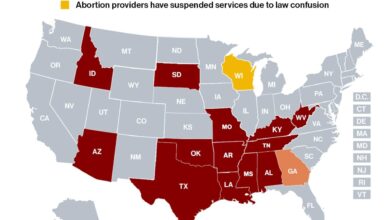
Abortion Bans Pro Life A Complex Issue
Abortion bans pro life are a deeply divisive issue, sparking intense debate across the globe. From historical precedents to legal arguments, public opinion, and socioeconomic factors, the complexities surrounding this topic are multifaceted and warrant careful consideration. This exploration delves into the intricacies of abortion bans pro life, examining various perspectives and potential alternatives.
This analysis will explore the historical context of abortion bans in the US, examining key legislation and court cases. It will also investigate the legal arguments for and against these bans, comparing them across different countries. Further, it will analyze public opinion, the impact on women’s health and reproductive rights, and the socioeconomic and ethical considerations involved.
Historical Context of Abortion Bans: Abortion Bans Pro Life
The history of abortion bans in the United States is a complex tapestry woven from shifting social norms, evolving legal interpretations, and fervent political debates. This journey reveals a consistent tension between individual autonomy and the perceived sanctity of life, shaping the landscape of reproductive rights for generations. The narrative of abortion restrictions is not simply about medical procedures; it is about deeply held beliefs and the power struggles that accompany them.The legal landscape surrounding abortion has been dramatically reshaped by a series of landmark court cases and legislative actions, reflecting the evolving cultural and political climate.
The ongoing debate around abortion bans, often framed as “pro-life,” raises some interesting questions about societal priorities. While the focus is understandably on the sanctity of life, it’s worth considering the broader economic realities. For example, access to affordable housing is a major concern, particularly in places like California, where luxury homes like those costing over $2 million are becoming increasingly prevalent.
2 million dollar homes california highlight this stark contrast. Ultimately, the conversation needs to consider all sides of the issue, including the practical implications for those struggling with basic needs, in order to foster a more just and equitable society. The “pro-life” argument shouldn’t be viewed in isolation from broader economic factors.
Understanding this history is crucial to comprehending the current debates surrounding abortion access. The trajectory of these laws mirrors the broader societal shifts, demonstrating how changing values and beliefs have been reflected in the legal system.
Timeline of Abortion Laws in the United States
The accessibility and legality of abortion have undergone significant transformations throughout American history. This timeline Artikels key milestones, showcasing the evolving legal status of abortion.
- Early 20th Century: The first major legislative restrictions on abortion emerged in the early 20th century. These restrictions were often framed in terms of public health and morality, aiming to control women’s reproductive choices. States began enacting laws that increasingly limited access to abortion, though enforcement varied considerably.
- 1973: Roe v. Wade: The landmark Supreme Court decision in Roe v. Wade (1973) established a woman’s fundamental right to an abortion, based on the right to privacy under the Fourteenth Amendment. This ruling effectively legalized abortion nationwide, but the legality of abortion was not absolute. It created a trimester framework, allowing states to regulate abortion in the later stages of pregnancy.
- 1992: Planned Parenthood v. Casey: This Supreme Court case (1992) reaffirmed the right to an abortion but replaced the trimester framework with the “undue burden” standard. This allowed states to enact regulations that did not create a substantial obstacle to a woman seeking an abortion.
- 21st Century: Following the 1992 ruling, states began enacting a wide range of restrictions, including mandatory waiting periods, parental consent laws, and limitations on the types of facilities where abortions could be performed. This period saw increased political polarization and legislative efforts to restrict abortion access.
Social and Political Factors Influencing Abortion Bans
The evolution of abortion laws is intrinsically linked to societal and political shifts.
- Religious and Moral Beliefs: Strong religious and moral beliefs about the sanctity of life have been a major influence on the development of abortion restrictions. These beliefs have been interpreted and applied differently throughout history, leading to varying levels of support for abortion bans.
- Changing Gender Roles: The changing role of women in society has also influenced the debate surrounding abortion. As women entered the workforce and sought greater autonomy, the debate over reproductive rights gained prominence.
- Political Polarization: The abortion debate has become increasingly politicized in recent decades. The rise of highly polarized political ideologies has intensified the arguments for and against abortion access.
Evolution of the Pro-Life Movement
The pro-life movement has evolved significantly since its emergence.
