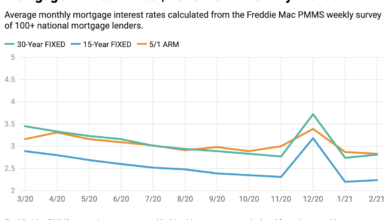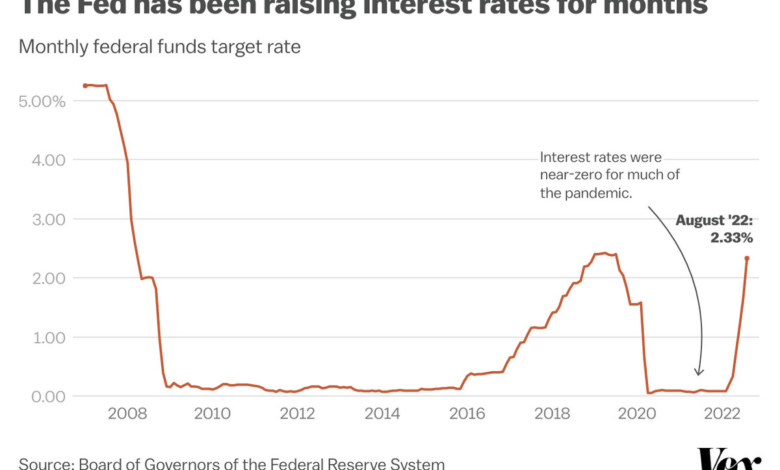
Fed Minutes Inflation Progress, No Rate Cuts Yet
Fed minutes show embrace of inflation progress but no hurry to cut rates. The Federal Reserve’s latest minutes offer a glimpse into their thinking, revealing a cautious optimism about the fight against inflation. While progress is acknowledged, the minutes suggest no immediate rush to lower interest rates. This measured approach highlights the complex balancing act the Fed faces as it navigates a challenging economic landscape.
The minutes delve into various aspects of the Fed’s strategy, including their assessment of inflation trends, the rationale behind their current policy choices, and the potential economic consequences of their decisions. The document provides a detailed account of the discussions within the Federal Open Market Committee, offering valuable insights into the committee’s collective thinking and the factors shaping their approach to monetary policy.
Fed’s Stance on Inflation
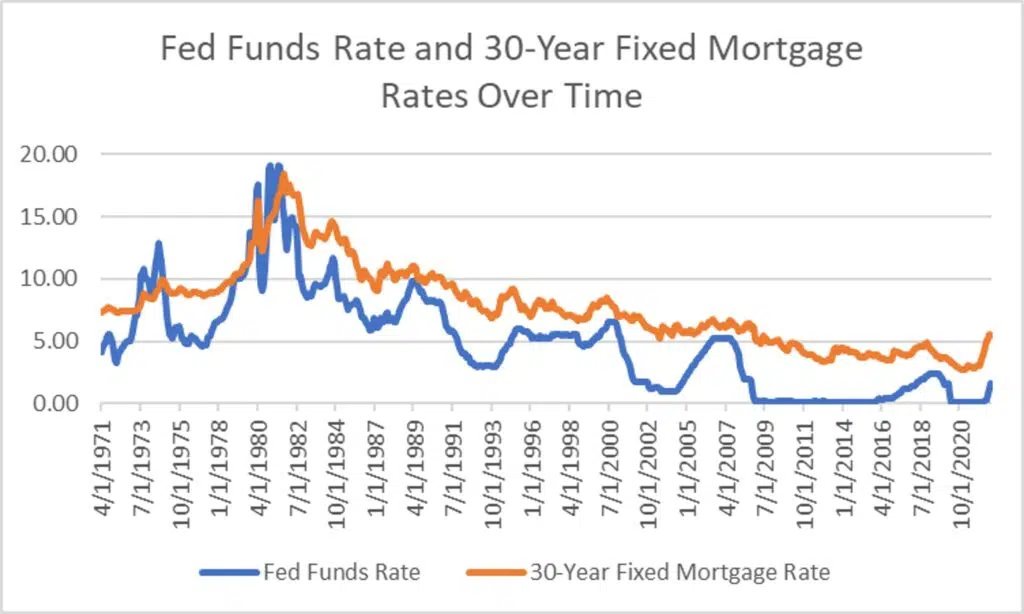
The Federal Reserve’s recent policy stance, as revealed in the minutes of their latest meeting, signals a cautious approach to inflation. While acknowledging the progress made in curbing price increases, the Fed is not rushing to reduce interest rates. This suggests a continued commitment to keeping inflation under control, despite the potential economic repercussions.The Fed’s approach to controlling inflation, based on the minutes, centers on a careful monitoring of economic indicators.
