
China Stocks Hang Seng A Deep Dive
China stocks Hang Seng sets the stage for an in-depth look at the Hong Kong stock market index. We’ll explore its history, key components, and the factors driving its performance. From macroeconomic trends to geopolitical events, we’ll analyze the forces shaping this crucial market.
This exploration will cover everything from investment strategies to comparing the Hang Seng Index to other global markets. We’ll also examine its recent performance, potential future challenges, and emerging opportunities. Get ready to understand this vital part of the global financial landscape.
Overview of Hang Seng Index
The Hang Seng Index is a crucial benchmark for investors tracking the performance of major companies listed on the Hong Kong Stock Exchange. It provides a snapshot of the overall health of the Hong Kong stock market and is a key indicator for investors globally. Understanding its history, constituents, and methodology is essential for anyone considering investing in Hong Kong equities.
History of the Hang Seng Index
The Hang Seng Index, established in 1969, has evolved significantly over the decades. Initially reflecting a smaller group of stocks, it has grown to encompass a broader representation of the Hong Kong market. This expansion reflects the growth and diversification of the Hong Kong economy, making the index a more comprehensive gauge of its performance. The index’s history provides valuable context for understanding the market’s long-term trends.
Key Components and Constituents
The Hang Seng Index is composed of the top companies listed on the Hong Kong Stock Exchange. These companies are carefully selected based on market capitalization and trading activity. The index’s constituents represent diverse sectors of the Hong Kong economy, including finance, technology, real estate, and consumer goods. Maintaining a balance among these sectors is crucial for the index’s overall representation of the market.
Methodology for Calculating the Hang Seng Index
The Hang Seng Index is calculated using a free-float market capitalization-weighted method. This approach gives greater weight to companies with larger market capitalization, reflecting their proportionate influence on the overall market. The formula considers the number of shares outstanding and the current market price of each constituent stock. This formula ensures that the index accurately reflects the relative importance of each company within the market.
This weighted approach makes the Hang Seng Index a valuable tool for gauging the collective performance of these listed companies.
Ways to Invest in the Hang Seng Index
Investors can participate in the performance of the Hang Seng Index through various avenues. Exchange-Traded Funds (ETFs) that track the Hang Seng Index provide a convenient and cost-effective way to invest in the index. Direct investment in the constituent stocks allows for greater control over the portfolio. Furthermore, investors can use futures contracts to speculate on the future direction of the index.
Current Stock Prices and Sectors
