon Landing Nasa Odysseus Intuitive Machines

The lunar landscape, once a destination for ambitious space programs, now beckons with the promise of sustained human presence. The synergy between NASA, Intuitive Machines, and Odysseus holds the key to unlocking this potential, paving the way for more comprehensive lunar exploration and resource utilization. These collaborations promise to not only extend the reach of human exploration but also lay the foundation for a future where the Moon becomes a crucial stepping stone for further ventures into the solar system.The future of lunar exploration hinges on the ability of these organizations to combine their strengths and expertise.
NASA’s deep space experience, Intuitive Machines’ proven capabilities in lunar surface operations, and Odysseus’ innovative approach to lunar resource utilization, create a powerful confluence of capabilities. This confluence promises to unlock new levels of efficiency, cost-effectiveness, and scientific advancement in lunar exploration.
Potential Collaborations
NASA, Intuitive Machines, and Odysseus can leverage their respective strengths to maximize the effectiveness of future lunar missions. NASA’s role as the overarching authority in space exploration, combined with Intuitive Machines’ proven lunar landing and surface operation expertise, and Odysseus’ innovative resource utilization technologies, creates a formidable alliance. Each entity can contribute unique strengths to a collaborative framework, facilitating a more holistic approach to lunar exploration.
Advancements in Lunar Exploration Through Collaboration
Collaboration among these entities can significantly advance lunar exploration by pooling resources, expertise, and technological advancements. This synergistic approach allows for the development of more comprehensive and sophisticated missions, enabling the exploration of previously inaccessible areas and the gathering of valuable scientific data. For example, NASA could provide the overarching mission design, while Intuitive Machines delivers the robotic surface operations, and Odysseus could focus on the extraction and utilization of lunar resources.
Potential Conflicts and Challenges
Potential conflicts and challenges in these collaborations might arise from differing priorities, conflicting timelines, and varying levels of technical expertise. Differences in organizational cultures and communication styles may also present obstacles. Furthermore, competition for limited resources, both financial and human, can be a source of tension. Successfully navigating these challenges requires strong leadership, clear communication, and a shared vision for lunar exploration.
Careful consideration and proactive mitigation strategies are crucial to avoid hindering the progress of lunar exploration.
The moon landing, NASA’s Odysseus mission, and Intuitive Machines’ contributions are fascinating, but I’ve been reflecting lately on the human element of space exploration. It’s a powerful reminder of the deep emotional responses connected to these monumental achievements, and how the loss and grief experienced by people like Sloane Crosley in her piece, ” grief is for people sloane crosley “, resonates surprisingly with the complex endeavors of space exploration.
Ultimately, the journey to the moon, and the advancements made by these companies, is a story about humanity’s ambition and its inherent capacity for profound emotions.
Table of Potential Future Missions
| Mission Name | NASA Role | Intuitive Machines Role | Odysseus Role | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lunar Resource Extraction Demonstration | Mission oversight, scientific analysis | Landing and surface operations, sample collection | Resource extraction and processing | Demonstrates the feasibility of extracting and processing lunar resources. |
| Lunar Sample Return Mission | Mission design, sample analysis | Rover operation, sample collection | Sample transfer and delivery to orbit | Focuses on returning samples from previously unexplored areas. |
| Lunar Base Camp Establishment | Strategic planning, long-term goals | Module deployment and maintenance | Resource utilization for construction materials | Establishes a sustainable base camp to support long-term lunar exploration. |
Lunar Surface Exploration
The Moon, Earth’s celestial neighbor, beckons with the promise of scientific discovery and resource utilization. Understanding the challenges of establishing a sustained human presence on its surface is crucial for planning future missions and realizing the potential of lunar exploration. The harsh lunar environment, from extreme temperature fluctuations to the lack of atmosphere and gravity, demands innovative solutions for sustained operations.
Technical Challenges of Lunar Exploration
Lunar exploration faces numerous technical hurdles. The extreme temperature variations, ranging from scorching daytime heat to frigid nighttime cold, pose a significant threat to equipment and human health. The lack of atmosphere necessitates the development of advanced life support systems and specialized protective gear. The low lunar gravity, while offering advantages in certain aspects of space operations, presents challenges for movement, construction, and the handling of equipment.
