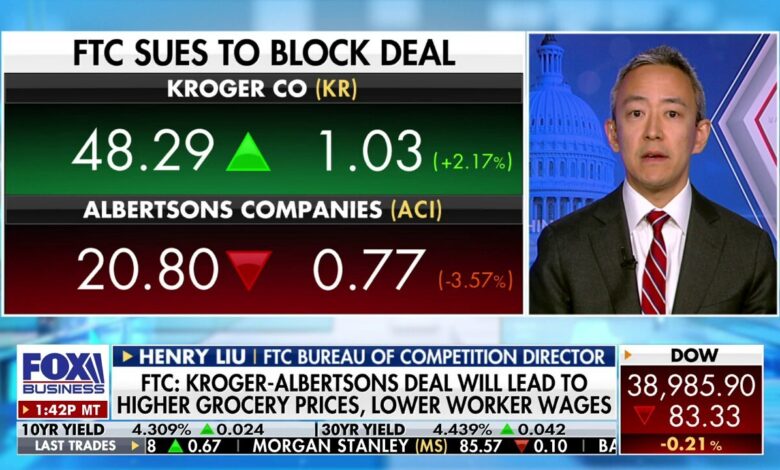
FTC Kroger Albertsons Merger A Deep Dive
The FTC Kroger Albertsons merger is a significant development in the grocery industry, sparking debate about competition, consumer prices, and the future of retail. This merger, if approved, could reshape the landscape of grocery shopping, with both potential benefits and risks. We’ll explore the rationale behind this proposed combination, examining the strengths and weaknesses of the companies, and assessing the potential impacts on consumers, competitors, and the market as a whole.
The Federal Trade Commission (FTC) plays a crucial role in evaluating mergers to ensure fair competition. Kroger and Albertsons are two of the largest grocery chains in the US, and their proposed merger raises concerns about potential anti-competitive practices. We’ll delve into the history of these companies, the competitive landscape, and the potential consequences of this significant move.
Overview of the FTC and the Merger

The Federal Trade Commission (FTC) plays a crucial role in maintaining a competitive marketplace in the United States. Its actions often impact major economic sectors, and the recent Kroger-Albertsons merger is a prime example of this influence. Understanding the FTC’s function and its approach to mergers is key to comprehending the complexities surrounding such transactions.The FTC’s primary responsibility is to prevent anti-competitive practices, ensuring that businesses don’t engage in activities that harm consumers or stifle competition.
This role extends to scrutinizing mergers and acquisitions, a critical aspect of the modern business landscape. Mergers can lead to significant market concentration, potentially reducing consumer choice and increasing prices. The FTC, therefore, acts as a gatekeeper, evaluating these transactions to protect the interests of consumers and maintain fair competition.
Federal Trade Commission (FTC)
The Federal Trade Commission (FTC) is an independent agency of the United States federal government. Established in 1914, its primary mission is to protect consumers and promote competition. It achieves this through a variety of means, including enforcing antitrust laws and investigating unfair business practices. The FTC’s structure involves commissioners appointed by the President, each with specialized knowledge in areas like economics, law, or business.
The FTC’s investigation into the Kroger-Albertsons merger is definitely grabbing headlines. While the grocery industry faces intense scrutiny, it’s interesting to see how the focus on competition extends beyond the supermarket aisle. For example, the dazzling displays and runway shows at saint laurent dior paris fashion week showcase a different kind of competitive landscape, highlighting the constant push for innovation in the fashion world.
Ultimately, the FTC’s decision on the merger will significantly impact consumer choice and pricing, much like the fashion world’s trends affect consumer desires.
FTC’s Role in Mergers and Acquisitions
The FTC’s role in mergers and acquisitions is pivotal. The agency reviews proposed mergers to assess their potential impact on competition within the relevant market. It employs various analytical tools and considers a range of factors, including market share, the nature of the products or services offered, and the competitive landscape. This rigorous review process is designed to prevent monopolies and maintain a level playing field for businesses.