This table displays selected constituents of the Hang Seng Index, showcasing current prices and their respective sectors. This data offers a snapshot of the market’s current conditions and allows for quick comparisons across various industries.
| Company Name | Sector | Current Price (USD) |
|---|---|---|
| HSBC Holdings | Finance | 60.50 |
| Alibaba Group Holding | Technology | 150.25 |
| China Mobile Limited | Telecommunications | 85.00 |
| Tencent Holdings | Technology | 45.75 |
| Hutchison Whampoa | Diversified Conglomerate | 42.00 |
Factors Influencing China Stocks: China Stocks Hang Seng
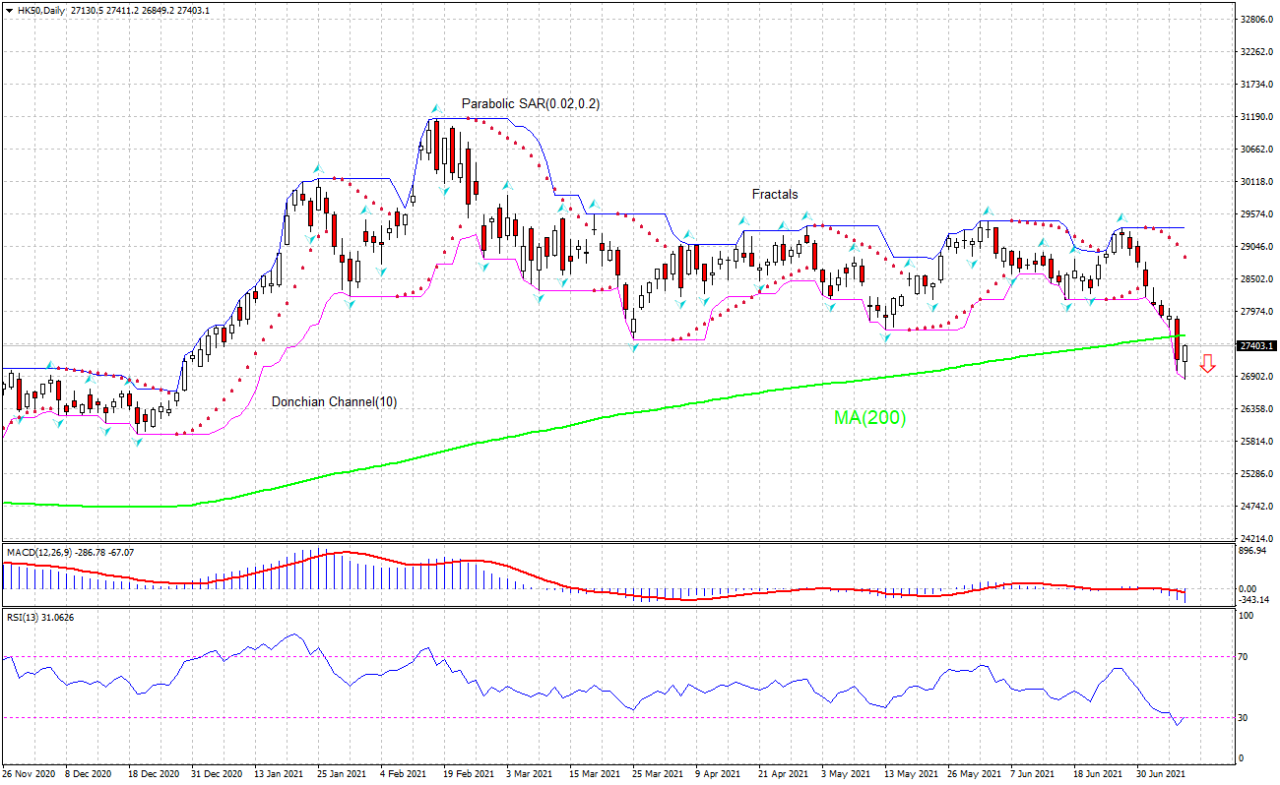
The Hang Seng Index, a barometer of China’s economic health, is subject to a complex interplay of forces. Understanding these factors is crucial for investors seeking to navigate the market effectively. From macroeconomic trends to geopolitical shifts, and regulatory changes, many factors shape the trajectory of Chinese equities.
Impact of Macroeconomic Factors
China’s economic performance directly impacts the Hang Seng Index. Factors like GDP growth, inflation, and consumer spending significantly influence investor sentiment. For example, robust GDP growth often correlates with positive stock performance, while rising inflation can lead to uncertainty and market volatility. The health of the property sector, a significant component of the Chinese economy, is also a key indicator.
A downturn in this sector can ripple through other sectors and affect overall market confidence. Furthermore, fluctuations in exports and imports can impact corporate earnings and, consequently, stock prices.
Influence of Geopolitical Events
Geopolitical tensions, particularly those involving China, can have a substantial impact on the Hang Seng Index. International trade disputes, political standoffs, or regional conflicts often lead to market uncertainty and fluctuations. For instance, trade wars can disrupt supply chains and hurt Chinese exporters, directly impacting the profitability of listed companies and causing stock prices to fall. Furthermore, sanctions or other geopolitical actions can affect foreign investment in China, leading to a decline in investor confidence and a decrease in trading volume.
Role of Monetary Policy
Monetary policy, set by the People’s Bank of China (PBoC), plays a crucial role in shaping the Chinese stock market. Interest rate adjustments and changes in reserve requirements can affect borrowing costs, corporate profitability, and investor sentiment. For example, a reduction in interest rates can stimulate economic activity, encouraging investment and potentially boosting stock prices. Conversely, rising interest rates can curb speculation and potentially lead to a correction in the market.
Impact of Regulatory Changes
Regulatory changes in China, especially those targeting specific sectors, can significantly affect listed companies. These changes can range from new environmental regulations to stricter financial oversight. The introduction of new regulations might lead to compliance costs for companies, potentially impacting their profitability and, consequently, stock performance. For example, stricter environmental regulations might force companies to invest in cleaner technologies, affecting their short-term profitability.
