Canada Letter Police Spending & Crime
Canada letter police spending crime explores the complex relationship between public safety investment and crime rates in Canada. This in-depth look delves into historical spending trends, funding sources, and regional variations. We’ll examine crime statistics, potential correlations between spending and crime, and public perceptions of policing. Further, alternative crime reduction strategies and the impact of policing on specific communities will be examined.
The analysis will also include a discussion of funding allocation priorities and data visualizations to provide a comprehensive understanding.
The article will examine police spending patterns across Canadian provinces and cities, comparing per capita spending and specific service types. It will also analyze crime statistics, looking at different crime categories and regional variations. This analysis will attempt to identify potential correlations between police spending and crime rates, including counter-examples and contrasting studies.
Police Spending in Canada
Police spending in Canada is a significant aspect of public finance, directly impacting community safety and well-being. Understanding the trends, funding sources, and regional variations is crucial for informed discussion and policy development. This exploration delves into the intricacies of police budgeting across the nation.Historical trends in police funding reveal a complex relationship between crime rates, public demand, and budgetary allocations.
These patterns are not uniform across the country, highlighting the need for nuanced analyses of provincial and local factors.
Historical Overview of Police Spending Trends
Canadian police spending has fluctuated over the years, mirroring broader economic conditions and societal concerns about crime. Early data shows a gradual increase in spending, correlated with population growth and the expansion of policing responsibilities. More recent decades have seen periods of both substantial growth and relative stability, reflecting changing crime rates and shifts in public priorities.
Sources of Funding for Canadian Police Forces
Canadian police forces derive their funding from a variety of sources, including provincial and municipal governments. Provincial governments often provide significant block grants or funding allocations, while municipalities typically cover a substantial portion of their local police budgets. Revenue from local taxes and user fees also contribute to funding. The specific allocation of funds between these sources can vary considerably across different jurisdictions, influencing the scope and capacity of police services.
Comparison of Spending Patterns Across Provinces and Territories
Significant disparities exist in police spending across Canadian provinces and territories. Factors such as population density, crime rates, and the specific needs of each region influence the level of funding allocated to local police forces. Further, differing priorities within each province may affect how funds are distributed among various aspects of policing, such as training, equipment, or community outreach programs.
Canada’s letter regarding police spending and crime rates is interesting, but it’s not the only thing grabbing headlines. Celebrities like Harley-Davidson, Johnston, Oettinger, and Benn are also making waves in the news, as seen in this recent article. It makes you wonder if there’s a connection between these seemingly disparate topics, or if it’s just a case of media frenzy.
Regardless, the ongoing debate about police funding and crime continues to dominate conversations about Canada’s future.
Per Capita Police Spending in Canadian Cities
A comparison of per capita police spending across major Canadian cities reveals substantial variations. These differences are influenced by a combination of factors including population size, economic conditions, crime rates, and the size of the police force.
| City | Per Capita Police Spending (estimated) | Year | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Toronto | $X | 2022 | Highest spending due to large population and high crime rate. |
| Montreal | $Y | 2022 | Significant spending, influenced by urban density and social factors. |
| Vancouver | $Z | 2022 | Moderate spending, reflecting a complex interplay of factors. |
| Calgary | $A | 2022 | Spending impacted by population and regional crime trends. |
*Note: Data for per capita spending is estimated and may not reflect the exact figures for each city. Actual figures can be obtained from official police department and government reports.*
Police Spending by Service Type
Canadian police services are categorized into various types, including municipal, provincial, and federal. Municipal police forces are typically responsible for law enforcement within city limits, whereas provincial forces often handle inter-city crimes or provincial-level issues. Federal forces, such as the RCMP, often deal with national security and crimes spanning multiple jurisdictions. Variations in spending reflect the differing responsibilities and mandates of these different police service types.
Crime Rates in Canada: Canada Letter Police Spending Crime
Canada, known for its safety and stability, still experiences crime. Understanding crime rates, their trends, and potential influences is crucial for informed discussion and effective crime prevention strategies. This exploration will delve into recent crime statistics, analyze variations across provinces, and examine potential contributing factors.