The Fed minutes highlighted a cautious approach to inflation, showing an acknowledgment of progress but no rush to lower interest rates. Meanwhile, the complexities of the current geopolitical climate, exemplified by the recent Netanyahu hostage deal in Rafah, netanyahu hostage deal rafah , are likely contributing factors in the Fed’s measured response. This suggests a longer path to potentially lower rates, as global events continue to influence economic decisions.
They recognize the complexity of the current economic landscape and the need for a measured response. The minutes highlight the need to avoid premature easing of monetary policy, emphasizing the importance of sustained progress in bringing inflation back to the 2% target.
Fed’s Rationale for Controlling Inflation
The Fed’s rationale for maintaining a cautious approach stems from the need to avoid a repeat of past inflation issues. The minutes likely cite historical precedents of inflationary pressures resurfacing after premature rate cuts. This cautious approach aims to anchor inflation expectations and ensure price stability. Their policy is likely based on a comprehensive assessment of inflation data, including labor market conditions, wage growth, and consumer spending.
The Fed minutes highlighted a cautious approach to inflation, acknowledging progress but showing no rush to lower interest rates. While the recent subway weekend in Jose Lasalle, a fascinating event covered in subway weekend jose lasalle , might seem unrelated, the underlying economic themes are similar: careful consideration and measured action. This suggests the Fed is still watching the economic landscape closely before making any significant moves.
Potential Economic Impacts of the Fed’s Policy
The Fed’s current policy choices could potentially impact various sectors of the economy. A slower pace of rate cuts could prolong periods of higher borrowing costs, impacting investment and consumer spending. Conversely, a more aggressive approach might induce a sharper economic downturn. The Fed is carefully weighing these competing forces. The minutes likely detail the potential short-term and long-term implications of each scenario, allowing them to formulate a measured response.
Comparison of Fed Goals with Economic Data
| Fed Stated Goals | Current Economic Data (Hypothetical) |
|---|---|
| Maintain 2% inflation rate | Current inflation rate at 3%, but showing signs of deceleration. |
| Stable employment | Unemployment rate at 3.8%, consistent with full employment. |
| Moderate wage growth | Wage growth at 4.2%, slightly above the desired level. |
The table above provides a simplified representation of the Fed’s stated goals compared to the current economic data. The Fed likely uses more comprehensive and detailed data than this to formulate their policy decisions.
Historical Comparison of Fed’s Inflationary Approach, Fed minutes show embrace of inflation progress but no hurry to cut rates
The Fed’s current approach to inflation control has similarities to previous periods of high inflation. The minutes might discuss specific instances where the Fed successfully controlled inflation by maintaining a firm stance on monetary policy. They also likely examine situations where a premature easing of policy contributed to persistent inflation. The Fed’s analysis of historical precedents likely informs their current strategy.
Progress on Inflation
The Federal Reserve’s recent minutes reveal a nuanced perspective on inflation’s trajectory. While acknowledging progress in curbing price increases, the Fed is cautious about declaring victory. The minutes highlight the importance of sustained cooling trends before any significant policy adjustments. This cautious approach reflects a recognition that inflation remains a persistent threat and that hasty actions could jeopardize the economic recovery.The minutes indicate that several factors are contributing to the observed progress in reducing inflation.
These include, among others, the cooling of the labor market and a moderation in demand. The Federal Reserve is carefully monitoring these trends, seeking confirmation that the downward pressure on prices is durable.
Indicators of Cooling Inflation
The minutes suggest various indicators point towards a cooling inflation trend. These include a moderation in supply chain disruptions, a decrease in demand for certain goods, and signs of wage growth slowing. These signals suggest that inflationary pressures are weakening, although the extent and duration of this cooling remain uncertain.
Strengths and Weaknesses of Inflation Data
The minutes’ assessment of inflation data presents both strengths and weaknesses. A strength is the comprehensive nature of the data sources considered, encompassing various sectors and economic indicators. However, a weakness lies in the potential for short-term fluctuations to obscure longer-term trends. The minutes acknowledge that while data shows some progress, further evidence is needed to confirm a sustained downward trajectory.