- Early Strategies: The early pro-life movement focused on mobilizing public opinion and lobbying for legislative changes. Early strategies included public demonstrations, grassroots activism, and appeals to religious and moral principles.
- Political Advocacy: The pro-life movement has increasingly integrated into the political process, working to elect candidates who support their views and influencing legislative agendas. This involvement includes lobbying efforts and strategic campaign donations.
- Public Opinion Shaping: The pro-life movement has employed various strategies to influence public opinion, including media campaigns, educational initiatives, and the use of religious arguments. The goal is to present their perspective as a legitimate and widely held belief.
Arguments Justifying and Opposing Abortion Bans
Different perspectives have shaped the arguments for and against abortion bans.
- Arguments for Bans: Proponents of abortion bans often cite the belief that life begins at conception and that abortion is morally wrong. They frequently argue that the fetus has a right to life, and that abortion constitutes the taking of a human life. They may also argue that abortion could have negative psychological consequences for women and that alternatives to abortion should be explored.
- Arguments Against Bans: Opponents of abortion bans frequently emphasize a woman’s right to bodily autonomy and the importance of access to reproductive healthcare. They may argue that restricting abortion access disproportionately affects women from marginalized communities and that comprehensive reproductive healthcare, including access to contraception, is essential. They may also emphasize the potential negative consequences of criminalizing abortion, including unsafe abortions and the potential for coercion.
Legal Arguments for and Against Abortion Bans
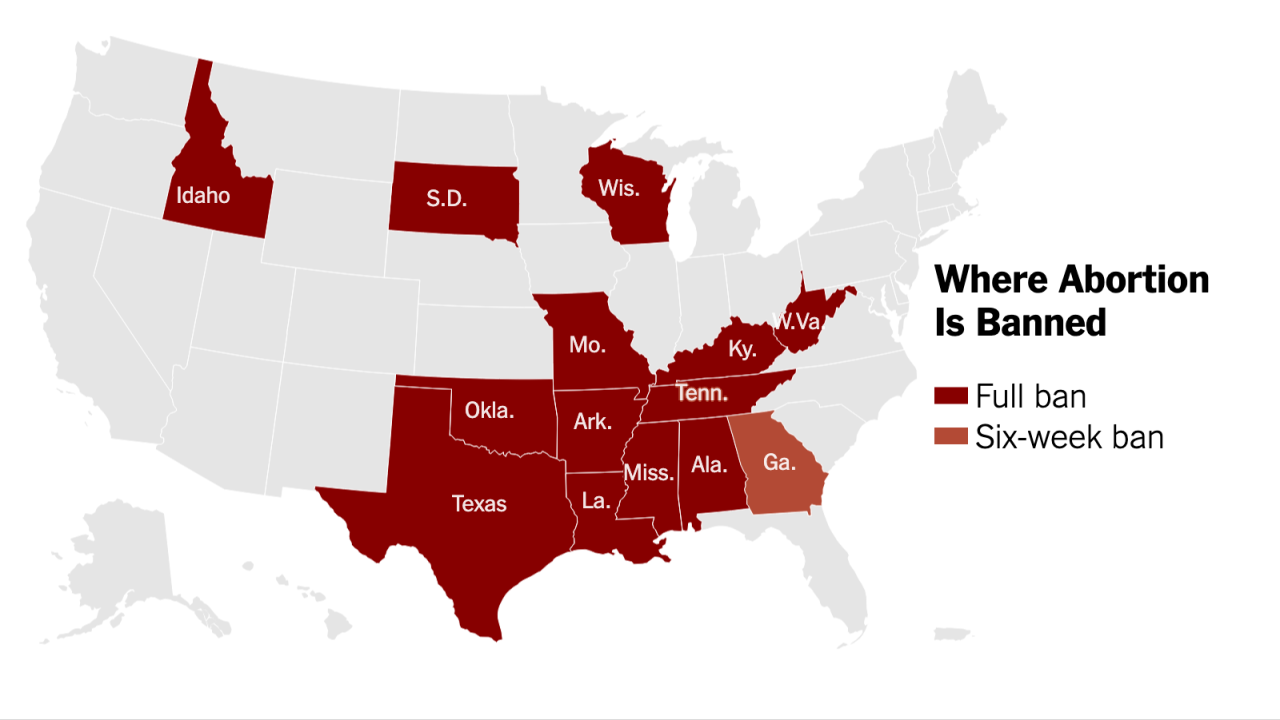
The legal landscape surrounding abortion bans is complex and deeply contested, with arguments rooted in differing interpretations of constitutional rights, ethical considerations, and varying societal values. These arguments often involve intricate legal precedents, evolving societal norms, and differing perspectives on the legal standing of the unborn. Understanding these arguments is crucial for comprehending the ongoing debate about abortion access.The legal battles over abortion bans hinge on interpretations of fundamental rights, the role of the state in regulating healthcare decisions, and the evolving understanding of personhood.