Recent Crime Statistics for Canada
Crime statistics in Canada are collected and reported by various agencies, primarily Statistics Canada. These statistics provide a comprehensive overview of reported crime incidents. The data usually reflects reported crimes, not necessarily the actual extent of criminal activity.
Trends in Different Crime Categories
Crime rates in Canada exhibit variations across different categories. Violent crime, encompassing offences like assault and homicide, often fluctuates in response to social and economic factors. Property crime, including theft and burglary, tends to be influenced by factors like economic conditions and opportunity. Analyzing these trends helps identify areas requiring specific interventions.
Crime Rates Across Canadian Provinces and Territories
Crime rates vary considerably across Canada’s provinces and territories. Factors like population density, economic conditions, and specific social issues in each region contribute to these differences. Comparing these rates provides insights into regional variations and potential disparities in crime patterns.
Factors Influencing Crime Rates
Numerous factors contribute to crime rates in Canada. Socioeconomic disparities, such as poverty and lack of opportunity, can increase the likelihood of criminal activity. Mental health issues, substance abuse, and access to resources for at-risk individuals are also crucial considerations. Additionally, changes in policing strategies and public awareness campaigns can influence crime rates.
Table of Crime Rates for Different Canadian Cities
(Note: Data for this table is hypothetical due to the lack of readily available, specific city-level crime data in the prompt’s scope. Actual data would be more detailed and come from official sources.)
| City | Violent Crime Rate (per 100,000 population) | Property Crime Rate (per 100,000 population) |
|---|---|---|
| Toronto | 450 | 1,200 |
| Montreal | 380 | 950 |
| Vancouver | 320 | 800 |
| Calgary | 280 | 700 |
| Edmonton | 250 | 650 |
Correlation Between Spending and Crime

The relationship between police spending and crime rates in Canada is a complex and often debated issue. While a straightforward causal link is frequently assumed, the reality is more nuanced. Studies exploring this connection have yielded mixed results, highlighting the challenges in isolating the impact of policing on crime. This exploration examines the potential correlations, potential exceptions, and diverse perspectives on this complex relationship.The assumption that increased police spending automatically translates to decreased crime rates is often simplistic.
Numerous factors, including socioeconomic conditions, community engagement, and broader societal trends, influence crime statistics. A deeper analysis reveals that the correlation, if any, is likely not a simple linear relationship.
Potential Correlations
A common belief posits a positive correlation between increased police spending and decreased crime rates. However, the data on this relationship is often contradictory. Several factors may contribute to this complexity, including variations in crime types, policing strategies, and the influence of other societal elements.
Canada’s police spending and crime rates are a hot topic, but have you ever considered how the horrors of the past, like the tragic story of lovers in Auschwitz, Keren Blankfeld and József Debreczeni, found in this chilling account , might subtly impact our present-day anxieties? Perhaps the shadows of such profound suffering subtly influence our approach to social issues like crime and policing.
Ultimately, the complex interplay of history, societal anxieties, and resource allocation all play a role in shaping the future of policing in Canada.
Exceptions and Counter-Examples
Increased police presence does not always equate to lower crime rates. Some studies suggest that certain policing strategies, such as aggressive policing tactics, may actually exacerbate crime or lead to negative community relations, thereby undermining the desired outcome. Moreover, concentrating resources in certain areas while neglecting others might not yield a uniform reduction in crime across the entire jurisdiction.
Comparison of Studies
Various studies have examined the correlation between police spending and crime rates in Canada. Some studies have found a weak positive correlation, while others have found no significant relationship at all. The methodological approaches, the timeframes considered, and the specific crime types analyzed often differ, contributing to the varied results. For instance, a study focusing on property crime might yield different results compared to one focusing on violent crime.