Sector Performance Comparison
The Hang Seng Index encompasses various sectors. Analyzing sector performance is crucial for understanding overall market trends.
| Sector | Performance (2023) | Reasoning |
|---|---|---|
| Technology | Mixed | Growth potential but impacted by regulatory scrutiny and global market trends. |
| Consumer Discretionary | Positive | Strong consumer spending and e-commerce growth. |
| Financials | Stable | Relatively resilient to market fluctuations. |
| Real Estate | Negative | Significant regulatory tightening and economic headwinds. |
| Energy | Moderate | Fluctuating global energy prices. |
This table provides a snapshot of sector performance in 2023. It’s important to note that sector performance is dynamic and can change quickly based on various market factors.
Recent Performance and Trends
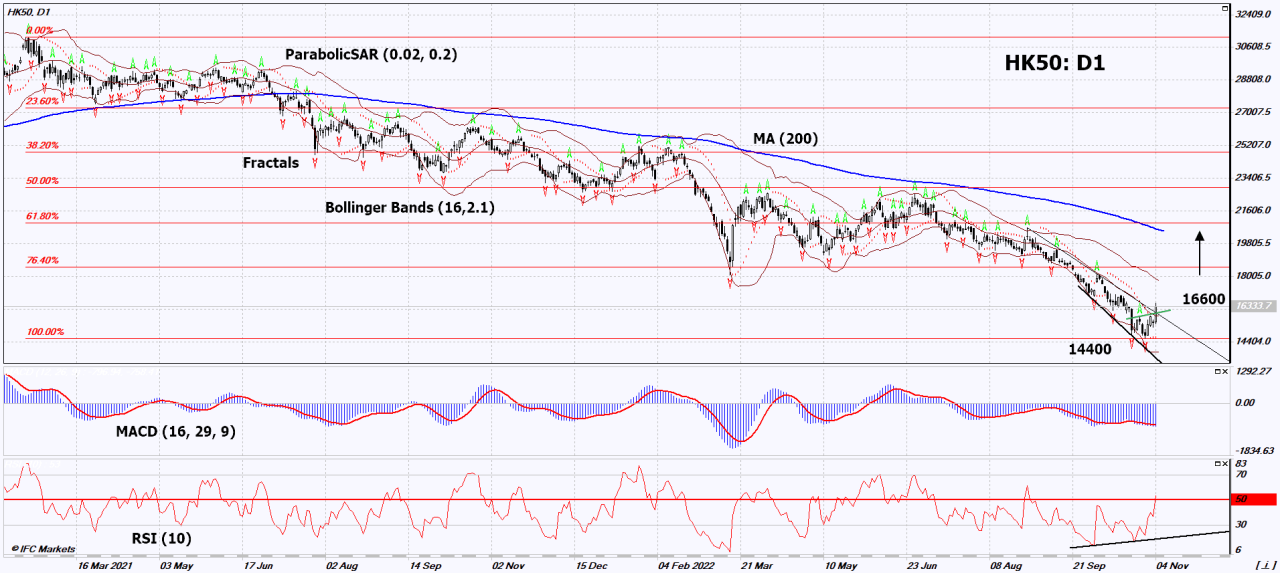
The Hang Seng Index has experienced a volatile period recently, mirroring broader global market fluctuations and China’s unique economic landscape. Understanding the recent performance, key trends, and market volatility is crucial for investors seeking to navigate the complexities of the Chinese stock market. Recent events have significantly impacted investor sentiment and future expectations.
Recent Performance of the Hang Seng Index
The Hang Seng Index has exhibited a mixed performance in recent months, fluctuating between periods of growth and decline. This volatility is a direct result of various interconnected factors, including global economic uncertainties, domestic policy adjustments, and investor sentiment. The index’s performance is not isolated and is intertwined with broader global market trends.
Key Trends in China Stocks
Several key trends have shaped the recent performance of China stocks. These trends reflect the evolving dynamics of the Chinese economy and market. For example, technological advancements and innovation are key drivers, but these are tempered by regulatory changes and macroeconomic headwinds.