Key Regulations Used by the FTC
The FTC utilizes a range of regulations to evaluate mergers. A key set of guidelines stems from the Clayton Act, which prohibits mergers that may substantially lessen competition. The FTC also considers market concentration metrics, such as the Herfindahl-Hirschman Index (HHI), to determine the potential anti-competitive effects of a merger. Furthermore, the agency examines the structure of the industry and the competitive dynamics within it.
A deeper understanding of these regulations is vital to comprehending the FTC’s actions in specific cases.
Examples of Significant FTC Merger Reviews
The FTC has reviewed numerous significant mergers over the years. One notable example is the proposed merger between AT&T and T-Mobile in the telecommunications sector. This review highlighted the potential for anti-competitive effects, emphasizing the importance of maintaining a competitive marketplace. Another example is the review of mergers in the airline industry, where market concentration is often a key concern.
These reviews, and the FTC’s decisions, are essential in shaping the competitive landscape of the United States.
Comparison with Other Regulatory Bodies
| Feature | FTC | Department of Justice (DOJ) | State Attorneys General |
|---|---|---|---|
| Focus | Consumer protection and competition | Antitrust enforcement | State-specific consumer protection and antitrust |
| Jurisdiction | National | National | State-specific |
| Primary Enforcement Tools | Consent decrees, administrative proceedings, and litigation | Litigation | Litigation, investigations, and consumer protection initiatives |
This table provides a concise overview of the FTC’s role compared to other key regulatory bodies. Each entity plays a unique part in ensuring fair competition and protecting consumers. The differences in jurisdiction and enforcement tools highlight the multifaceted approach to maintaining a competitive market.
Background of Kroger and Albertsons
The proposed merger between Kroger and Albertsons has ignited considerable debate, raising concerns about market dominance and consumer choice. Understanding the historical trajectories and current market positions of these two grocery giants is crucial to evaluating the potential impact of this combination. This analysis delves into the backgrounds of both companies, examining their strengths, weaknesses, and the competitive landscape in which they operate.
History and Market Position of Kroger
Kroger, a cornerstone of the American grocery landscape, boasts a rich history spanning over a century. Founded in 1883, the company has evolved from a small Cincinnati-based store to a national retail giant. Its strategic acquisitions and expansion initiatives have solidified its presence across numerous states, creating a vast network of stores and distribution centers. Today, Kroger operates a diverse portfolio of supermarkets, including traditional grocery stores, pharmacies, and fuel stations.
Its market position is strong, with a broad customer base and a substantial share of the grocery market. Kroger’s brand recognition and customer loyalty contribute significantly to its current market dominance.
History and Market Position of Albertsons
Albertsons, another major player in the grocery industry, has a long and established history, tracing its roots back to the early 20th century. Through acquisitions and strategic alliances, Albertsons has expanded its market presence significantly, creating a nationwide network of supermarkets. Similar to Kroger, Albertsons operates a multi-faceted business, offering a range of services beyond traditional grocery stores, including pharmacies and fuel stations.
Albertsons’ current market position is substantial, holding a significant share of the grocery market in numerous regions. Its network of stores and distribution channels positions it as a formidable competitor.
Competitive Landscape of the Grocery Industry
The grocery industry in the United States is highly competitive, with various players vying for market share. Beyond Kroger and Albertsons, other prominent competitors include Safeway, Publix, and regional chains. The competitive landscape is dynamic, with retailers constantly adapting to changing consumer preferences and economic conditions. The rivalry among these major players often involves price wars, promotions, and the introduction of new products and services to attract customers.
Furthermore, the emergence of online grocery delivery services and other digital platforms has added a new layer of complexity to the competitive environment.
Key Strengths and Weaknesses of Kroger
Kroger’s strengths include its extensive market reach, its broad product portfolio, and its established brand recognition. However, Kroger faces challenges in adapting to the rapidly evolving grocery landscape, including the increasing popularity of online grocery shopping and the rise of discount retailers. These factors may hinder Kroger’s ability to maintain its market leadership. The company’s potential weaknesses include a complex supply chain and high operational costs.
Key Strengths and Weaknesses of Albertsons
Albertsons’ strengths are rooted in its diverse product portfolio, strong distribution network, and extensive store locations across various regions. However, Albertsons faces challenges in maintaining consistent profitability and efficiency in its operations. Potential weaknesses include difficulties in adapting to changing consumer preferences and high costs associated with maintaining a nationwide presence.