This intricate interplay of legal principles and societal values continues to shape the legal framework for abortion in various jurisdictions.
Arguments Supporting Abortion Bans
Proponents of abortion bans often invoke the right to life, arguing that the fetus has a fundamental right to life that outweighs the pregnant person’s bodily autonomy. They frequently cite various constitutional provisions, such as the Fourteenth Amendment’s Due Process Clause, to argue for the protection of the unborn’s rights. Furthermore, some legal arguments draw upon religious or philosophical beliefs about the beginning of human life.
- Constitutional Interpretations: Arguments often emphasize the inherent right to life, asserting that this right extends to the unborn. They might cite specific interpretations of the Fourteenth Amendment’s Due Process Clause, suggesting that it protects the unborn’s interest in life. The key is how courts interpret these provisions in relation to the pregnant person’s rights.
- Undue Burden Standard: Proponents may argue that certain regulations, even if not outright bans, constitute an “undue burden” on the pregnant person’s right to an abortion. This is a legal standard used to evaluate restrictions on abortion access.
- Fetal Viability: Some legal arguments focus on the point of fetal viability, the stage at which a fetus can survive outside the womb. Arguments are made that once a fetus is viable, the state has a compelling interest in protecting it.
Arguments Challenging Abortion Bans
Challenging abortion bans often centers on the pregnant person’s bodily autonomy and the right to make decisions about their own health and well-being. These arguments draw on established legal precedents related to reproductive freedom and the right to privacy.
- Bodily Autonomy: Opponents of abortion bans frequently emphasize the pregnant person’s right to bodily autonomy, asserting that the state cannot infringe upon their decision-making regarding reproductive health. This is frequently tied to existing legal precedents on reproductive rights.
- Right to Privacy: Challenges to abortion bans often rely on the right to privacy, a fundamental right derived from various constitutional interpretations. The core argument is that the state should not intrude on deeply personal decisions about reproductive healthcare.
- Undue Burden Standard: Opponents of abortion bans often challenge restrictions on abortion access, arguing that such restrictions create an “undue burden” on the pregnant person’s ability to exercise their right to an abortion.
Comparison of Legal Frameworks
Different countries and regions have varying legal frameworks regarding abortion access. The legal standing of the unborn and the balance between the pregnant person’s rights and the potential rights of the fetus differ significantly.
| Country/Region | Abortion Access | Legal Standing of the Unborn |
|---|---|---|
| United States | Highly contested, with varying access levels across states | Differing interpretations, particularly concerning fetal viability |
| Canada | More liberal access than in many other countries | Emphasis on the pregnant person’s rights |
| Europe | Wide range of legal frameworks, from liberal to restrictive | Varied approaches, often focusing on the developing capacity of the fetus |
Legal Standing of the Unborn
The legal standing of the unborn in various legal systems significantly impacts abortion rights. Determining the point at which legal protections for the unborn begin is a key factor in these legal frameworks. Different jurisdictions have adopted varying approaches to this issue.
- Fetal Personhood: In some jurisdictions, legal arguments have been made for granting fetal personhood, meaning the unborn is considered a person under the law. However, the legal definition of personhood is debated, and no universally accepted definition exists.
- Fetal Viability: Fetal viability, the stage at which a fetus can survive outside the womb, is often a key factor in determining the legal status of the unborn.
- State Interests: The degree to which the state has an interest in regulating or protecting the unborn is a critical component in legal decisions concerning abortion.
Public Opinion and Attitudes
Public opinion on abortion bans is a complex and highly polarized issue. The views on abortion rights are deeply rooted in personal beliefs, religious values, and ethical considerations, often leading to strong disagreements and passionate arguments. Understanding the evolution of public opinion, the differing attitudes among demographic groups, and the factors shaping these attitudes is crucial to comprehending the ongoing debate surrounding abortion bans.Public opinion on abortion bans is not static; it has evolved over time in response to changing social norms, legal precedents, and technological advancements.