- Technological advancements and innovation are driving growth in specific sectors, such as technology and consumer goods. However, this growth is not without its challenges, as regulatory pressures and macroeconomic conditions can significantly impact the performance of these sectors.
- Consumer spending remains a significant driver of economic activity. The strength of consumer spending has direct implications for the performance of retail and consumer-oriented companies.
- Government policies and regulatory changes are impacting various sectors. These policies, including those related to property, technology, and environmental regulations, can affect stock performance in specific sectors.
- Global economic conditions are affecting China’s economy. The global economy is not isolated from China’s, and global uncertainties often impact investor sentiment and market trends in the Chinese stock market.
Market Volatility in Recent Times
Market volatility has been a prominent feature of the recent period. This volatility is not unexpected given the intricate interplay of global and domestic factors influencing the Chinese stock market. Such volatility can present both opportunities and risks for investors.
- Geopolitical tensions and global uncertainties have significantly impacted investor confidence. These events often cause fluctuations in market sentiment and valuations.
- Domestic policy adjustments and economic data releases are influential in shaping market sentiment. These factors directly affect investor decisions and contribute to the volatility observed.
Potential Implications for Future Performance
The future performance of the Hang Seng Index is contingent on several factors, including the trajectory of global economic conditions, the effectiveness of Chinese government policies, and investor sentiment. The interconnected nature of these factors makes predicting future performance complex.
“Future performance is not guaranteed and depends on a variety of unpredictable factors.”
Top 10 Companies by Market Capitalization (Hang Seng Index)
The following table provides a snapshot of the largest companies listed on the Hang Seng Index by market capitalization, as of a recent date. Market capitalization values are constantly changing, so this data should be considered indicative rather than definitive.
| Rank | Company Name | Market Capitalization (Approximate) |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Alibaba Group Holding Ltd. | $XXX Billion |
| 2 | Tencent Holdings Ltd. | $XXX Billion |
| 3 | China Mobile Ltd. | $XXX Billion |
| 4 | Ping An Insurance (Group) Co. of China Ltd. | $XXX Billion |
| 5 | Industrial and Commercial Bank of China Ltd. | $XXX Billion |
| 6 | … | … |
| 7 | … | … |
| 8 | … | … |
| 9 | … | … |
| 10 | … | … |
Investment Strategies
Navigating the complexities of the Chinese stock market requires a well-defined investment strategy. Understanding various approaches, the importance of diversification, and the use of technical analysis are crucial for success. This section delves into these aspects, providing a framework for investors seeking exposure to the potential of China’s equities.Investment strategies for China stocks encompass a spectrum of approaches, each with its own set of risks and rewards.
Investors must carefully weigh their risk tolerance, investment horizon, and financial goals when selecting a suitable strategy. A well-defined strategy, coupled with diligent research, can significantly enhance the likelihood of achieving investment objectives.
Different Investment Strategies, China stocks hang seng
Various strategies can be employed for investing in China stocks, including value investing, growth investing, and dividend investing. Value investing focuses on identifying undervalued companies with strong fundamentals, potentially offering higher returns compared to their intrinsic worth. Growth investing targets companies with high growth potential, often with aggressive expansion plans and promising future earnings. Dividend investing emphasizes companies that consistently pay out substantial dividends, offering a steady stream of income for investors.
These strategies, when combined with a thorough understanding of the market, can help investors navigate the dynamic landscape of Chinese equities.
Role of Diversification
Diversification is a cornerstone of sound investment practices. Including China stocks within a diversified portfolio mitigates risk by spreading investments across various asset classes, industries, and geographies. This approach reduces the impact of any single investment’s poor performance on the overall portfolio, enhancing stability and resilience during market fluctuations. A well-diversified portfolio, including China stocks, helps investors manage risk and potentially improve long-term returns.
Technical Analysis in Assessing the Market
Technical analysis involves evaluating historical price and volume data to identify patterns and predict future market movements. Analyzing charts, identifying support and resistance levels, and recognizing trends can provide valuable insights into the market’s short-term direction. This approach, combined with fundamental analysis, offers a more comprehensive view of market dynamics, although it’s important to remember that past performance is not indicative of future results.