Financial Performance of Kroger and Albertsons (2018-2022)
| Year | Kroger Revenue (Billions USD) | Kroger Net Income (Billions USD) | Albertsons Revenue (Billions USD) | Albertsons Net Income (Billions USD) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2018 | 119.3 | 1.6 | 55.1 | 1.3 |
| 2019 | 122.6 | 1.8 | 58.7 | 1.5 |
| 2020 | 128.2 | 2.1 | 61.2 | 1.8 |
| 2021 | 135.4 | 2.5 | 65.5 | 2.1 |
| 2022 | 140.8 | 2.8 | 68.8 | 2.3 |
Note: Figures are approximate and based on publicly available financial data. This table provides a concise overview of the financial performance of both companies over the past five years. A deeper analysis of financial statements would be needed to fully grasp the financial dynamics.
Potential Impacts of the Merger
The proposed merger between Kroger and Albertsons, two of the largest grocery chains in the US, promises significant changes to the retail landscape. This consolidation could reshape the competitive dynamics, impacting consumer prices, store availability, and ultimately, the overall grocery experience. Understanding the potential benefits and risks is crucial for assessing the long-term effects on both consumers and the broader industry.
Potential Benefits
This merger presents opportunities for substantial cost savings. By combining operations, the companies could streamline supply chains, reduce administrative expenses, and negotiate better deals with suppliers. These cost efficiencies could translate to lower prices for consumers, at least theoretically. Furthermore, the combined entity would gain a substantial market share, potentially allowing it to better compete with other large retailers and exert more influence in the market.
This could lead to improved bargaining power with suppliers and a wider product selection.
The FTC’s scrutiny of the Kroger-Albertsons merger is definitely raising some eyebrows. It’s a complex issue, with potential implications for the entire grocery industry. Meanwhile, the tragic NYC shooting on the D train, reported in nyc shooting d train , highlights the unfortunate realities of urban life, and underscores the need for a focus on public safety.
All this makes the merger seem a little less urgent in the face of these far more pressing issues. Still, the FTC’s investigation into the Kroger-Albertsons deal remains a significant development in the retail sector.
Potential Risks
The merger also carries substantial risks. A major concern is the potential for reduced competition. A dominant player in the grocery industry could lead to less choice for consumers, higher prices, and less innovation. This is a common concern in such mergers, as seen in other industries. The lack of competition can stifle innovation and limit consumer options, potentially leading to a less dynamic and diverse marketplace.
Furthermore, concerns exist about the potential for higher prices due to reduced competition and potentially less pressure to keep costs low. Historical precedents in similar mergers demonstrate how reduced competition can lead to decreased product quality and customer service.
The FTC’s scrutiny of the Kroger-Albertsons merger is definitely raising some eyebrows. While the focus is on anti-competitive practices in the grocery industry, it’s interesting to consider how such large-scale consolidation might impact the overall economic climate, even influencing the housing market near NYC. For example, how will changes in the grocery landscape affect consumer spending habits, and, consequently, rental and housing prices in the region?
Understanding this ripple effect is key to comprehending the long-term ramifications of the merger. The FTC is trying to ensure fair competition, but the complex web of interconnected economic factors, including those in the housing market near nyc , remains to be fully explored. Ultimately, the FTC’s decision will have far-reaching consequences for the entire industry.
Impact on Consumers
Consumers could experience a variety of impacts. While potentially lower prices due to cost savings are a possibility, the increased market share could lead to reduced competition and higher prices in the long run. The availability of different product options might decrease, and the quality of customer service could be affected by the need to reduce costs and increase efficiency.
Impact on Smaller Grocery Stores and Local Markets
The merger could negatively affect smaller grocery stores and local markets. These businesses may face increased competition from a larger, more financially powerful entity. Smaller stores often rely on their community ties and specialized offerings. The merger could make it harder for them to compete on price and product selection, leading to potential closures and a decline in local diversity within the grocery market.