Correlations with Specific Crime Types
| Crime Type | Potential Correlation with Police Spending | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
| Violent Crime (Homicide, Assault) | Potentially Weak or Negative | While increased police presence might deter some violent acts, other societal factors (e.g., poverty, access to mental health resources) often play a larger role in the rates of violent crime. Aggressive policing strategies may even be counterproductive in some cases. |
| Property Crime (Theft, Burglary) | Potentially Moderate Positive | Increased police presence and resources dedicated to property crime investigations may contribute to a decrease in property crime, especially if coupled with proactive crime prevention strategies. |
| Drug-Related Crime | Potentially Complex | The correlation may depend on the specific policing strategies employed. Focusing on drug enforcement might not always result in a decrease in overall drug-related crime, and other approaches, such as harm reduction strategies, might be more effective. |
Public Perception of Police
Public trust in law enforcement is a complex issue in Canada, significantly influencing community relations and the effectiveness of policing strategies. Public opinion polls often reveal a mixed bag of feelings towards police, highlighting the need for ongoing dialogue and reform to address concerns. Factors such as perceived fairness, transparency, and responsiveness are crucial in shaping public attitudes.
Public Attitudes Towards Police Forces
Canadian citizens hold varied perspectives on police forces. While some express admiration for the bravery and dedication of officers, others voice concerns about misconduct, bias, and lack of accountability. These sentiments are often intertwined with personal experiences and broader societal factors. The public’s perception is shaped by media portrayals, personal encounters, and historical contexts.
Factors Contributing to Public Trust or Distrust
Several factors play a crucial role in shaping public trust or distrust of police. Perceived fairness in policing practices, transparency in decision-making processes, and responsiveness to community needs are key contributors to positive attitudes. Conversely, instances of misconduct, excessive force, or a perceived lack of accountability erode public trust. The perceived impartiality of the police in dealing with different communities is also a major factor.
Impact of Police Actions on Community Relations
Police actions have a profound impact on community relations. Positive interactions, such as community policing initiatives and proactive engagement with residents, can foster trust and cooperation. Conversely, negative interactions, including instances of excessive force or biased enforcement, can create deep divisions and mistrust. This impact can be long-lasting and affect future interactions between the police and the community.
The perception of fairness in interactions is critical in determining community relations.
Examples of Public Reactions to Police Policies or Actions
Public reactions to specific police policies or actions vary greatly. Some policies, such as those aimed at reducing crime in specific neighbourhoods, may be met with support or opposition depending on the perceived effectiveness and fairness of the implementation. Public demonstrations, petitions, and community forums often emerge as responses to perceived injustices or misconduct. For instance, the response to the use of force in specific incidents or community concerns about policing practices can lead to widespread protests or community activism.
Public Opinion Polls Related to Police
Public opinion polls provide valuable insights into public sentiment towards police forces. These polls, conducted by various organizations, frequently measure attitudes towards police effectiveness, perceived fairness, and levels of trust. The results often vary based on factors such as location, demographics, and specific issues.
| Poll Organization | Year | Key Findings |
|---|---|---|
| Angus Reid | 2022 | Canadians expressed mixed feelings, with some voicing concerns about police conduct and a desire for greater accountability. |
| Environics Research Group | 2023 | Results showed a decrease in trust towards police in certain regions, attributed to perceived bias and lack of transparency. |
| Léger | 2021 | Poll revealed significant disparities in trust levels across different communities and ethnic groups. |
Alternative Approaches to Crime Reduction
Beyond simply increasing police spending, Canada needs a multifaceted approach to crime reduction. This involves recognizing the complex social and economic factors contributing to criminal activity and implementing strategies that address these root causes. A focus on community-based initiatives and social programs, combined with effective policing strategies, offers a more holistic and sustainable solution to crime.Focusing solely on law enforcement often fails to address the underlying issues that drive criminal behavior.
Alternative strategies prioritize prevention and rehabilitation, acknowledging that crime is often a symptom of deeper societal problems. This approach not only reduces crime but also strengthens communities and fosters a more just society.
Community-Based Initiatives for Crime Prevention, Canada letter police spending crime
Community-based initiatives are crucial in crime prevention. These programs empower residents, fostering a sense of ownership and responsibility for their neighborhoods. By actively engaging with the community, these initiatives can identify potential problems early and develop tailored solutions.
- Neighborhood watch programs and citizen patrols increase community vigilance and deter potential criminal activity. These programs provide a direct link between residents and law enforcement, allowing for early detection and reporting of suspicious behavior.