Basic Investment Strategy for a Hypothetical Investor
A basic investment strategy for a hypothetical investor with a moderate risk tolerance and a five-year investment horizon could involve a diversified portfolio. This portfolio might allocate 20% to China stocks, focusing on established companies with a history of consistent dividend payouts. The remaining 80% could be allocated to a mix of domestic stocks, bonds, and potentially real estate investments.
This strategy seeks to balance risk and potential reward while aligning with the investor’s timeframe and risk tolerance. Regular portfolio reviews and adjustments based on market conditions are vital for long-term success.
Risks Associated with Investing in China Stocks
Investing in China stocks presents several risks, including political and regulatory uncertainties, economic volatility, and currency fluctuations. Geopolitical tensions and policy changes can significantly impact market performance, requiring investors to be vigilant and adapt to evolving circumstances. Market volatility, a characteristic of emerging markets, can lead to substantial price swings, potentially resulting in losses. Currency fluctuations between the Chinese Yuan and other currencies also introduce additional risks.
China stocks on the Hang Seng index are showing some volatility today. Political events like the upcoming Nevada caucus primary, which you can learn more about in this explainer, Nevada caucus primary explainer , often influence global markets. This is definitely something to keep an eye on as the week progresses and the Hang Seng index continues its current trajectory.
A comprehensive understanding of these risks is essential for developing a sound investment strategy.
Comparing with Other Stock Markets
The Hang Seng Index, representing Hong Kong’s equities market, is a crucial component of the broader Asian and global investment landscape. Understanding its performance relative to other major stock markets, such as the S&P 500, is vital for investors seeking diversification and a comprehensive investment strategy. This comparison helps illuminate potential risks and opportunities unique to the Hong Kong market.
Performance Comparison with the S&P 500
The performance of the Hang Seng Index is influenced by a variety of factors, including regional economic conditions, geopolitical events, and investor sentiment. Comparing it with the S&P 500, the benchmark index for the US market, offers valuable insights into these influences. Different economic cycles, regulatory environments, and investment opportunities shape the performance trajectories of these two indices.
Market Dynamics and Similarities
Both the Hang Seng Index and the S&P 500 reflect the economic health of their respective regions. Similarities exist in their response to global economic events, with both markets often exhibiting correlated movements during periods of global uncertainty or recovery. However, their individual sensitivities to regional factors can vary significantly. For example, the Hang Seng is often more susceptible to changes in Chinese economic policies, while the S&P 500 reacts more to US-specific developments like interest rate hikes.
China’s Hang Seng index seems to be mirroring recent global market trends. While there’s been some volatility, the recent win for Thailand’s Pita in the court case, as detailed in this article , might be a factor influencing investor sentiment, potentially impacting China stocks as well. Overall, the Hang Seng’s current performance is still somewhat unpredictable.
Market Dynamics and Differences
The fundamental differences in the economic structures and political landscapes of Hong Kong and the United States result in varied market dynamics. Hong Kong’s economy is closely tied to China, making it more susceptible to China-specific shocks, while the US economy operates with greater autonomy. This results in different levels of risk associated with investing in each market.
Different sectors within the indices also contribute to variations in market behavior. The technology sector, for example, plays a much more significant role in the S&P 500 than in the Hang Seng Index.
Strengths and Weaknesses of Investing in the Hang Seng Index
Investing in the Hang Seng Index presents unique opportunities, primarily stemming from Hong Kong’s role as a financial hub and its access to the Chinese market. However, it also comes with risks, including potential volatility stemming from political or economic uncertainty in China. The strengths of the Hang Seng Index are often tied to opportunities in specific sectors within the index.
Weaknesses stem from the inherent risks associated with exposure to a smaller, more concentrated market, as well as political or regulatory changes in the region.
Correlation Between the Hang Seng and Other Indices
Correlation between the Hang Seng Index and other indices, like the S&P 500, provides a crucial measure of their interconnectedness. A high positive correlation indicates that the indices tend to move in tandem. A low or negative correlation signifies less of a direct relationship. This understanding is crucial for portfolio diversification strategies, as investors can use the correlation to potentially offset risks.