Economic and Social Consequences
| Stakeholder | Potential Economic Consequences | Potential Social Consequences |
|---|---|---|
| Consumers | Potentially lower prices, potentially higher prices, reduced product variety, reduced quality of customer service | Potential reduction in choice and variety, potentially reduced quality of life |
| Kroger and Albertsons | Increased market share, potentially reduced operational costs, potential for increased profits | Potential for increased influence and market dominance, possible negative impacts on smaller competitors |
| Suppliers | Increased bargaining power from the combined entity, potential for reduced pricing power | Potential for reduced options for smaller suppliers, potential for reduced innovation and product variety |
| Smaller grocery stores | Increased competition, potential for decreased market share, possible closures | Potential for loss of local businesses, reduced community ties |
| Local markets | Loss of local diversity, potential reduction in local economic activity | Reduced options for locally-sourced products, decreased community ties and identity |
Public Response and Stakeholder Concerns
The proposed merger between Kroger and Albertsons has sparked a wide range of reactions, from enthusiastic support to fervent opposition. This response reflects the complex interplay of economic, social, and political factors surrounding the consolidation of such a significant retail presence. Stakeholder concerns span a broad spectrum, highlighting the potential ramifications of this unprecedented merger on competition, labor practices, and consumer welfare.The public’s response to the proposed merger is multifaceted, ranging from anxieties about potential price increases and reduced product variety to hopes for improved efficiency and streamlined operations.
A key aspect of this complex issue is the need to carefully analyze the perspectives of various stakeholders to fully grasp the potential impact of the merger.
Public Opinions and Reactions
The public’s response to the merger has been characterized by a mix of optimism and apprehension. Some consumers anticipate lower prices and increased selection due to economies of scale, while others fear reduced competition and higher prices. Online discussions and social media posts reveal both positive and negative sentiments, reflecting the varying perspectives on the potential outcomes of this mega-merger.
The FTC’s investigation into the Kroger-Albertsons merger is certainly a hot topic right now, raising questions about market dominance and consumer choice. While the potential consequences of such a large merger are being heavily scrutinized, it’s worth remembering similar, high-profile events like the recent armorer Alec Baldwin Rust shooting incident. Ultimately, both situations highlight the complex web of factors affecting industries and daily life, and the FTC’s decision on the merger will be crucial in shaping the future of grocery retail.
The diversity of opinions underscores the need for careful consideration of all viewpoints.
Concerns of Labor Unions
Labor unions have expressed significant concerns regarding job security, wages, and working conditions. They fear potential job losses or cuts in benefits if the merged entity seeks to streamline operations by reducing staff. Union representatives have initiated discussions with both companies to address their concerns and ensure that the merger does not negatively impact their members’ employment prospects.
They emphasize the importance of maintaining fair labor practices and protecting the rights of workers.
Concerns of Competitors
Competitors in the grocery industry have voiced concerns about the diminished competitive landscape. They worry that a combined Kroger-Albertsons would wield significant market power, potentially leading to higher prices and reduced innovation. This fear of reduced competition is a critical factor in the ongoing debate about the merger’s overall impact on the market. These concerns highlight the importance of maintaining a healthy level of competition in the grocery industry.
Concerns of Consumer Groups
Consumer advocacy groups have expressed worries about potential price increases and reduced product variety. They fear that the merged entity could use its expanded market share to raise prices on essential goods, impacting the affordability of groceries for consumers. These groups emphasize the importance of preserving consumer choice and ensuring the availability of affordable and diverse products. Their concern lies in the potential for market manipulation and reduced consumer options.
Arguments in Favor of the Merger from the Companies’ Perspective
Kroger and Albertsons have presented arguments in favor of the merger, citing potential cost savings and improved operational efficiencies. They assert that these benefits could be passed on to consumers in the form of lower prices and greater selection. The companies argue that a combined entity would have greater negotiating power with suppliers, enabling them to procure goods at more competitive rates.
They also emphasize the potential for enhanced distribution networks and streamlined supply chains, leading to improved efficiency and consumer convenience.