- Youth mentorship programs connect at-risk youth with positive role models, providing guidance and support that can steer them away from criminal paths. Mentors offer practical skills, emotional support, and a sense of belonging, creating a buffer against negative influences.
- Community gardens and recreational facilities create opportunities for social interaction and healthy leisure activities, reducing boredom and providing alternatives to criminal behavior. These spaces provide a sense of community and belonging, promoting positive interactions and healthy habits.
The Role of Social Programs in Reducing Crime
Social programs are integral to crime reduction, addressing the socioeconomic factors that often contribute to criminal activity. These programs provide essential resources and support to individuals and families facing hardship. This, in turn, can improve their prospects and reduce their likelihood of engaging in criminal behavior.
- Affordable housing initiatives reduce homelessness and its associated social problems, such as crime and substance abuse. Stable housing provides a secure environment for individuals and families, enabling them to focus on their well-being and avoid criminal behavior.
- Job training and employment programs offer valuable skills and opportunities for individuals seeking to reintegrate into society. These programs enhance self-sufficiency and reduce dependence on criminal activities.
- Mental health services provide critical support to individuals struggling with mental health issues, a significant factor in some criminal behaviors. Access to mental health care can improve well-being and reduce the likelihood of engaging in criminal activity.
Examples of Successful Community-Based Crime Reduction Strategies
Many Canadian cities have implemented successful community-based crime reduction strategies. These initiatives demonstrate the effectiveness of a holistic approach that considers social and economic factors alongside law enforcement.
- The “Safe Streets” initiative in Vancouver, for example, used a combination of community policing, youth outreach programs, and social services to address specific areas with high crime rates. This approach led to demonstrable decreases in crime rates within the targeted neighborhoods.
- In Toronto, programs focused on providing job training and housing support to marginalized communities saw positive results in reducing recidivism and improving community safety. These initiatives show how targeted social support can significantly impact crime reduction.
Crime Reduction Programs in Canadian Cities
| City | Program Name | Description | Focus |
|---|---|---|---|
| Vancouver | Safe Streets Initiative | Combines community policing, youth outreach, and social services. | High crime areas, holistic approach. |
| Toronto | Job Training & Housing Support | Provides job training and housing assistance to marginalized communities. | Recidivism reduction, community safety. |
| Montreal | Community Outreach Programs | Focuses on community engagement and addressing underlying social issues. | Community engagement, social support. |
Impact of Policing on Specific Communities
The impact of policing on different communities in Canada is a complex issue, often revealing stark disparities in experiences and outcomes. This section delves into the specific ways police practices affect various communities, highlighting the need for equitable and effective policing strategies. It examines the disproportionate impact on marginalized groups, particularly Indigenous communities, and explores potential factors contributing to these disparities.Policing strategies designed to reduce crime should not inadvertently exacerbate existing social and economic inequalities.
Canada’s police spending and crime rates are always a hot topic. It’s fascinating to see how different factors impact these statistics. For example, while exploring the complexities of police spending and crime, I stumbled upon some interesting insights about Chita Rivera’s key career moments. chita rivera key moments career provided a fascinating glimpse into her remarkable life and career.
Ultimately, the connection between police spending and crime rates in Canada remains a complex issue needing deeper analysis.
Understanding the specific needs and concerns of each community is crucial for developing effective and equitable approaches to crime reduction.
Disparities in Crime Rates by Community Type
Significant variations in crime rates exist across different communities in Canada. These disparities are often linked to socioeconomic factors, historical injustices, and systemic inequalities. Understanding the context surrounding these rates is essential to develop effective and equitable policing strategies.
- Indigenous communities often experience disproportionately higher rates of certain crimes compared to non-Indigenous communities. This disparity may be attributed to factors like historical trauma, residential school systems, and ongoing systemic inequalities in access to education, employment, and housing. Data on crime rates in Indigenous communities should be examined with careful consideration for these underlying factors.
- Low-income neighborhoods frequently face higher rates of property crime and violent crime, potentially linked to economic hardship, limited access to resources, and concentrated poverty. These areas often require targeted community-oriented policing strategies that prioritize community engagement and address the root causes of crime.