Correlation is often dynamic, varying over time.
Historical Performance Comparison (Hang Seng vs. S&P 500)
| Year | Hang Seng Index Return (%) | S&P 500 Return (%) |
|---|---|---|
| 2020 | 18.7 | 16.3 |
| 2021 | -0.8 | 28.7 |
| 2022 | -19.2 | -19.4 |
| 2023 (YTD) | +12.5 | +10.5 |
Note: Data represents annualized returns. Past performance is not indicative of future results. This table highlights the year-on-year variability in both indices. Correlation analysis over longer periods would provide a more complete picture.
Future Outlook
The future of China’s stock market, specifically the Hang Seng Index, presents a complex interplay of opportunities and challenges. Global economic trends, geopolitical dynamics, and technological advancements will all shape the path forward. While China’s economic resilience remains a key driver, navigating potential headwinds and capitalizing on emerging opportunities will be crucial for investors.
China stocks, specifically the Hang Seng, are showing some volatility today, likely influenced by broader global market trends. Meanwhile, the recent Carroll verdict and its implications for Haley and Trump, as seen in the carroll verdict haley trump coverage, could be a factor in the shifting dynamics. Ultimately, the future direction of China stocks hangs in the balance, mirroring the uncertainty in the global political landscape.
Potential Challenges for China Stocks
Several factors could pose challenges to China stocks in the coming year. Geopolitical tensions, particularly those related to international trade and strategic competition, could create uncertainty and volatility in the market. Fluctuations in global economic conditions, including interest rate adjustments and recessionary pressures in key markets, could negatively impact China’s export-oriented sectors. Furthermore, regulatory changes, such as those impacting technology companies, could affect investor confidence and market sentiment.
Outlook for the Hang Seng Index
The Hang Seng Index’s performance over the next year will likely be influenced by the interplay of these factors. A stable global economy and a continuation of China’s economic reforms could support a positive trajectory. However, any significant global economic downturn or escalation of geopolitical tensions could lead to a decline in investor confidence and a negative impact on the index.
Analysts predict a potential range of outcomes, from modest growth to significant corrections, depending on the external environment.
Opportunities for Investors in China Stocks
Despite the potential challenges, China stocks still offer attractive opportunities for investors. The country’s burgeoning consumer market, particularly in areas like e-commerce and technology, presents significant growth potential. Investment in sectors like renewable energy and sustainable infrastructure could yield returns as China transitions to a greener economy. Furthermore, the ongoing digital transformation across various sectors creates opportunities for companies embracing technological advancements.
Analysis of Potential Future Scenarios
Several scenarios could unfold for the Hang Seng Index in the coming year. A scenario of moderate global growth and stable geopolitical relations could lead to a gradual rise in the index, with investors focusing on established companies and sectors. Conversely, a scenario marked by heightened global uncertainty and economic slowdown could trigger a correction in the market, potentially impacting investor sentiment and requiring a more cautious approach.
Impact of Emerging Technologies on China Stocks
Emerging technologies like artificial intelligence (AI), cloud computing, and biotechnology are poised to significantly reshape China’s economy and stock market. Companies embracing these technologies are likely to experience strong growth, attracting investment and enhancing market valuations. The rise of these technologies presents both opportunities and risks, requiring investors to carefully analyze the long-term implications and adapt their strategies accordingly.
Examples of companies leading the way in these technologies could include those involved in AI-driven manufacturing or data analysis.
Visual Representation

Visual representation is crucial for understanding and interpreting complex financial data. Charts and graphs can transform raw numbers into easily digestible insights, highlighting trends, correlations, and potential risks associated with the Hang Seng Index and its constituent stocks. This section will explore various visual tools to illustrate the historical performance, correlations, event impacts, and future projections of the Hang Seng Index.
Historical Performance of the Hang Seng Index
The historical performance of the Hang Seng Index is best visualized using a line chart. The x-axis should represent time (e.g., years or months), and the y-axis should display the index value. A clear upward trend would indicate a positive performance, while a downward trend would signify negative performance. Fluctuations in the line would highlight periods of volatility and market corrections.