Furthermore, the vacuum environment presents issues related to equipment reliability and the preservation of delicate samples. Radiation exposure from solar and cosmic rays also demands shielding and mitigation strategies for both equipment and personnel.
Strategies to Overcome Challenges
Several strategies are employed to mitigate the aforementioned challenges. Advanced thermal control systems, utilizing materials with high heat capacity and efficient insulation, are critical for maintaining stable operating temperatures. Closed-loop life support systems are essential for creating sustainable habitats and recycling resources on the lunar surface. Specialized spacesuits and habitats must be meticulously designed to withstand the harsh conditions and protect personnel.
Radiation shielding, employing materials like tungsten or polyethylene, is crucial for mitigating the harmful effects of cosmic radiation. Furthermore, the development of advanced robotics and autonomous systems can enhance efficiency and reduce the risk to human crews.
Methods for Collecting and Analyzing Lunar Samples
Precise and meticulous methods are employed for collecting and analyzing lunar samples. Specialized robotic arms, equipped with advanced sensors and sample-handling tools, can gather samples from diverse locations, minimizing contamination and maximizing scientific value. Samples are then carefully transported back to Earth for comprehensive analysis. Sophisticated laboratory equipment allows scientists to determine the age, composition, and structure of the lunar materials.
Detailed analysis, often involving multiple techniques such as spectroscopy and microscopy, provides crucial insights into the Moon’s history and evolution.
Maintaining a Lunar Presence
Maintaining a long-term human presence on the Moon requires a robust and sustainable infrastructure. Modular habitats, constructed from reusable materials, can adapt to evolving needs and expansion. Resource utilization, including water ice extraction and in-situ resource utilization (ISRU) techniques, will be vital for reducing reliance on Earth-based supplies. Efficient energy production systems, utilizing solar power or lunar resources, are essential for powering equipment and sustaining operations.
Robust communication systems are necessary for reliable data transmission and coordination with Earth. This includes advanced technologies that allow astronauts to communicate with each other and mission control.
Lunar Surface Operations Challenges and Solutions
| Challenges | Proposed Solutions |
|---|---|
| Extreme Temperature Fluctuations | Advanced thermal control systems, utilizing materials with high heat capacity and efficient insulation. |
| Lack of Atmosphere | Closed-loop life support systems, specialized spacesuits, and habitats. |
| Low Lunar Gravity | Specialized spacesuits and habitats, advanced robotics and autonomous systems for movement and construction. |
| Vacuum Environment | Thorough testing and validation of equipment before deployment, robust construction techniques. |
| Radiation Exposure | Radiation shielding, employing materials like tungsten or polyethylene, and advanced radiation monitoring systems. |
| Limited Resources | In-situ resource utilization (ISRU) techniques for water ice extraction and other resources, efficient energy production systems. |
Final Conclusion
In conclusion, the moon landing, NASA’s Odysseus program, and Intuitive Machines’ innovative approach represent a convergence of human ingenuity and ambition. This exploration highlights the evolving landscape of lunar exploration, from the historical context of the Space Race to the potential for future lunar outposts. The interconnectedness of these endeavors suggests a promising future for space exploration, with the possibility of substantial advancements in technology and international cooperation.
The journey towards a sustained human presence on the moon is underway, and this exploration has offered a glimpse into its complexities and potential rewards.
FAQ Compilation
What are the potential challenges in establishing a lunar outpost?
Establishing a sustainable lunar outpost presents significant challenges, including the extreme lunar environment, the logistical complexities of transporting resources, and the technical hurdles of maintaining long-term operations in a vacuum. Radiation exposure, temperature fluctuations, and the limited availability of water ice on the lunar surface are all crucial factors.
What are the key technological advancements that facilitated the moon landing?
The moon landing was a testament to the technological advancements of the time, including rocketry, navigation, materials science, and communication systems. The development of powerful rockets like the Saturn V, precise navigation systems, and reliable communication technologies were critical to achieving this historic feat.
What are the potential uses of lunar resources for future space missions?
Lunar resources, including water ice, regolith, and minerals, could provide crucial support for future space missions. Water ice can be broken down into hydrogen and oxygen, which are essential rocket fuels. Regolith can be used to create construction materials and support habitats. The exploitation of these resources could drastically reduce the need to transport materials from Earth, lowering costs and increasing sustainability.