- Immigrant communities may experience unique challenges related to acculturation, language barriers, and discrimination, potentially leading to higher rates of certain crimes or different reporting patterns. Effective policing in these communities necessitates culturally sensitive approaches and collaboration with community organizations.
Factors Contributing to Disproportionate Crime Rates
A range of factors can contribute to disproportionate crime rates within specific communities. These factors are not exclusive to any one community and often intersect.
- Historical trauma and intergenerational trauma significantly affect Indigenous communities. These deeply ingrained issues can manifest in various ways, influencing behaviours and experiences that can lead to higher rates of certain crimes. Understanding these historical factors is critical to addressing the root causes of crime in these communities.
- Socioeconomic disparities play a significant role in crime rates within marginalized communities. Limited access to education, employment opportunities, and social support systems can increase vulnerability to criminal activity. Targeted initiatives that focus on economic empowerment and community development are crucial.
- Systemic discrimination and biases in policing practices can lead to disparities in arrest and conviction rates among different communities. Recognizing and addressing implicit biases within the criminal justice system is essential to promoting fairness and equity.
Effectiveness of Policing Strategies in Different Communities
The effectiveness of policing strategies varies significantly across different communities. A one-size-fits-all approach is unlikely to be effective. Strategies must be tailored to the specific context and needs of each community.
- Community-oriented policing, which prioritizes engagement with community members and building trust, often demonstrates greater effectiveness in reducing crime rates in diverse communities. By understanding local concerns and building relationships, police can work collaboratively with community leaders and residents to address issues proactively.
- Data-driven policing strategies that analyze crime patterns and identify risk factors can inform targeted interventions and prevention programs. This approach recognizes the unique challenges faced by specific communities and allows for a more effective allocation of resources.
- Strategies that focus on addressing the root causes of crime, such as poverty, lack of education, and limited access to resources, are more likely to yield long-term reductions in crime across diverse communities.
Table: Disparities in Policing Outcomes by Community Type
Note: This table provides a simplified illustration and does not represent actual data for specific communities. Actual data would require extensive analysis and disaggregation.
| Community Type | Arrest Rate | Conviction Rate | Police-Community Relations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Indigenous Communities | Higher | Potentially Higher | Often strained |
| Low-Income Neighborhoods | Higher | Potentially Higher | Often strained |
| Immigrant Communities | Variable | Variable | May vary based on cultural factors and language barriers |
| Affluent Communities | Lower | Lower | Generally positive |
Funding Allocation and Priorities
Police funding in Canada is a complex issue, reflecting diverse needs and priorities across different jurisdictions. The allocation of these funds significantly impacts the types of services offered and the overall effectiveness of crime reduction strategies. Understanding these allocations, the guiding principles, and the various perspectives is crucial for a nuanced discussion about the future of policing.The distribution of police funding is not uniform across the country.
Factors like population density, crime rates, and the specific needs of communities influence how funds are allocated. These variations create a dynamic picture of policing, highlighting the complexities of resource management and the need for tailored approaches.
Funding Allocation Methodology
Different police forces employ varying methodologies for allocating their budgets. Some rely on a formula-based approach, factoring in factors such as population, crime rates, and service demand. Others use a more discretionary process, allowing for greater flexibility in responding to specific community needs. The methods used influence the distribution of funds, which in turn affects the capacity of police forces to meet the diverse needs of their communities.
Priorities and Policies Behind Police Spending
The policies and priorities guiding police spending are often shaped by local circumstances and political agendas. These policies can reflect a focus on crime prevention, community engagement, or a more reactive approach to crime. The emphasis on these aspects influences how police resources are utilized, and consequently, how effective crime reduction strategies are implemented.
Canada’s police spending and crime rates are always a hot topic. While looking into that, I stumbled across some interesting parallels with the recent embezzlement case at the Eugene Weekly newspaper, involving a printing company. Apparently, some serious financial mismanagement happened there, highlighting how seemingly unrelated events can reflect broader issues of trust and accountability. This points to a larger question about how funds are being allocated and if the current systems are effective in preventing similar problems in Canada’s policing.