China’s Hang Seng stocks are showing some interesting volatility today, mirroring recent global market trends. It’s worth noting that the recent news surrounding Chris Young and the dropped charges against him might be having an indirect effect on investor sentiment, potentially influencing the overall direction of the Hang Seng. Hopefully, this won’t be a long-term concern, and the Hang Seng will continue its steady trajectory, Chris Young’s charges being dropped will likely have little impact in the long run.
The Hang Seng is still a key indicator of the Chinese economy and its future performance.
Adding a moving average line can provide context by smoothing out short-term fluctuations, allowing investors to see the overall long-term trend more clearly. For example, a 200-day moving average could be overlaid on the chart to provide a sense of the average price over that period.
Correlation between the Hang Seng and Other Indices
A scatter plot is an effective way to illustrate the correlation between the Hang Seng Index and other major global indices. Each data point on the scatter plot would represent a specific date and the corresponding values of the Hang Seng and the other index. A strong positive correlation would be shown by points clustering along a rising diagonal line, while a negative correlation would be reflected by points clustering along a falling diagonal line.
The strength of the correlation can be quantified using a correlation coefficient, which would be displayed on the graph itself. A coefficient of 1 indicates a perfect positive correlation, -1 indicates a perfect negative correlation, and 0 indicates no correlation.
Impact of a Major Event on the Hang Seng
A bar chart can be used to illustrate the impact of a major event on the Hang Seng. The x-axis would represent time periods, and the y-axis would display the index value. A vertical bar chart representing the Hang Seng index value on the day before the event, and the value on the day after the event, would show the magnitude of the impact.
The impact could be measured by calculating the percentage change in the index value from the day before to the day after the event. For example, the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on the Hang Seng in 2020 could be depicted using this method.
China’s Hang Seng index seems to be mirroring the global uncertainty. While the market is watching closely, it’s hard to ignore the current political climate, especially with Israel’s foreign minister heading to Brussels amid discord at home over the war here. This external pressure could be a significant factor influencing investor sentiment and potentially impacting the Hang Seng’s future direction.
Possible Scenario for Future Hang Seng Index Performance
A combination of line charts and scenario analysis can effectively visualize potential future performance. The x-axis would represent time, and the y-axis would display the index value. Three or four lines could be plotted on the chart, each representing a different projected scenario based on various economic assumptions. For instance, one line could represent a “base case” scenario, another a “bullish” scenario, and a third a “bearish” scenario.
The use of different colors or line styles would differentiate the scenarios.
Visual Representation of Company Stock Performance within the Hang Seng
A candlestick chart is ideal for displaying the performance of individual stocks within the Hang Seng. Each candlestick represents the opening, closing, high, and low prices of a stock for a specific period (e.g., a day, a week). A green candlestick indicates a positive trading day, while a red candlestick indicates a negative trading day. Volume data can also be overlaid on the chart, providing a visual representation of trading activity.
For example, a sudden increase in trading volume alongside a significant price movement could indicate heightened investor interest or a significant event.
Final Review
In conclusion, China stocks Hang Seng presents a complex but fascinating investment landscape. Understanding its historical context, current trends, and future outlook is crucial for anyone considering investing in this market. We’ve highlighted the key factors influencing its performance, allowing you to form your own informed opinions. Remember to do your own thorough research before making any investment decisions.
Commonly Asked Questions
What is the history of the Hang Seng Index?
The Hang Seng Index, a crucial benchmark for Hong Kong stocks, has a rich history dating back to 1969. It’s been a key indicator of the region’s economic health and a significant driver of investor interest in the Asian markets.
What are the common investment strategies for China stocks?
Several strategies exist, including value investing, growth investing, and more aggressive approaches. Diversification across sectors and companies is crucial for mitigating risk. Technical analysis can also provide valuable insights, though it’s not a foolproof method.
How does the Hang Seng Index perform compared to other major global indices?
Comparing the Hang Seng Index to the S&P 500 or other benchmarks reveals both similarities and differences. Factors like regional economic trends, political climates, and regulatory environments play a major role in shaping these performance disparities.
What are the potential risks associated with investing in China stocks?
Political instability, economic fluctuations, and regulatory changes can pose significant risks. Thorough due diligence and a well-defined investment strategy are essential to mitigate these risks effectively.