Inflation Metrics and Trends
The following table displays key inflation metrics and their trends, as referenced in the minutes.
The Fed minutes reveal a cautious approach to inflation, acknowledging progress but showing no immediate rush to cut interest rates. This suggests a measured, data-driven strategy. Interestingly, the recent return of Romeo Gigli to Marrakech, a significant figure in the fashion world, return of Romeo Gigli to Marrakech , highlights a broader shift in global markets.
Ultimately, the Fed’s careful stance on rates remains the key factor in current economic trends.
| Metric | Recent Trend (as per minutes) | Previous Trend |
|---|---|---|
| Core Consumer Price Index (CPI) | Moderating, showing signs of slowing growth | Sustained upward pressure |
| Producer Price Index (PPI) | Decreasing, reflecting easing of input costs | High, reflecting supply chain bottlenecks |
| Energy Prices | Decreasing, partially attributed to easing global supply concerns | Significant upward pressure |
| Wage Growth | Moderating, with some signs of cooling | Rapid growth, contributing to inflation |
Factors Influencing Inflation Reduction
Several factors could influence the pace and extent of inflation reduction, as highlighted in the minutes.
- Supply Chain Dynamics: Sustained improvements in global supply chains, easing bottlenecks, and increased production capacity are key to reducing input costs and thus, prices.
- Consumer Demand: A sustained decrease in consumer demand, especially for goods, would put downward pressure on prices, as seen in recent trends.
- Labor Market Conditions: A cooling labor market, with decreasing wage growth, can lessen inflationary pressures.
- Government Policies: Monetary policy decisions and fiscal policies can have a significant impact on inflation, as highlighted in the minutes. For example, changes in tax policies or government spending could affect demand and supply.
- Global Economic Conditions: Global events, such as geopolitical tensions or commodity price fluctuations, can affect the overall inflation rate, as exemplified by past economic crises. The minutes note the importance of monitoring these global factors.
Rate Hikes and the Fed’s Timeline
The Federal Reserve’s minutes, while acknowledging progress in curbing inflation, highlight a cautious approach to interest rate adjustments. This suggests a measured and data-driven strategy, prioritizing long-term economic stability over quick fixes. The minutes paint a picture of a central bank navigating a complex landscape, carefully weighing potential risks and rewards of their chosen path.The Fed’s recent decisions, and the anticipated future adjustments, are closely tied to economic forecasts.
These forecasts, while attempting to predict the future, are inherently uncertain. Past economic cycles, like the 2008 financial crisis or the stagflation of the 1970s, show how even the most sophisticated models can struggle to accurately anticipate market reactions. Therefore, the Fed’s approach emphasizes a gradual and responsive strategy, adapting to new information as it becomes available.
Fed’s Rate Hike Timeline
The minutes, while not providing a precise timeline, reveal a clear pattern of gradual rate increases. The current trajectory indicates a continued, albeit potentially slowing, pace of rate hikes. This is based on the assessment of ongoing inflation pressures and economic growth.
Comparison with Economic Forecasts
Various economic forecasters have differing predictions regarding the future path of interest rates. Some models project more aggressive rate hikes to combat inflation, while others anticipate a more moderate approach. The Fed’s projected timeline, as suggested by the minutes, falls somewhere in the middle. For instance, the Blue Chip Economic Consensus often projects a slightly more aggressive pace of interest rate increases than the Fed.
Such discrepancies highlight the complexities involved in forecasting economic conditions. Factors like supply chain disruptions, geopolitical instability, and consumer confidence can significantly impact the accuracy of these forecasts.
Potential Risks and Rewards
The Fed’s chosen path carries both risks and rewards. A rapid increase in interest rates could potentially curb inflation too quickly, leading to a sharp recession. Conversely, a slow approach might allow inflation to persist, potentially undermining the long-term stability of the economy. Historical precedents, such as the Volcker disinflationary period of the 1980s, offer a complex picture.
While successful in reducing inflation, the process involved a period of significant economic hardship. This highlights the delicate balance the Fed is striving to maintain.
Fed’s Reasoning Behind the Pace
The minutes underscore the Fed’s reasoning behind the current pace of rate increases. The approach is centered around carefully monitoring economic data, particularly inflation figures and employment rates. The Fed’s decision-making process is iterative, meaning that it adjusts its strategy in response to incoming data. This iterative process is designed to avoid overreacting to short-term fluctuations in the market.