Potential Legal Challenges and Regulatory Hurdles
The Federal Trade Commission (FTC) has initiated an investigation into the proposed merger, signaling potential regulatory hurdles. The FTC’s scrutiny reflects concerns about the potential impact of the merger on competition in the grocery industry. The outcome of the FTC’s investigation will be crucial in determining the merger’s future. Potential legal challenges and regulatory hurdles highlight the need for careful consideration of the legal implications of the proposed merger.
Summary of Stakeholder Arguments and Concerns
| Stakeholder Group | Arguments | Concerns |
|---|---|---|
| Labor Unions | Maintaining fair labor practices, job security, and benefits. | Potential job losses, wage reductions, and negative impact on working conditions. |
| Competitors | Maintaining a healthy level of competition in the grocery industry. | Reduced competition, higher prices, and diminished innovation. |
| Consumer Groups | Preserving consumer choice and ensuring affordability. | Potential price increases, reduced product variety, and market manipulation. |
| Kroger and Albertsons | Cost savings, improved operational efficiencies, and greater negotiating power. | Regulatory hurdles and legal challenges. |
Potential Market Analysis
The Kroger-Albertsons merger presents a significant opportunity for market consolidation in the grocery industry. Understanding the dynamics of this sector and the potential ramifications of the merger is crucial for assessing its impact on consumers, competitors, and the overall market structure. This analysis will delve into the evolving grocery landscape, the merger’s potential market share implications, and the possible effects on pricing, product offerings, and the supply chain.
Grocery Industry Market Dynamics and Trends
The grocery industry is experiencing substantial transformation, driven by evolving consumer preferences, technological advancements, and increased competition from online retailers and smaller, specialized grocers. E-commerce is rapidly changing the way consumers shop for groceries, with online ordering and delivery services becoming increasingly popular. This trend is challenging traditional brick-and-mortar stores to adapt and innovate. Furthermore, consumers are increasingly demanding healthier, sustainable, and locally sourced products, influencing the types of goods offered and the supply chains used.
These trends are impacting existing market structures and creating opportunities for companies to differentiate themselves.
Potential Market Share Implications
The merger’s impact on market share will depend on several factors, including the effectiveness of the combined company’s strategies and the competitive response from other retailers. A significant consolidation of market share could potentially lead to reduced competition, potentially impacting consumer choices and prices. A larger entity with a broader reach could leverage its scale to negotiate lower prices with suppliers, potentially leading to lower prices for consumers.
However, reduced competition could also lead to higher prices in the long term if the merged entity doesn’t face enough competitive pressure.
Influence on Pricing Strategies and Product Offerings
The merger may influence pricing strategies in several ways. A combined entity could potentially leverage its size to negotiate better deals with suppliers, leading to lower prices for consumers. However, the absence of strong competition might encourage the merged company to raise prices, especially in the absence of countervailing factors such as strong price competition from other retailers or new entrants.
Furthermore, the expanded product offerings of the combined company might include a broader range of products, potentially catering to diverse consumer preferences. This could include more specialty items, private label products, and options for consumers seeking healthier or sustainable choices.
Effects on Supply Chain and Distribution Networks
The merger could lead to significant changes in the supply chain and distribution networks. A larger, integrated entity might streamline operations, potentially leading to improved efficiency and lower costs. This could be beneficial for both the merged company and consumers. However, potential disruptions to existing supply chains and distribution networks could also occur during the transition phase, possibly leading to shortages or increased costs.
The FTC’s investigation into the Kroger-Albertsons merger is a complex issue, raising questions about market dominance and consumer choice. It’s a reminder of how big business decisions can ripple through the economy, much like the emotional turmoil felt by the individuals featured in the poignant piece “Grief is for people sloane crosley” grief is for people sloane crosley.
Ultimately, the FTC’s decision on the merger will likely have far-reaching consequences for the grocery industry, influencing pricing and accessibility for everyone.
The ability of the merged entity to effectively manage these complexities will be crucial to the success of the merger.