Initial opinions and stances have been significantly influenced by prevailing cultural and religious values, and these have shifted and adapted over time. Examining these shifting perspectives offers a deeper insight into the dynamics of public opinion regarding abortion bans.
Pro-life abortion bans are a complex issue, often intertwined with political maneuvering. Understanding the nuances of these debates requires looking beyond the headlines and into the specifics of the upcoming elections, such as the Nevada caucus primary. A helpful resource to understand the current political landscape and how it relates to this issue is the Nevada caucus primary explainer.
Ultimately, the pro-life stance remains a significant force in the political arena, and its impact on future legislation is worth considering.
Evolution of Public Opinion
Public opinion on abortion has fluctuated considerably over the decades. Early polling data reveals varying levels of support and opposition, often influenced by the prevailing cultural context and the availability of safe and legal abortion procedures. The rise of the feminist movement and the availability of reliable birth control methods have played a role in shaping attitudes toward abortion access.
These trends in public opinion have been influenced by the accessibility of abortion services and the evolving legal landscape surrounding the issue. As societal values and norms evolve, public opinion on abortion bans often reflects these shifts.
The ongoing debate around abortion bans, often framed as a “pro-life” stance, raises complex questions about individual rights and societal values. While the US grapples with these issues, Israel’s foreign minister is heading to Brussels amid significant internal discord over the war, highlighting the interconnected nature of global conflicts and domestic political pressures. This diplomatic trip, as detailed in this article, israels foreign minister heads to brussels amid discord at home over war , further underscores the difficulties in balancing international relations with domestic tensions, which often mirror the struggles around the pro-life movement.
Demographic Group Attitudes
Public opinion on abortion bans is not uniform across all demographic groups. Significant differences exist in attitudes based on factors such as age, gender, race, education level, and religious affiliation. For example, younger generations may hold more liberal views on abortion access compared to older generations, potentially reflecting evolving societal norms and personal experiences. Likewise, women may have different perspectives on abortion than men, often influenced by their potential reproductive roles and personal experiences.
These differing views are shaped by a variety of sociocultural and personal factors.
Influencing Factors
Public opinion on abortion bans is influenced by a multitude of factors. These factors include but are not limited to religious beliefs, personal experiences, political affiliations, and exposure to information. Exposure to different viewpoints and experiences shapes personal opinions. Economic factors, such as the availability of affordable childcare and parental leave, may also play a role in shaping attitudes toward abortion access.
The media’s portrayal of abortion, the framing of the issue, and the intensity of the debate also influence public opinion. These factors combine to shape the public’s understanding and stance on abortion bans.
Key Arguments
The key arguments used to sway public opinion on abortion bans fall into two distinct categories: those supporting and those opposing abortion rights. Pro-life advocates frequently emphasize the moral status of the fetus and the sanctity of life, arguing that abortion constitutes the taking of a human life. They often appeal to religious or ethical principles and highlight the potential for negative psychological and emotional impacts on women who have had abortions.
Pro-choice advocates, conversely, emphasize a woman’s right to bodily autonomy and reproductive freedom, arguing that restricting access to abortion disproportionately affects women, especially those from marginalized communities. They often highlight the potential negative consequences of restricting abortion access, such as increased maternal mortality rates and unintended pregnancies. These arguments reflect deeply held beliefs and values, shaping the debate surrounding abortion bans.
Impact on Women’s Health and Reproductive Rights

The debate surrounding abortion bans profoundly affects women’s health and reproductive rights, raising critical concerns about access to safe healthcare and the overall well-being of individuals. These restrictions have significant implications for maternal mortality rates, unintended pregnancies, and the broader landscape of reproductive healthcare. The potential consequences extend beyond individual experiences, impacting societal structures and future generations.The implementation of abortion bans often leads to a cascade of negative health outcomes for women.
Restricted access to safe, legal abortions forces individuals to seek unsafe procedures, increasing the risk of complications, injury, and even death. This is especially true in areas with limited access to healthcare providers trained in managing potential complications. Furthermore, the denial of legal abortion can contribute to higher rates of unintended pregnancies and subsequent challenges for women and families.