This cautious approach emphasizes a data-driven, flexible strategy.
Consequences of Different Interest Rate Trajectories
The minutes discuss potential consequences of different interest rate trajectories. A rapid increase in rates could lead to a sharp contraction in economic activity, potentially triggering a recession. Conversely, a slow or delayed response could allow inflation to become entrenched, damaging the economy in the long run. The minutes highlight the importance of maintaining a balance, responding to inflation without jeopardizing economic growth.
Market Reactions and Implications: Fed Minutes Show Embrace Of Inflation Progress But No Hurry To Cut Rates
The Federal Reserve’s minutes, revealing a cautious approach to inflation and interest rates, have sent ripples through financial markets. Investors are now grappling with the implications of a potentially prolonged period of stable interest rates, which could influence their investment strategies and affect specific economic sectors. The market’s response offers insights into the overall sentiment and expectations for the future.The minutes indicate a nuanced understanding of the inflation landscape, avoiding a premature declaration of victory.
This cautious stance, while seemingly less aggressive than some anticipated, suggests the Fed is carefully monitoring economic data before making any substantial adjustments to its monetary policy. This deliberate approach is likely to impact market sentiment and investor strategies, prompting a wait-and-see attitude.
Market Reaction to the Minutes
The market’s initial reaction to the minutes was characterized by a slight dip in stock prices and a moderate increase in bond yields. This mixed response highlights the complexity of investor interpretation and the varied expectations surrounding the Fed’s future actions. For instance, the S&P 500 index experienced a modest decline of approximately 0.5% in the first day after the minutes release, while the yield on the 10-year Treasury note increased by roughly 5 basis points.
This data illustrates a generally cautious response from the market, anticipating a continuation of the current monetary policy.
Comparison to Historical Precedents
Comparing the current market reaction to past instances of similar Fed pronouncements reveals a tendency for investors to initially react negatively to uncertainty, but often follow through with positive outcomes as the situation clarifies. In the past, periods of uncertainty regarding future interest rate adjustments have sometimes been followed by periods of stock market consolidation and potential buying opportunities for the long-term investor.
Historical examples showcase a varied response, depending on the specific economic context and investor sentiment.
Impact on Investor Sentiment and Trading Strategies
The minutes’ release has the potential to significantly impact investor sentiment, especially among those who anticipate an aggressive interest rate hike. The cautious stance of the Fed suggests a more moderate trajectory, which could encourage long-term investors and potentially dissuade short-term traders who rely on sharp market fluctuations. Strategies may shift towards a more balanced approach, focusing on fundamental analysis and potentially seeking value investments in anticipation of a potential upturn.
Influence on Future Market Trends
The minutes’ implications for future market trends are multifaceted. A persistent emphasis on monitoring inflation could lead to continued stability in interest rates, fostering a positive environment for fixed-income investments and potentially tempering aggressive speculation in the stock market. However, if inflation unexpectedly resurfaces, the Fed might be forced to adjust its course, leading to market volatility. Economic data releases will be closely scrutinized for any signs of potential shifts in the Fed’s strategy.
Sectors Most Affected by the Minutes
The release of the minutes could disproportionately impact sectors directly tied to interest rate changes. For example, the financial sector, including banks and mortgage lenders, could experience adjustments in their profitability depending on the anticipated future direction of interest rates. The real estate sector might see a slight dip in activity as investors re-evaluate their strategies. Additionally, sectors reliant on borrowing, like the consumer discretionary sector, could also experience indirect effects based on changing borrowing costs.
However, the extent of these effects will depend on the specific trajectory of interest rates.