Comparison with Historical Trends in Similar Mergers
| Merger | Potential Impact | Historical Trends |
|---|---|---|
| Kroger-Albertsons | Increased market share, potential for price adjustments, shift in product offerings, and supply chain changes. | Past mergers in the grocery industry have shown varying results. Some have resulted in efficiency gains and lower prices, while others have faced challenges in integrating operations and maintaining competitive pressures. |
| Other Similar Mergers (Example: A&P and Safeway) | Increased consolidation and potential impacts on competition and pricing. | Historically, similar mergers have sometimes led to increased prices and reduced variety in some regions. |
A detailed examination of past mergers and acquisitions within the grocery industry will provide further insights into the potential consequences of this proposed merger. Analysis of these past cases should be examined to evaluate potential success or failure factors and guide future strategies for the merged entity.
Legal and Regulatory Considerations: Ftc Kroger Albertsons Merger
The Kroger-Albertsons merger presents a complex web of legal and regulatory hurdles. Navigating these complexities is crucial for both companies, and the outcome will significantly impact the future of the grocery industry. Understanding the legal framework governing mergers, the FTC’s authority, potential challenges, and precedent-setting cases is vital to assessing the merger’s viability.The US antitrust laws, primarily the Clayton Act and the Sherman Act, establish a framework for scrutinizing mergers and acquisitions to prevent anti-competitive practices.
These laws aim to maintain a competitive marketplace, ensuring that consumers benefit from diverse choices and fair pricing. The FTC, as a regulatory body, plays a pivotal role in enforcing these laws.
Legal Framework Surrounding Mergers and Acquisitions
Antitrust laws, particularly the Clayton Act and Sherman Act, govern mergers and acquisitions. These statutes aim to prevent anti-competitive practices, promoting a competitive market. The Clayton Act specifically addresses mergers that may substantially lessen competition, while the Sherman Act prohibits restraint of trade and monopolies. These laws establish standards for evaluating mergers, focusing on the potential impact on competition within relevant markets.
FTC’s Legal Authority to Intervene
The Federal Trade Commission (FTC) possesses substantial legal authority to intervene in mergers and acquisitions. The FTC can challenge mergers that it deems anti-competitive, potentially harming consumers by reducing competition, raising prices, or diminishing product choices. This authority is based on the FTC Act and related legal precedents. The agency’s ability to investigate, gather evidence, and file lawsuits is critical in ensuring fair competition.
Potential Legal Strategies to Challenge or Defend the Merger
Both parties in a merger case can employ various legal strategies. Challenging parties may argue that the merger substantially reduces competition, harming consumers. They may present evidence of market concentration, reduced output, or price increases. Defending parties, on the other hand, may argue that the merger benefits consumers through increased efficiency, lower prices, or enhanced product offerings.
They may emphasize economies of scale and synergies.
Key Legal Precedents Related to Similar Mergers
Numerous previous merger cases provide valuable precedent. Examples include recent antitrust challenges to other large mergers in the retail industry, which often focus on market share, geographic reach, and the potential for reduced consumer choice. These precedents guide the FTC in evaluating the current merger and influence the strategies used by both parties. Cases such as the Staples-Office Depot merger or the recent hospital consolidation cases, for instance, highlight the scrutiny faced by mergers involving similar market dynamics.
Legal Steps Involved in the Merger Approval Process
| Step | Description |
|---|---|
| Notification | The merging companies notify the FTC and relevant state agencies about their intent to merge, providing necessary details. |
| Investigation | The FTC investigates the potential impact of the merger on competition. This involves analyzing market share, pricing, and consumer choices. |
| Potential Challenges | The FTC may challenge the merger based on its analysis of potential anti-competitive effects. |
| Negotiations and Settlements | The merging companies may negotiate with the FTC to address concerns or modify the merger agreement. |
| Court Action | If no agreement is reached, the FTC can file a lawsuit to block the merger. |
| Final Decision | A court ultimately determines whether the merger will be allowed to proceed. |
Alternatives to the Merger
The proposed merger between Kroger and Albertsons has sparked considerable debate, raising concerns about potential anti-competitive effects. However, the grocery giants could have pursued alternative strategies to achieve their growth and market expansion goals without the complexities and risks of a large-scale merger. Exploring these alternatives is crucial for understanding the broader landscape of potential outcomes and the long-term implications for the grocery industry.Alternative strategies, including strategic alliances and joint ventures, could offer numerous benefits without the potential pitfalls of a full-scale merger.