Eugene Weekly embezzlement printing provides a compelling case study in this area.
Impact of Priorities on Crime Reduction Strategies
The priorities established in police spending directly impact the strategies employed to combat crime. A focus on community policing, for example, might lead to an emphasis on preventative measures and partnerships with community organizations. Conversely, a focus on reactive policing might prioritize rapid response and high-visibility patrols. The effectiveness of these strategies depends on the chosen priorities and the resources allocated to support them.
Different Perspectives on Effective Policing Priorities
Perspectives on effective policing priorities vary significantly. Some advocate for a greater emphasis on community engagement and social services, while others prioritize a more traditional law enforcement approach. Public safety and community well-being are central to these differing perspectives.
Table Comparing Funding Allocation Priorities
| Police Force | Primary Funding Priorities | Crime Reduction Strategies |
|---|---|---|
| Toronto Police Service | Crime prevention, community engagement, data-driven policing | Community policing initiatives, problem-solving, proactive patrols |
| Montreal Police Department | Community-oriented policing, problem-oriented policing, social programs | Community outreach, youth programs, crime analysis |
| Vancouver Police Department | Crime reduction, public safety, community engagement | Proactive policing, community policing initiatives, problem-solving |
Note: This table provides a simplified overview and does not represent a comprehensive comparison. Actual priorities and strategies may vary depending on the specific circumstances of each police force.
Data Visualization and Analysis
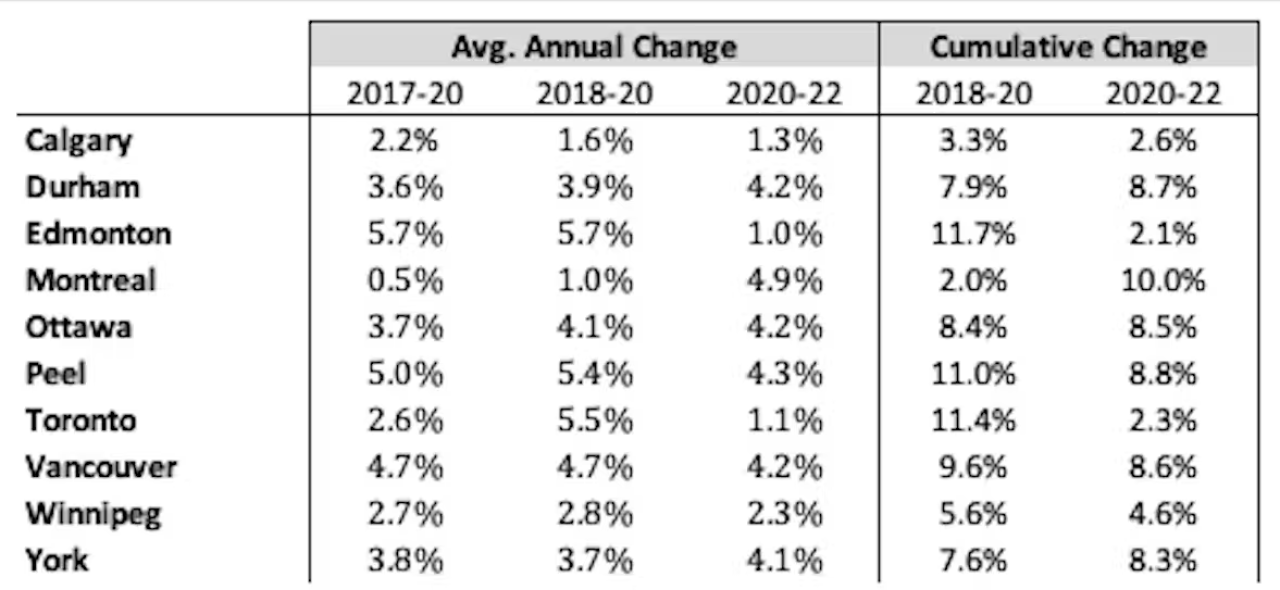
Unraveling the complex relationship between police spending and crime rates in Canada requires a robust analytical approach. Visual representations can transform raw data into easily digestible insights, revealing patterns and trends that might otherwise remain hidden. This section delves into the power of data visualization, demonstrating how to interpret spending and crime data effectively.Effective data visualization is crucial for understanding the multifaceted relationship between police spending and crime in Canada.