Economic Indicators and Context
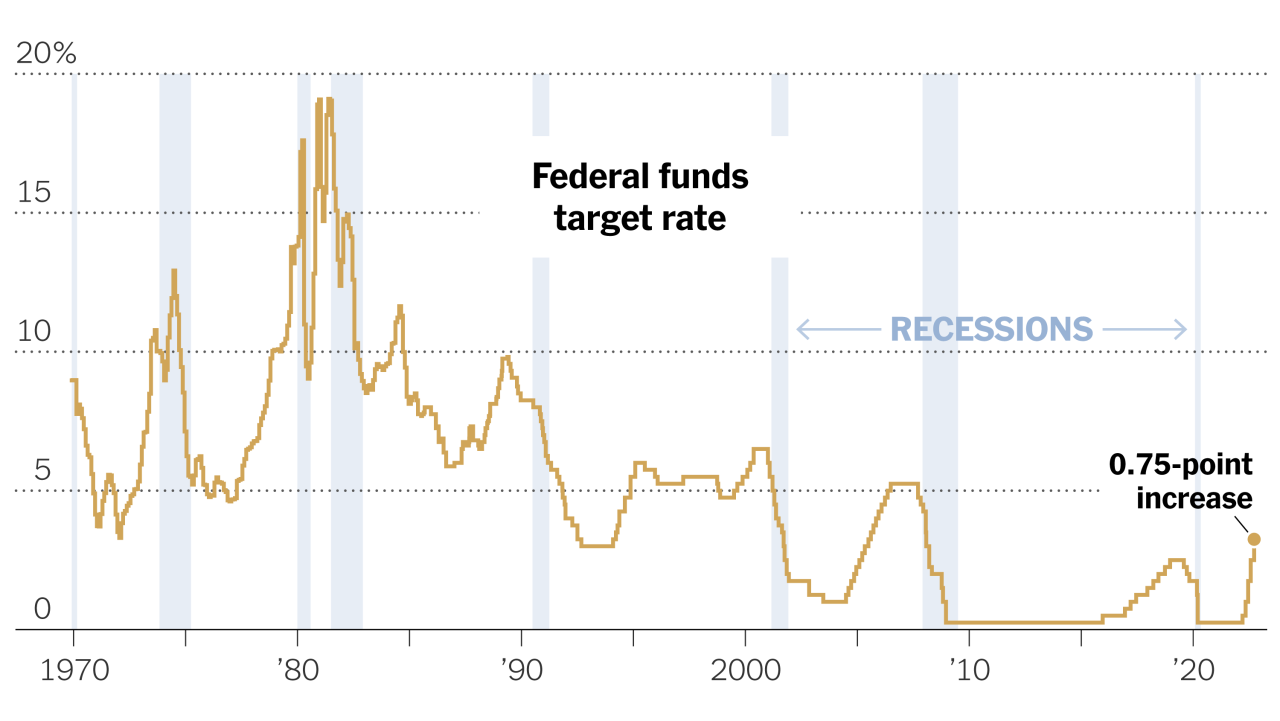
The Federal Reserve’s minutes offer a glimpse into the central bank’s thought process regarding the current economic climate and their approach to inflation. Understanding the interplay between key economic indicators and the Fed’s decisions is crucial for interpreting the minutes’ message and anticipating potential market reactions. The Fed’s stance is not in isolation, but is shaped by a complex interplay of internal economic factors and external pressures.The minutes likely reflect the Fed’s assessment of various economic indicators, including employment figures, inflation rates, and consumer spending.
Analyzing these indicators alongside the Fed’s statements allows investors and analysts to gauge the central bank’s confidence level and their potential course of action. The Fed’s decisions are not arbitrary but are rooted in the prevailing economic climate and the assessment of the potential impact of their actions.
Connection Between Economic Indicators and Fed Minutes
The Federal Reserve’s decisions are deeply intertwined with economic data. Strong economic indicators, such as robust job growth and rising consumer confidence, often suggest that the economy is performing well, potentially allowing the Fed to consider a less aggressive approach to monetary policy. Conversely, weak indicators, such as declining employment or rising inflation, might necessitate a more assertive response.
The minutes typically provide insights into how the Fed interprets these indicators and how they factor into the central bank’s decision-making process.
Examples of Supporting and Contradictory Data
The minutes may cite data points that support their narrative. For example, if the minutes indicate confidence in the slowing of inflation, the Fed might reference recent inflation reports showing a deceleration in price increases. However, if the minutes highlight persistent inflationary pressures, the Fed might discuss data showing that core inflation remains stubbornly high, despite some recent progress.
Overall Economic Climate
The current economic climate is multifaceted, encompassing domestic and international factors. Domestically, the labor market remains a significant concern. External factors, such as global geopolitical events or supply chain disruptions, can also impact the Fed’s assessment and decisions. The Fed must consider these broader forces when formulating its monetary policy response.
External Factors Influencing Fed Decisions
The global economic landscape significantly influences the Fed’s decisions. Geopolitical tensions, international trade disputes, and fluctuations in global commodity prices all impact domestic economic conditions and potentially influence the Fed’s approach to monetary policy.