These alternatives can provide a pathway for achieving similar market objectives while mitigating regulatory hurdles and fostering innovation in the grocery sector.
Strategic Alliances and Joint Ventures
Strategic alliances and joint ventures represent a powerful means of collaboration that can yield considerable benefits for both Kroger and Albertsons. These collaborative ventures can facilitate market expansion and resource sharing without the substantial regulatory hurdles of a merger. A successful example is the collaboration between various companies in the technology sector, where alliances have been instrumental in developing new products and services.
- Shared Distribution Networks: A strategic alliance could focus on optimizing distribution networks, enabling both companies to leverage each other’s strengths and economies of scale. This could lead to lower operational costs and enhanced supply chain efficiency. For instance, one company could provide warehousing facilities while the other handles transportation, streamlining the entire process.
- Joint Marketing Campaigns: A joint venture could encompass integrated marketing campaigns, leveraging both companies’ existing customer bases to expand market reach and drive sales. This synergy could involve joint advertising and promotional initiatives tailored to target specific customer segments.
- Shared Technology Platforms: Pooling resources and expertise could result in a shared technology platform, allowing both companies to streamline operations and enhance customer experience. This would involve the joint development of mobile apps, online ordering systems, and other digital tools to improve efficiency and customer satisfaction.
Potential Benefits of Alternative Approaches
Alternative strategies, such as strategic alliances or joint ventures, offer potential benefits that extend beyond the scope of a merger. These benefits include a more gradual approach to market expansion, enhanced operational efficiency, and a reduced regulatory burden. For example, a joint venture could focus on a specific segment of the market, allowing the companies to target a niche with increased focus and resources.
Potential Drawbacks of Alternative Approaches, Ftc kroger albertsons merger
While alternative approaches present opportunities, they also come with potential drawbacks. The decision to pursue an alliance or joint venture may involve relinquishing some degree of control over operational decisions and strategic direction. There could also be complexities in coordinating efforts and sharing resources.
Comparative Analysis of Strategic Alternatives
| Strategic Alternative | Potential Outcomes | Benefits | Drawbacks |
|---|---|---|---|
| Merger | Potential for significant market share gains, economies of scale, and operational efficiencies. | Increased market power, economies of scale, enhanced brand visibility | Regulatory scrutiny, potential antitrust concerns, cultural integration challenges |
| Strategic Alliance | Focused expansion into specific markets or product segments. | Reduced regulatory hurdles, flexibility, shared resources | Potential limitations in market reach, loss of control over specific operations |
| Joint Venture | New entity with focused market objectives, increased market penetration. | Synergy, shared expertise, reduced risk | Complexity in decision-making, potential for conflicts of interest |
Summary
In conclusion, the FTC Kroger Albertsons merger presents a complex scenario with numerous implications. While potential cost savings and increased market share are cited as benefits, concerns about reduced competition and higher prices for consumers are also valid. The FTC’s scrutiny and public response will be critical in shaping the outcome of this merger, potentially setting a precedent for future large-scale acquisitions in the grocery sector.
Further analysis and discussion are needed to fully understand the long-term effects on the industry and consumers.
FAQ Guide
What are the key regulations the FTC uses to evaluate mergers?
The FTC evaluates mergers based on various regulations aimed at preventing anti-competitive practices. These regulations consider market concentration, potential harm to competition, and the overall impact on consumers. Specific criteria and thresholds are applied to assess the potential for harm.
What are some alternative strategies Kroger and Albertsons could pursue besides merging?
Alternatives to the merger include strategic alliances, joint ventures, or focused acquisitions of smaller players within the industry. These alternatives can achieve similar business objectives while minimizing potential antitrust concerns.
How might this merger affect smaller grocery stores?
A merger of this scale could potentially lead to reduced competition for smaller grocery stores, potentially impacting their ability to compete and survive in the market. The impact would likely vary depending on the specific geographic area and the overall competitive landscape.
What are the arguments in favor of the merger from Kroger and Albertsons’ perspective?
Arguments in favor of the merger might include enhanced economies of scale, cost savings, and increased purchasing power, potentially leading to lower prices for consumers. However, the exact specifics of these arguments would need to be reviewed in the public filings.