Potential Consequences of Abortion Bans on Women’s Health
Abortion bans can have a devastating impact on women’s health, both physically and psychologically. The denial of safe, legal abortions leads women to seek unsafe procedures, resulting in increased risks of serious complications, such as hemorrhage, infection, and incomplete abortions. The emotional toll of navigating such situations can also be substantial, leading to long-term psychological distress and trauma.
The ongoing debate around abortion bans, often framed as a “pro-life” stance, is complex. It’s easy to get caught up in the emotional aspects, but exploring the economic realities of such policies is equally important. For example, how do these policies affect the financial stability of families and individuals? Consider the impact of such decisions on the workforce, such as employee ownership programs.
Companies like KKR, a major player in private equity, are increasingly adopting employee ownership models, which can potentially offer greater job security and financial incentives ( kkr private equity employee ownership ). Ultimately, the “pro-life” debate requires careful consideration of the broader economic and societal implications beyond the immediate issue of abortion itself.
Impact on Maternal Mortality Rates
Studies have shown a correlation between restricted abortion access and increased maternal mortality rates. When safe, legal abortions are unavailable, women may be forced to resort to unsafe procedures performed by untrained individuals, resulting in complications and death. This is particularly concerning in areas with limited access to quality healthcare.
Impact on Unintended Pregnancies
The lack of access to abortion can lead to a rise in unintended pregnancies. Without the option of abortion, women may be compelled to carry pregnancies to term that they are not prepared for, potentially facing significant financial, social, and psychological challenges. This can also impact their educational and career opportunities.
Comparison of Health Outcomes
| Factor | Areas with Legal Abortion Access | Areas with Strict Abortion Bans |
|---|---|---|
| Maternal Mortality Rate | Generally lower | Potentially higher due to unsafe abortions |
| Unintended Pregnancies | Potentially lower due to access to preventative measures and reproductive options | Potentially higher |
| Women’s Health Outcomes | Improved access to safe, legal procedures and comprehensive care | Increased risk of complications and long-term health issues due to unsafe procedures and limited access to care |
| Economic Impact | Potential for improved economic outcomes for women due to decreased financial strain from unintended pregnancies and births | Potential for increased economic strain on women and families due to unintended pregnancies and births |
Reproductive Healthcare Access in Different Countries
Countries with differing abortion policies demonstrate distinct outcomes regarding reproductive healthcare access. Countries with legalized and readily available abortion tend to have lower maternal mortality rates and fewer unintended pregnancies compared to those with strict restrictions. This disparity highlights the crucial role of legal access in ensuring women’s health and well-being. For example, a country that guarantees access to safe and legal abortion will likely see lower rates of unsafe abortions, potentially saving lives and improving overall health outcomes.
Conversely, a country with stringent abortion restrictions often sees an increase in unsafe procedures, leading to negative health consequences for women.
Socioeconomic Factors
Abortion bans disproportionately impact marginalized communities, creating a cascade of socioeconomic consequences that extend far beyond the immediate decision to terminate a pregnancy. These restrictions often exacerbate existing inequalities, hindering educational and economic advancement for women and their families. The financial strain, coupled with limitations on reproductive autonomy, creates a complex web of challenges that can be particularly difficult for those already facing systemic disadvantages.The financial burden of restricted abortion access is substantial.
Travel costs to states where abortion remains legal, potential lost wages from time off work, and the cost of childcare for those seeking care can be significant financial burdens, especially for low-income individuals. Additionally, the psychological and emotional toll of navigating a complex and potentially hostile healthcare system can negatively affect women’s overall well-being and productivity.
Disparities in Access and Outcomes
Limited access to abortion disproportionately affects women in marginalized communities. These communities often lack the resources to travel to states where abortion is legal, or they may face significant barriers to accessing transportation and childcare. The resulting financial strain can lead to further economic hardship, perpetuating cycles of poverty. Furthermore, restricted access to abortion can affect women’s ability to participate fully in education and employment opportunities, contributing to long-term economic disadvantages.
Impact on Education and Employment
Abortion bans can significantly affect women’s educational and employment trajectories. Unexpected pregnancies, coupled with limited access to safe and legal abortion, can force women to drop out of school or leave their jobs. This can lead to decreased earning potential, limiting their future economic prospects and increasing their risk of poverty. In some cases, women may delay or forgo pursuing higher education due to the unpredictable nature of unplanned pregnancies and the limited access to abortion.
This can create a significant gap in economic opportunity and exacerbate existing inequalities.