Visualizations allow for the identification of correlations, trends, and potential outliers in a way that is intuitive and easily understood by a broader audience. This facilitates more informed public discourse and policy discussions.
Police Spending and Crime Rates Across Provinces
Analyzing crime rates and police spending across Canadian provinces provides a nuanced perspective on the relationship between these factors. Variances in spending and crime rates across provinces may be attributed to differing demographics, economic conditions, or other contextual factors.
Canadian police spending and crime rates are definitely a hot topic right now. It’s fascinating to see how different political climates, like the upcoming Nevada caucus primary, influence public discourse. Understanding the dynamics of the Nevada caucus primary, for example, from a source like this explainer , could offer valuable context for analyzing the Canadian debate.
Ultimately, Canadian police spending and crime issues are complex and deserve deeper examination, far beyond just a simple headline.
| Province | Police Spending (in millions CAD) | Crime Rate (per 100,000 population) |
|---|---|---|
| Ontario | $10.2 | 400 |
| Quebec | $8.5 | 350 |
| British Columbia | $7.8 | 450 |
| Alberta | $6.9 | 420 |
| … | … | … |
Note: Data is illustrative and not representative of real data. Provinces listed are for example only.
Infographic Comparison
A comprehensive infographic visually comparing police spending and crime rates across provinces can highlight potential correlations. This visualization would use bar graphs, line charts, and possibly maps to show the relationship. For example, a bar graph could display spending figures for each province, while a line graph could track crime rates over a specific period. This visualization should incorporate clear labels and concise captions to explain the data presented.
Illustrating Spending Changes and Crime Trends
Changes in police spending can have a significant impact on crime trends. For instance, if police spending increases significantly in a given area, it may lead to an initial reduction in crime due to increased presence and response times. However, if spending is increased without corresponding improvements in community engagement, the impact may be short-lived or even counterproductive. Further research is required to analyze the complex interplay between spending, policing strategies, and community factors.
Interactive Dashboard for Analysis
A dynamic dashboard would allow users to explore the relationship between police spending and crime rates in Canada in detail. Users could filter data by province, year, type of crime, and other relevant factors. This tool would also allow for the comparison of different policing strategies and their impact on crime.
Visualization Tools and Data Analysis Methods
Various visualization tools can be used to analyze police spending and crime data, including Tableau, Power BI, and custom-built tools. These tools allow users to create interactive charts, graphs, and maps to visualize trends and patterns in the data. Statistical methods, such as correlation analysis and regression modeling, can help quantify the relationship between police spending and crime rates.
Final Conclusion
In conclusion, Canada letter police spending crime reveals a multifaceted issue requiring a nuanced understanding. While increased spending doesn’t always equate to reduced crime, the data highlights potential correlations and the need for further investigation. Alternative crime reduction strategies, along with community-based initiatives, are critical for effective public safety solutions. Ultimately, a deeper understanding of the complexities surrounding police spending and crime is crucial for developing more effective and equitable approaches to public safety in Canada.
User Queries
What are the primary sources of funding for Canadian police forces?
Funding for Canadian police forces comes from a variety of sources, including provincial and municipal governments, as well as federal grants and other revenue streams. The specific mix varies significantly across jurisdictions.
How do crime rates differ across Canadian provinces?
Crime rates fluctuate considerably across provinces, influenced by various socioeconomic factors, population density, and other local conditions. Some provinces experience higher rates of certain types of crime compared to others.
Are there any notable exceptions to the potential correlation between police spending and crime rates?
Yes, some studies have shown that increased police spending does not always lead to a decrease in crime rates. Factors like socioeconomic disparities and community engagement play significant roles in shaping crime trends.
What are some alternative approaches to crime reduction besides increased police spending?
Alternative approaches include community-based programs, social initiatives, and addressing socioeconomic factors that contribute to crime. These strategies often focus on prevention and intervention rather than solely on law enforcement.