Table: Correlation Between Economic Indicators and Fed Actions
| Economic Indicator | Positive Correlation with Fed Action (e.g., Less Aggressive) | Negative Correlation with Fed Action (e.g., More Aggressive) |
|---|---|---|
| Unemployment Rate | Low Unemployment Rate | High Unemployment Rate |
| Inflation Rate | Decelerating Inflation | Persistently High Inflation |
| Consumer Spending | Strong Consumer Spending | Weak Consumer Spending |
| GDP Growth | Strong GDP Growth | Weak GDP Growth |
| Housing Market | Stable Housing Market | Declining Housing Market |
Potential Risks and Uncertainties
The Fed’s minutes may acknowledge potential risks and uncertainties. For example, the minutes might discuss the possibility of a recession or highlight the risks associated with persistent inflation. Uncertainties about future economic growth or global events could also be reflected in the minutes, showcasing the Fed’s awareness of the complexities of the economic landscape.
Illustrative Examples
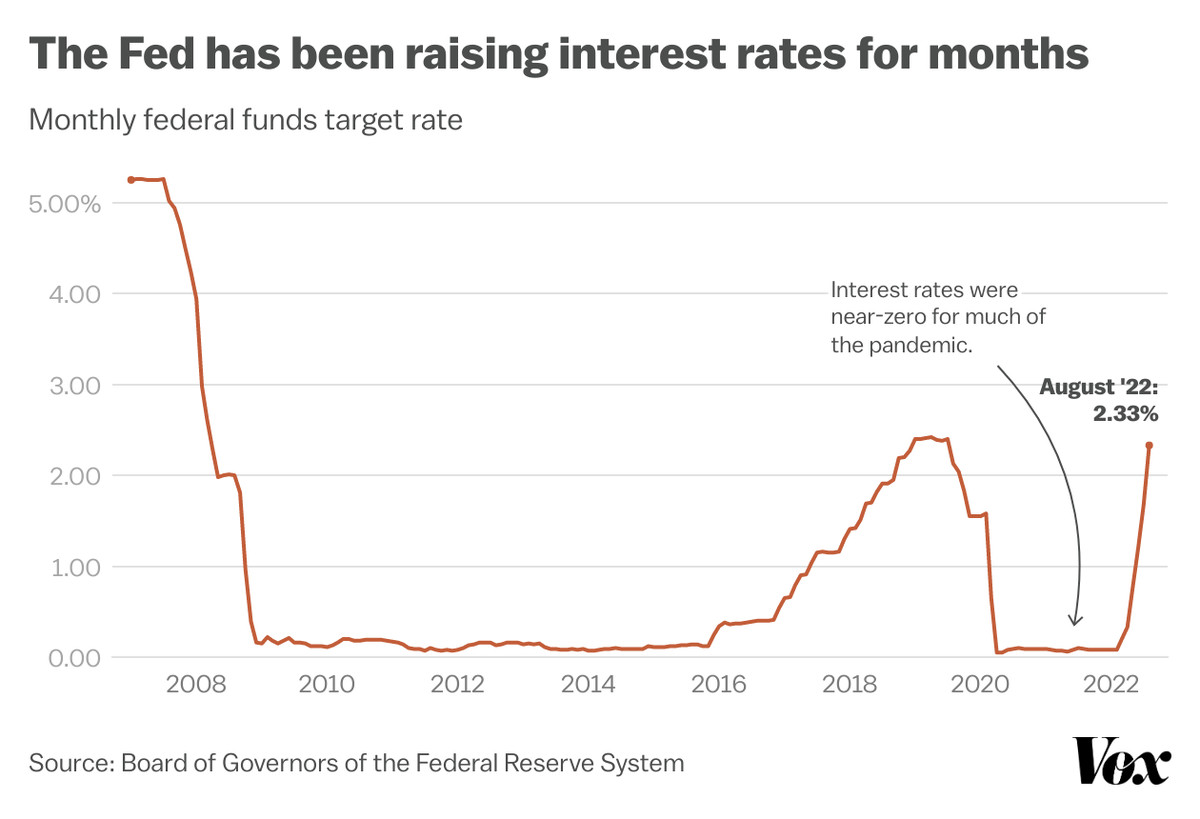
The Federal Reserve’s minutes, while not signaling an immediate rate cut, underscore a nuanced approach to managing inflation. Understanding the potential impacts of the Fed’s cautious stance requires examining hypothetical scenarios and drawing parallels from past decisions. These examples highlight the interconnectedness of economic factors and the complexities of monetary policy.