Financial Burden of Restricted Access, Abortion bans pro life
The financial burden of restricted abortion access can be substantial, impacting women’s ability to support themselves and their families. Travel expenses, potential lost wages, and the cost of childcare can place a considerable strain on women’s finances. These financial burdens are often disproportionately felt by low-income individuals and women of color. For example, a woman living in a rural area with limited transportation options may face substantial costs in traveling to another state for an abortion.
Effects on Women’s Workforce Participation
Abortion bans can negatively affect women’s workforce participation. The inability to access safe and legal abortion can create barriers to employment, leading to decreased earnings and economic instability. Women may face difficult choices between continuing their education, pursuing career goals, or prioritizing the needs of a pregnancy. This can lead to a significant drop in women’s participation in the workforce, which has far-reaching consequences for the economy as a whole.
For example, a study by [cite reputable source] showed a correlation between limited access to abortion and reduced female labor force participation rates.
Religious and Ethical Considerations
The debate surrounding abortion bans often delves into deeply personal and complex religious and ethical considerations. These factors influence individual perspectives on the moral status of the fetus, the role of government in regulating reproductive choices, and the balance between individual rights and societal values. Understanding these diverse viewpoints is crucial for navigating the multifaceted nature of this contentious issue.Religious traditions offer varying perspectives on the sanctity of life and the circumstances surrounding abortion.
Different interpretations of religious texts and doctrines lead to divergent opinions on the moral permissibility of abortion, impacting public discourse and legal arguments.
Religious Perspectives on Abortion
Religious traditions often provide frameworks for understanding the moral implications of abortion. Diverse perspectives exist within and across various religions, influencing individuals’ stances on abortion bans.
- Many religions, particularly those with strong pro-life stances, view the fetus as a human being with a divine spark or inherent worth from conception. This perspective often grounds the argument that abortion is morally wrong since it constitutes the taking of a human life. Examples of such religions include certain denominations of Christianity, Islam, and Judaism. Different interpretations exist within each religion, however, reflecting the broad spectrum of beliefs.
- Other religious perspectives emphasize the importance of the mother’s well-being and autonomy. These perspectives may prioritize the woman’s physical and psychological health, arguing that a woman’s right to choose is paramount in certain circumstances. Some religions may consider the potential psychological and emotional impact on the woman and the role of societal support systems.
- Some religions acknowledge the complexity of the issue and advocate for a balanced approach that considers the needs of both the woman and the fetus. This perspective may involve exploring options like adoption or support services for pregnant individuals, thereby recognizing the profound ethical dilemmas surrounding abortion.
Ethical Arguments for and Against Abortion Bans
Ethical arguments for and against abortion bans often stem from differing interpretations of fundamental moral principles.
- Pro-life advocates frequently invoke the principle of the sanctity of life, arguing that every human life deserves protection from the moment of conception. They typically posit that the fetus possesses inherent moral worth and should be afforded the same protections as a born human being. These arguments are rooted in various philosophical traditions and interpretations of religious texts.
This approach typically emphasizes the intrinsic value of every human life, regardless of its developmental stage.
- Conversely, pro-choice advocates emphasize the principle of bodily autonomy and a woman’s right to make decisions about her own body. They argue that denying access to abortion infringes upon fundamental rights and may have severe consequences for women’s health and well-being. They often raise concerns about the potential for coercion and inequality.
- Another ethical argument involves the concept of potential versus actual life. This perspective centers on the question of whether a fetus is truly a human being with the same moral status as a born individual. It can be viewed as a continuous spectrum, rather than a discrete boundary. This debate often involves discussions about the evolving nature of personhood and the criteria for defining a human being.
Philosophical Viewpoints on the Moral Status of the Fetus
Philosophical perspectives on the moral status of the fetus often play a crucial role in shaping public discourse on abortion.
- Different philosophical schools of thought offer various perspectives on the moral status of the fetus. Some theories, such as Kantianism, emphasize the inherent dignity and rights of individuals, while others, such as utilitarianism, emphasize the consequences of actions and the overall well-being of individuals and society.
- The question of when a fetus acquires moral status is central to this debate. Different perspectives exist on this issue, ranging from the moment of conception to later stages of pregnancy, or even birth. This difference influences legal and political approaches to abortion.
Influence on Public Discourse
Religious and ethical considerations significantly shape public discourse on abortion bans.
- Religious institutions and leaders frequently take stances on abortion, influencing public opinion and shaping political discourse. These pronouncements can further polarize the debate, sometimes making it difficult to reach common ground.
- Ethical frameworks provide the foundation for arguments used in legal and political debates about abortion. Philosophical perspectives shape legal reasoning and public discussions surrounding abortion rights and restrictions.
International Perspectives on Abortion Bans
A global examination of abortion laws reveals a complex and often contentious landscape. Different countries and regions have adopted vastly varying approaches to abortion access, reflecting diverse cultural, religious, and political viewpoints. Understanding these international variations is crucial to comprehending the broader implications of abortion bans and their impact on women’s health and human rights globally.The global approach to abortion rights varies significantly, influenced by a multitude of factors.
The ongoing debate surrounding abortion bans, often framed as “pro-life,” touches on deeply personal values. It’s a complex issue with diverse perspectives. Interestingly, the recent career trajectory of Chita Rivera, a legendary performer, offers a fascinating contrast, highlighting the multifaceted nature of life choices and the diverse paths individuals take. Exploring her key moments in chita rivera key moments career reveals the power of dedication and resilience.
Ultimately, these considerations highlight the importance of thoughtful dialogue when discussing such sensitive topics as abortion bans pro life.
These factors include historical context, cultural norms, religious beliefs, and political ideologies. The resulting legal frameworks for abortion range from highly restrictive to relatively permissive, highlighting the lack of a universally accepted standard.
Variations in Abortion Laws Across Countries
Different countries and regions exhibit a wide spectrum of abortion laws and policies. Some countries have liberalized abortion access, while others maintain stringent restrictions. These differences underscore the absence of a globally standardized approach to reproductive healthcare.
Comparing Legal Frameworks for Abortion
A comprehensive comparison of legal frameworks for abortion across various countries and regions reveals significant disparities.
| Country/Region | Legal Status of Abortion | Restrictions (if any) |
|---|---|---|
| United States | Highly variable by state; some states have near-total bans | Varying restrictions on gestational age, reasons for seeking abortion, and parental consent |
| Canada | Legal in most circumstances | Some restrictions exist, but access is generally protected |
| China | Legal in certain circumstances | Restrictions often related to social and economic factors |
| South Korea | Legal in specific circumstances | Restrictions, including gestational limits and mandatory waiting periods |
| United Kingdom | Legal in most circumstances | Restrictions on late-term abortions |
This table provides a limited overview, as the specific regulations and nuances vary significantly within each country and region. Factors like socioeconomic status, access to healthcare, and cultural norms can further influence the practical application of these laws.
International Human Rights Implications of Abortion Bans
Abortion bans often intersect with international human rights principles. The right to health, including reproductive health, is frequently cited as a fundamental right. These rights are enshrined in international human rights instruments, such as the Universal Declaration of Human Rights. When abortion access is restricted, it can directly impact women’s health and well-being, potentially violating their rights to health, safety, and equality.
Different Approaches to Abortion Rights in International Law
International law’s approach to abortion rights is multifaceted and not always explicit. While the right to health is a recognized principle, its application to abortion remains contested. Various international human rights instruments and declarations provide differing perspectives on the issue.Some international organizations and bodies recognize access to safe and legal abortion as an essential aspect of reproductive health, citing the importance of women’s autonomy and bodily integrity.
Other perspectives prioritize the protection of the fetus, emphasizing the inherent value of human life from conception.
Alternatives to Abortion Bans
Abortion bans, often driven by differing ethical and religious viewpoints, frequently overlook the multifaceted needs of individuals facing unplanned pregnancies. Addressing this complex issue requires a comprehensive approach that prioritizes support, education, and access to resources beyond the simple prohibition of a medical procedure. A society that truly values the well-being of all its members must explore alternatives that prevent unwanted pregnancies and offer assistance to those who find themselves in these situations.Comprehensive strategies, encompassing both preventative measures and supportive services, are crucial for mitigating the potential negative consequences of abortion bans.
These alternatives can significantly improve the lives of individuals facing unplanned pregnancies and contribute to a more equitable and compassionate society.