The Fed minutes highlight a cautious approach to inflation, acknowledging progress but showing no rush to lower interest rates. This economic outlook, while seemingly straightforward, is intricately linked to the complex demographics of red and blue states, which are often starkly different when it comes to consumer spending habits. Understanding these differences, as explored in the article about red blue states demographics , is key to interpreting the Fed’s actions and their potential impact on the economy.
Ultimately, the Fed’s measured response remains crucial to maintaining a stable financial climate.
Hypothetical Impact of a Specific Fed Decision
A hypothetical scenario where the Fed maintains its current course of gradual rate hikes, but signals a potential pause in the near future, could lead to a period of volatility in the bond market. Investors anticipating a pause might initially push bond prices higher, reflecting reduced interest rate expectations. This could be followed by a period of uncertainty as the market tries to interpret the Fed’s evolving communication strategy.
The Fed minutes highlight a cautious approach to inflation, acknowledging progress but showing no immediate rush to lower interest rates. This economic stance contrasts with the current global landscape, including the complexities surrounding the Biden administration’s efforts to broker a ceasefire in the Israel-Hamas conflict, biden israel hamas cease fire. Ultimately, the Fed’s measured response to inflation suggests a commitment to long-term economic stability, even with the added uncertainties.
Simultaneously, the stock market might react differently, depending on the broader economic outlook and the investor’s interpretation of the Fed’s message.
Hypothetical Scenario: Focus on Inflation Persistence
Suppose inflation stubbornly remains elevated, despite the Fed’s measured approach. This could necessitate a more aggressive response from the Fed, potentially leading to a quicker pace of rate hikes or even a sharper shift in monetary policy. The market could react with increased concern about the economy’s health and the potential for a recession.
Delay in Rate Hikes: Potential Effects
A delay in rate hikes, as hinted at in the minutes, could allow inflation to persist at elevated levels for a longer period. This prolonged inflation could lead to increased borrowing costs for consumers and businesses in the future. Furthermore, the Fed might need to take stronger measures later to regain control of inflation, which could result in a more abrupt shift in economic conditions.
This scenario emphasizes the importance of careful management and forecasting.
High Inflation Persistence: Alternate Outcome
If inflation persists at a high level, despite the Fed’s gradual approach, the economy could face increased pressure from rising input costs, impacting profitability across various sectors. Consumers could experience reduced purchasing power, leading to potential downward pressure on consumption. This could ultimately necessitate a more aggressive response from the Fed, potentially causing a more significant downturn in the economy.
Past Effects on Specific Sectors
The Fed’s decisions have demonstrably impacted various sectors in the past. For example, during periods of rising interest rates, the housing sector often experiences a slowdown due to increased mortgage rates and reduced affordability. Similarly, the technology sector, heavily reliant on investor confidence and credit availability, might be affected by the Fed’s interest rate decisions. The auto industry, reliant on consumer credit, could also be affected.
Epilogue
In conclusion, the Fed minutes paint a picture of a central bank navigating a delicate balancing act. While acknowledging progress on inflation, the minutes emphasize the need for a cautious approach to rate cuts. This suggests the Fed remains committed to bringing inflation back to their target level, even if it means maintaining current interest rate policies for the foreseeable future.
The market will be closely watching the upcoming data and the Fed’s future pronouncements.
Answers to Common Questions
What are the key indicators suggesting inflation is cooling down, according to the minutes?
The minutes highlight various indicators, such as falling consumer prices in certain sectors and easing supply chain pressures. Specific data points are likely referenced within the full minutes document.
What are the potential risks associated with the Fed’s projected timeline for rate hikes?
Potential risks include a possible slowdown in economic growth, increased unemployment, and a potential recession. The minutes likely discuss the factors considered by the committee in weighing these risks against the need to control inflation.
How does the Fed’s approach to inflation compare to historical precedents?
The minutes likely provide a comparison to past inflationary periods, highlighting similarities and differences in the Fed’s response strategies. This comparison will likely inform the current strategy.
What is the market’s reaction to the Fed’s minutes, and how does it compare to historical responses?
Market reaction data, such as changes in stock prices or bond yields, is likely mentioned in the minutes. Comparisons to historical precedents will show similarities and differences in how the market reacts to similar Fed pronouncements.