Potential Alternatives to Abortion Bans
These alternatives aim to decrease the need for abortion by addressing the underlying issues contributing to unplanned pregnancies. They provide support and resources to pregnant individuals and new parents, ultimately promoting a healthier and more supportive environment.
| Alternative | Description |
|---|---|
| Comprehensive Sex Education | Providing accurate and age-appropriate information about sexual health, relationships, and contraception can empower individuals to make informed decisions about their reproductive choices. This includes education about consent, healthy relationships, and the potential consequences of sexual activity. |
| Access to Contraception | Ensuring affordable and accessible contraception, such as birth control pills, condoms, and long-acting reversible contraceptives (LARCs), can significantly reduce unintended pregnancies. Removing barriers to access, like cost and availability, is essential. |
| Support Services for Pregnant Individuals | Offering counseling, financial assistance, housing support, and childcare resources to pregnant individuals and new parents can significantly ease the transition and improve outcomes. This support can be particularly critical in communities with limited resources. |
| Affordable Childcare | Access to affordable and high-quality childcare is essential for working parents. This allows parents to pursue education or employment opportunities without financial hardship. |
| Parental Leave Policies | Implementing robust parental leave policies can provide crucial time for bonding and caregiving, especially in the early stages of parenthood. This can help new parents adjust to their roles and responsibilities. |
A Model for Support Systems
Creating a robust support system for pregnant individuals and new parents in communities with restricted abortion access requires a multi-faceted approach. This should be tailored to the specific needs of the community and involve various stakeholders.
“A comprehensive support system should not only provide immediate assistance but also create pathways for long-term stability and well-being.”
This model should include:
- Counseling and Support Groups: Providing access to trained counselors and support groups can offer emotional and practical guidance to pregnant individuals and new parents, fostering a sense of community and shared experience. These groups should also focus on addressing potential mental health concerns.
- Financial Assistance: Offering financial assistance programs, such as grants, subsidies, or low-interest loans, can alleviate the financial burden of raising a child. These programs should also consider the long-term needs of the family.
- Housing Support: Providing access to safe and stable housing is crucial for new parents. This could involve temporary housing assistance or connecting families with affordable housing options.
- Childcare Resources: Ensuring access to high-quality, affordable childcare allows parents to participate in education or employment opportunities, which can foster economic stability.
- Healthcare Access: Guaranteeing access to comprehensive healthcare services, including prenatal care, postnatal care, and ongoing medical support, is essential for the well-being of both the parent and the child.
Comprehensive Reproductive Healthcare Options
Expanding access to comprehensive reproductive healthcare, including preventative care and family planning services, can significantly impact the need for abortion. Comprehensive reproductive healthcare acknowledges the diverse needs of individuals and empowers them to make informed choices about their bodies and lives.This encompasses:
- Comprehensive Sex Education: Providing age-appropriate, comprehensive sex education equips individuals with the knowledge to make responsible choices about their sexuality and reproduction.
- Increased Access to Contraception: Ensuring affordable and accessible contraception reduces the likelihood of unintended pregnancies. This includes removing financial and logistical barriers to accessing these essential services.
- Support for Individuals Facing Unplanned Pregnancies: Offering practical support, including counseling, financial assistance, and childcare resources, can alleviate the burden on individuals facing unplanned pregnancies and promote healthy outcomes.
Last Word
In conclusion, abortion bans pro life are a complex issue with deeply entrenched historical, legal, ethical, and social dimensions. The discussion necessitates careful consideration of all perspectives, from the historical context to potential alternatives like comprehensive sex education and support services. Understanding the varied impacts on women’s health, reproductive rights, and socioeconomic factors is critical to a nuanced understanding of this issue.
General Inquiries
What are the potential financial burdens of restricted abortion access?
Restricted access to abortion can lead to increased healthcare costs for women, including emergency care for complications from unsafe abortions. It can also affect women’s ability to participate fully in the workforce and contribute to the economy.
How do international human rights implications relate to abortion bans?
International human rights laws often protect reproductive rights, and abortion bans can potentially violate these rights, particularly concerning the right to health and bodily autonomy. Different countries and regions have varying interpretations and applications of these laws.
What are some alternatives to abortion bans, besides comprehensive sex education and contraception?
Alternatives to abortion bans also include increased support services for pregnant individuals, including access to affordable childcare, parental leave, and mental health resources. Comprehensive reproductive healthcare options can also decrease the need for abortion.
How do socioeconomic disparities impact the effects of abortion bans, particularly for marginalized communities?
Abortion bans can disproportionately affect marginalized communities who already face socioeconomic challenges. Limited access to healthcare, financial resources, and social support can exacerbate existing inequalities and limit opportunities for women in these groups.